1998 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1998 (Internet Archive)
Geography
Area
total: 43,094 sq km land: 42,394 sq km water: 700 sq km note: includes the island of Bornholm in the Baltic Sea and the rest of metropolitan Denmark, but excludes the Faroe Islands and Greenland
Area-comparative
slightly less than twice the size of Massachusetts
Climate
temperate; humid and overcast; mild, windy winters and cool summers
Coastline
7,314 km
Elevation extremes
lowest point: Lammefjord -7 m highest point: Ejer Bavnehoj 173 m
Environment-current issues
air pollution, principally from vehicle and power plant emissions; nitrogen and phosphorus pollution of the North Sea; drinking and surface water becoming polluted from animal wastes and pesticides
Environment-international agreements
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Law of the Sea
Geographic coordinates
56 00 N, 10 00 E
Geography-note
controls Danish Straits (Skagerrak and Kattegat) linking Baltic and North Seas; about one-quarter of the population lives in Copenhagen
Irrigated land
4,350 sq km (1993 est.)
Land boundaries
total: 68 km border countries: Germany 68 km
Land use
arable land: 60% permanent crops: 0% permanent pastures: 5% forests and woodland: 10% other: 25% (1993 est.)
Location
Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, on a peninsula north of Germany
Map references
Europe
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 4 nm continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation exclusive economic zone: 200 nm territorial sea: 3 nm
Natural hazards
flooding is a threat in some areas of the country (e.g., parts of Jutland, along the southern coast of the island of Lolland) that are protected from the sea by a system of dikes
Natural resources
petroleum, natural gas, fish, salt, limestone, stone, gravel and sand
Terrain
low and flat to gently rolling plains
People and Society
Age structure
0-14 years: 18% (male 496,886; female 471,891) 15-64 years: 67% (male 1,807,384; female 1,760,353) 65 years and over: 15% (male 330,385; female 466,718) (July 1998 est.)
Birth rate
12.18 births/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Death rate
11.08 deaths/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Ethnic groups
Scandinavian, Eskimo, Faroese, German
Infant mortality rate
5.17 deaths/1,000 live births (1998 est.)
Languages
Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic (an Eskimo dialect), German (small minority)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 76.31 years male: 73.64 years female: 79.12 years (1998 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write total population: 99% (1980 est.) male: NA% female: NA%
Nationality
noun: Dane(s) adjective: Danish
Net migration rate
3.77 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Population
5,333,617 (July 1998 est.)
Population growth rate
0.49% (1998 est.)
Religions
Evangelical Lutheran 91%, other Protestant and Roman Catholic 2%, other 7% (1988)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.71 male(s)/female (1998 est.)
Total fertility rate
1.68 children born/woman (1998 est.)
Government
Administrative divisions
metropolitan Denmark-14 counties (amter, singular-amt) and 2 kommunes*; (stad); Arhus, Bornholm, Fredericksberg*, Frederiksborg, Fyn, Kobenhavn, Kobenhavn*, Nordjylland, Ribe, Ringkobing, Roskilde, Sonderjylland, Storstrom, Vejle, Vestsjalland, Viborg note: see separate entries for the Faroe Islands and Greenland, which are part of the Danish realm and self-governing administrative divisions
Constitution
1849 was the original constitution; there was a major overhaul 5 June 1953, allowing for a unicameral legislature and a female chief of state
Country name
conventional long form: Kingdom of Denmark conventional short form: Denmark local long form: Kongeriget Danmark local short form: Danmark
Data code
DA
Executive branch
chief of state: Queen MARGRETHE II (since 14 January 1972); Heir Apparent Crown Prince FREDERIK, elder son of the queen (born 26 May 1968) head of government: Prime Minister Poul Nyrup RASMUSSEN (since 25 January 1993) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the queen elections: none; the queen is a constitutional monarch; prime minister appointed by the queen
FAX
- [1] (202) 328-1470 consulate(s) general: Chicago, Los Angeles, and New York Diplomatic representation from the US: chief of mission: Ambassador Edward E. ELSON embassy: Dag Hammarskjolds Alle 24, 2100 Copenhagen mailing address: PSC 73, APO AE 09716 telephone: [45] (31) 42 31 44
- [45] (35) 43 02 23
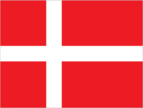
Flag description
