1990 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1990 (Project Gutenberg)
Geography
Climate
temperate; humid and overcast; mild, windy winters and cool summers
Coastline
3,379 km
Comparative area
slightly more than twice the size of Massachusetts
Contiguous zone
4 nm;
Continental shelf
200 meters or to depth of exploitation;
Disputes
Rockall continental shelf dispute involving Iceland, Ireland, and the UK (Ireland and the UK have signed a boundary agreement in the Rockall area); Denmark has challenged Norway's maritime claims between Greenland and Jan Mayen
Environment
air and water pollution
Exclusive fishing zone
200 nm;
Land boundaries
68 km with FRG
Land use
61% arable land; NEGL% permanent crops; 6% meadows and pastures; 12% forest and woodland; 21% other; includes 9% irrigated
Natural resources
crude oil, natural gas, fish, salt, limestone
Note
controls Danish Straits linking Baltic and North Seas
Terrain
low and flat to gently rolling plains
Territorial sea
3 nm
Total area
43,070 km2; land area: 42,370 km2; includes the island of Bornholm in the Baltic Sea and the rest of metropolitan Denmark, but excludes the Faroe Islands and Greenland
People and Society
Birth rate
12 births/1,000 population (1990)
Death rate
11 deaths/1,000 population (1990)
Ethnic divisions
Scandinavian, Eskimo, Faroese, German
Infant mortality rate
6 deaths/1,000 live births (1990)
Labor force
2,760,000; 51% services, 34% industry, 8% government, 7% agriculture, forestry, and fishing (1988)
Language
Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic (an Eskimo dialect); small German-speaking minority
Life expectancy at birth
73 years male, 79 years female (1990)
Literacy
99%
Nationality
noun--Dane(s); adjective--Danish
Net migration rate
NEGL migrants/1,000 population (1990)
Organized labor
65% of labor force
Population
5,131,217 (July 1990), growth rate NEGL% (1990)
Religion
97% Evangelical Lutheran, 2% other Protestant and Roman Catholic, 1% other
Total fertility rate
1.6 children born/woman (1990)
Government
Administrative divisions
metropolitan Denmark--14 counties (amter, singular--amt) and 1 city* (stad); Arhus, Bornholm, Frederiksborg, Fyn, Kobenhavn, Nordjylland, Ribe, Ringkobing, Roskilde, Sonderjylland, Staden Kobenhavn*, Storstrom, Vejle, Vestsjaelland, Viborg; note--see separate entries for the Faroe Islands and Greenland which are part of the Danish realm and self-governing administrative divisions
Capital
Copenhagen
Constitution
5 June 1953
Diplomatic representation
Ambassador Peter Pedersen DYVIG; Chancery at 3200 Whitehaven Street NW, Washington DC 20008; telephone (202) 234-4300; there are Danish Consulates General at Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, and New York; US--Ambassador Keith L. BROWN; Embassy at Dag Hammarskjolds Alle 24, 2100 Copenhagen O (mailing address is APO New York 09170); telephone [45] (31) 42 31 44
Elections
Parliament--last held 10 May 1988 (next to be held by May 1992); results--Social Democrat 29.9%, Conservative 19.3%, Socialist People's 13.0%, Liberal 11.8%, Radical Liberal 9.0%, Center Democratic 5.6%, Christian People's 2.0%, Common Course 2.7%, other 6.7%; seats--(175 total; includes 2 from Greenland and 2 from the Faroe Islands) Social Democratic 55, Conservative 35, Socialist People's 24, Liberal 22, Progress 16, Radical Liberal 10, Center Democratic 9, Christian People's 4
Executive branch
monarch, heir apparent, prime minister, Cabinet
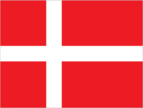
Flag
red with a white cross that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side and that design element of the Dannebrog (Danish flag) was subsequently adopted by the other Nordic countries of Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden
Independence
became a constitutional monarchy in 1849
Judicial branch
Supreme Court
Leaders
Chief of State--Queen MARGRETHE II (since January 1972); Heir Apparent Crown Prince FREDERIK, elder son of the Queen (born 26 May 1968); Head of Government--Prime Minister Poul SCHLUTER (since 10 September 1982)
Legal system
civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations
Legislative branch
unicameral Parliament (Folketing)
Long-form name
Kingdom of Denmark
Member of
ADB, CCC, Council of Europe, DAC, EC, EMS, ESA, FAO, GATT, IAEA, IBRD, ICAC, ICAO, ICES, ICO, IDA, IDB, Inter-American Development Bank, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IHO, ILO, ILZSG, IMF, IMO, INTELSAT, INTERPOL, IPU, ISO, ITC, ITU, IWC--International Wheat Council, NATO, Nordic Council, OECD, UN, UNESCO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WSG
National holiday
Birthday of the Queen, 16 April (1940)