red with a white cross that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side, and that design element of the Dannebrog (Danish flag) was subsequently adopted by the other Nordic countries of Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden
Government type
constitutional monarchy
Independence
in 10th century first organized as a unified state; in 1849 became a constitutional monarchy
International organization participation
AfDB, AG (observer), AsDB, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CCC, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECE, EIB, ESA, EU, FAO, G9, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Inmarsat, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, MTCR, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OECD, OSCE, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIKOM, UNMIBH, UNMOGIP, UNMOP, UNMOT, UNOMIG, UNPREDEP, UNTSO, UPU, WEU (observer), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTrO, ZC Diplomatic representation in the US: chief of mission: Ambassador Knud-Erik TYGESEN chancery: 3200 Whitehaven Street NW, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 234-4300
Judicial branch
Supreme Court, judges are appointed by the monarch for life Political parties and leaders: Social Democratic Party [Poul Nyrup RASMUSSEN]; Conservative Party [Torben RECHENDORFF]; Liberal Party [Uffe ELLEMANN-JENSEN]; Socialist People's Party [Holger K. NIELSEN]; Progress Party [Kirsten JAKOBSEN]; Center Democratic Party [Mimi JAKOBSEN]; Social Liberal Party [Marianne JELVED]; Unity Party [none]; Danish People's Party [Pia KJAERSGAARD]; Radical Liberal Party [Margrethe VESTAGER]; Conservative People's Party [Torben RECHENDORFF]
Legal system
civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations
Legislative branch
unicameral Parliament or Folketing (179 seats; members are elected on the basis of proportional representation to serve four-year terms) elections: last held 11 March 1998 (next to be held NA 2002) election results: percent of vote by party-NA; seats by party-progovernment parties: Social Democrats 65, Socialist People's Party 13, Radical Liberal Party 7, Unity Party 5; opposition: Progress Party 42, Conservative People's Party 16, Danish People's Party 13, Center Democrats 8, other parties 10
National capital
Copenhagen
National holiday
Birthday of the Queen, 16 April (1940)
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Economy
Agriculture-products
grain, potatoes, rape, sugar beets; meat, dairy products; fish
Budget
revenues: $62.1 billion expenditures: $66.4 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (1996 est.)
Currency
1 Danish krone (DKr) = 100 oere
Debt-external
$44 billion (1996 est.)
Economic aid
donor: ODA, $1.34 billion (1993)
Economy-overview
This thoroughly modern market economy features high-tech agriculture, up-to-date small-scale and corporate industry, extensive government welfare measures, comfortable living standards, and high dependence on foreign trade. Denmark is a net exporter of food. The center-left coalition government will concentrate on reducing the persistently high unemployment rate and the budget deficit as well as following the previous government's policies of maintaining low inflation and a current account surplus. The coalition also vows to maintain a stable currency. The coalition has lowered marginal income taxes while maintaining overall tax revenues; boosted industrial competitiveness through labor market and tax reforms and increased research and development funds; and improved welfare services for the neediest while cutting paperwork and delays. Prime Minister RASMUSSEN's reforms focus on adapting Denmark to the criteria for European integration by 1999; Copenhagen has won from the European Union (EU) the right to opt out of the European Monetary Union (EMU). Denmark is, in fact, one of the few EU countries likely to fit into the EMU on time. Growth may fall off slightly to 2.8% in 1998, and inflation may rise to 2.5%.
Electricity-capacity
10.604 million kW (1995)
Electricity-consumption per capita
6,432 kWh (1995)
Electricity-production
34.244 billion kWh (1995)
Exchange rates
Danish kroner (DKr) per US$1-6.916 (January 1998), 6.604 (1997), 5.799 (1996), 5.602 (1995), 6.361 (1994), 6.484 (1993)
Exports
total value: $48.8 billion (f.o.b., 1996) commodities: machinery and instruments 25%, meat and meat products, fuels, dairy products, ships, fish, chemicals partners: Germany 22.5%, Sweden 9.7%, UK 7.9%, Norway 5.9%, France 5.4%, Netherlands 4.4%, US 4.0% (1995)
Fiscal year
calendar year Communications
GDP
purchasing power parity-$122.5 billion (1997 est.)