Political parties and leaders
Social Democratic, Svend Auken; Liberal, Uffe Ellemann-Jensen; Conservative, Poul Schluter; Radical Liberal, Niels Helveg Petersen; Socialist People's, Gert Petersen; Communist, Ole Sohn; Left Socialist, Elizabeth Brun Olesen; Center Democratic, Mimi Stilling Jakobsen; Christian People's, Flemming Kofoed-Svendsen; Justice, Poul Gerhard Kristiansen; Progress Party, Aage Brusgaard; Socialist Workers Party, leader NA; Communist Workers' Party (KAP); Common Course, Preben Moller Hansen; Green Party, Inger Borlehmann
Suffrage
universal at age 21
Type
constitutional monarchy
Economy
Agriculture
accounts for 7% of GNP and employs 1.8% of labor force (includes fishing); farm products account for nearly 16% of export revenues; principal products--meat, dairy, grain, potatoes, rape, sugar beets, fish; self-sufficient in food production
Aid
donor--ODA and OOF commitments (1970-87) $4.8 billion
Budget
revenues $34 billion; expenditures $34 billion, including capital expenditures of $19 billion (1988)
Currency
Danish krone (plural--kroner); 1 Danish krone (DKr) = 100 ore
Electricity
11,215,000 kW capacity; 30,910 million kWh produced, 6,030 kWh per capita (1989)
Exchange rates
Danish kroner (DKr) per US$1--6.560 (January 1990), 7.310 (1989), 6.732 (1988), 6.840 (1987), 8.091 (1986), 10.596 (1985)
Exports
$27.7 billion (f.o.b., 1989 est.); commodities--meat and meat products, dairy products, transport equipment, fish, chemicals, industrial machinery; partners--US 6.0%, FRG, Norway, Sweden, UK, other EC, Japan
External debt
$41.1 billion (1989 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP
$73.7 billion, per capita $14,300; real growth rate 1.4%
Imports
$26.4 billion (c.i.f., 1989 est.); commodities--petroleum, machinery and equipment, chemicals, grain and foodstuffs, textiles, paper; partners--US 7.0%, FRG, Netherlands, Sweden, UK, other EC
Industrial production
growth rate 0.9% (1988)
Industries
food processing, machinery and equipment, textiles and clothing, chemical products, electronics, construction, furniture, and other wood products
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
4.25% (1989 est.)
Overview
This modern economy features high-tech agriculture, up-to-date small-scale and corporate industry, extensive government welfare measures, comfortable living standards, and high dependence on foreign trade. Growth in output, however, has been sluggish in 1987-89, and unemployment in early 1989 stood at 9.6% of the labor force. The government is trying to revitalize growth in preparation for the economic integration of Europe in 1992.
Unemployment rate
9.6% (1989)
Communications
Airports
130 total, 114 usable; 27 with permanent-surface runways; none with runways over 3,659 m; 9 with runways 2,440-3,659 m; 6 with runways 1,220-2,439 m
Civil air
58 major transport aircraft
Highways
66,482 km total; 64,551 km concrete, bitumen, or stone block; 1,931 km gravel, crushed stone, improved earth
Inland waterways
417 km
Merchant marine
252 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 4,498,611 GRT/6,711,011 DWT; includes 12 short-sea passenger, 82 cargo, 15 refrigerated cargo, 28 container, 36 roll-on/roll-off cargo, 1 railcar carrier, 37 petroleum, oils, and lubricants (POL) tanker, 13 chemical tanker, 12 liquefied gas, 4 livestock carrier, 12 bulk; note--Denmark has created a captive register called the Danish International Ship Register (DIS) as its own internal register; DIS ships do not have to meet Danish manning regulations, and they amount to a flag of convenience within the Danish register; by the end of 1990, most Danish flag ships will belong to the DIS
Pipelines
crude oil, 110 km; refined products, 578 km; natural gas, 700 km
Ports
Alborg, Arhus, Copenhagen, Esbjerg, Fredericia; numerous secondary and minor ports
Railroads
2,675 km 1.435-meter standard gauge; Danish State Railways (DSB) operate 2,025 km (1,999 km rail line and 121 km rail ferry services); 188 km electrified, 730 km double tracked; 650 km of standard-gauge lines are privately owned and operated
Telecommunications
excellent telephone, telegraph, and broadcast services; 4,237,000 telephones; stations--2 AM, 15 (39 repeaters) FM, 27 (25 repeaters) TV stations; 7 submarine coaxial cables; 1 satellite earth station operating in INTELSAT, 4 Atlantic Ocean, EUTELSAT, and domestic systems
Military and Security
Branches
Royal Danish Army, Royal Danish Navy, Royal Danish Air Force
Defense expenditures
2.1% of GDP, or $1.5 billion (1989 est.)
Military manpower
males 15-49, 1,368,013; 1,180,865 fit for military service; 37,228 reach military age (20) annually