GDP-composition by sector
agriculture: 4% industry: 27% services: 69% (1995)
GDP-per capita
purchasing power parity-$23,200 (1997 est.)
GDP-real growth rate
3% (1997 est.)
Imports
total value: $43.2 billion (c.i.f., 1996) commodities: machinery and equipment, petroleum 25%, chemicals, grain and foodstuffs, textiles, paper partners: Germany 21.7%, Sweden 11.7%, Netherlands 7.0%, UK 6.6%, France 5.2%, Norway 4.9%, US 4.7%, Japan 3.5%, FSU 1.7% (1995)
Industrial production growth rate
1.3% (1996)
Industries
food processing, machinery and equipment, textiles and clothing, chemical products, electronics, construction, furniture, and other wood products, shipbuilding
Inflation rate-consumer price index
2.2% (1997 est.)
Labor force
total: 2,895,950 by occupation: private services 40%, government services 30%, manufacturing and mining 19%, construction 6%, agriculture, forestry, and fishing 5% (1995)
Radio broadcast stations
AM 2, FM 3, shortwave 0
Radios
NA
Telephone system
excellent telephone and telegraph services domestic: buried and submarine cables and microwave radio relay form trunk network, four cellular radio communications systems international: 18 submarine fiber-optic cables linking Denmark with Norway, Sweden, Russia, Poland, Germany, Netherlands, UK, Faroe Islands, Iceland, and Canada; satellite earth stations-6 Intelsat, 10 Eutelsat, 1 Orion, 1 Inmarsat (Blaavand-Atlantic-East); note-the Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden) share the Danish earth station and the Eik, Norway, station for world-wide Inmarsat access
Telephones
4.025 million (1995 est.), of which 822,000 are mobile telephones
Television broadcast stations
50 (1996 est.)
Televisions
3 million (1996 est.)
Unemployment rate
7.9% (1997 est.)
Transportation
Airports
118 (1997 est.) Airports-with paved runways: total: 28 over 3,047 m: 2 2,438 to 3,047 m: 7 1,524 to 2,437 m: 3 914 to 1,523 m: 13 under 914 m: 3 (1997 est.) Airports-with unpaved runways: total: 90 1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 914 to 1,523 m: 7 under 914 m: 82 (1997 est.)
Highways
total: 71,600 km paved: 71,600 km (including 880 km of expressways) unpaved: 0 km (1996 est.)
Merchant marine
total: 327 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 4,972,331 GRT/6,894,091 DWT ships by type: bulk 14, cargo 118, chemical tanker 16, container 76, liquefied gas tanker 24, livestock carrier 6, oil tanker 25, railcar carrier 1, refrigerated cargo 14, roll-on/roll-off cargo 22, short-sea passenger 9, specialized tanker 2 note: Denmark has created its own internal register, called the Danish International Ship register (DIS); DIS ships do not have to meet Danish manning regulations, and they amount to a flag of convenience within the Danish register (1997 est.)
Pipelines
crude oil 110 km; petroleum products 578 km; natural gas 700 km Ports and harbors: Alborg, Arhus, Copenhagen, Esbjerg, Fredericia, Grena, Koge, Odense, Struer
Railways
total: 3,358 km (510 km privately owned and operated) standard gauge: 3,358 km 1.435-m gauge (440 km electrified; 760 km double track) (1996)
Waterways
417 km
Military and Security
Military branches
Royal Danish Army, Royal Danish Navy, Royal Danish Air Force, Home Guard
Military expenditures-dollar figure
$2.9 billion (1997 est.)
Military expenditures-percent of GDP
1.6% (1997 est.)
Military manpower-availability
males age 15-49: 1,324,150 (1998 est.) Military manpower-fit for military service: males: 1,137,563 (1998 est.)
Military manpower-military age
20 years of age
Military manpower-reaching military age annually
males: 32,918 (1998 est.)
Transnational Issues
Disputes-international
Rockall continental shelf dispute involving Iceland, Ireland, and the UK (Ireland and the UK have signed a boundary agreement in the Rockall area)