1989 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1989 (Internet Archive)
Geography
Climate
- temperate; humid and overcast; mild, windy winters and cool summers
- desert; torrid, dry
Coastline
- 3,379 km
- 314 km
Comparative area
- slightly more than twice the size of Massachusetts
- slightly larger than Massachusetts
Contiguous zone
- 4 nm
- 24 nm
Continental shelf
200 meters or to depth of exploitation
Disputes
- Rockall continental shelf dispute involving Iceland, Ireland, and the UK (Ireland and the UK have signed a boundary agreement in the Rockall area); Denmark has challenged Norway's maritime claims between Greenland and Jan Mayen
- possible claim by Somalia based on unification of ethnic Somalis
Environment
- air and water pollution
- vast wasteland
Exclusive fishing zone
200 nm
Extended economic zone
200 nm
Land boundaries
- 68 km with FRG
- 517 km total; Ethiopia 459 km, Somalia 58 km
Land use
- 61% arable land; NEGL% permanent crops; 6% meadows and pastures; 12% forest and woodland; 21% other; includes 9% irrigated
- 0% arable land; 0% permanent crops; 9% meadows and pastures; NEGL% forest and woodland; 91% other
Natural resources
- crude oil, natural gas, fish, salt, limestone
- geothermal areas
Note
- controls Danish Straits linking Baltic and North Seas
- strategic location near world's busiest shipping lanes and close to Arabian oilfields; terminus of rail traffic into Ethiopia
Terrain
- low and flat to gently rolling plains
- coastal plain and plateau separated by central mountains
Territorial sea
- 3 nm
- 12 nm
Total area
- 43,070 km2; land area: 42,370 km2; includes the island of Bornholtn in the Baltic Sea and the rest of metropolitan Denmark, but excludes the Faroe Islands and Greenland
- 22,000 km2; land area: 21,980 km2
Total area
100 km Faroe Islands and Greenland are separate entries sec regional mtp V
People and Society
Birth rate
- 12 births/ 1,000 population (1990)
- 43 births/ 1 ,000 population (1990)
Death rate
- 11 deaths/ 1,000 population (1990)
- 17 deaths/ 1,000 population (1990)
Ethnic divisions
- Scandinavian, Eskimo, Faroese, German
- 60% Somali (Issa); 35% Afar, 5% French, Arab, Ethiopian, and Italian
Infant mortality rate
- 6 deaths/ 1,000 live births (1990)
- 119 deaths/ 1,000 live births (1990)
Labor force
- 2,760,000; 51% services, 34% industry, 8% government, 7% agriculture, forestry, and fishing (1988)
- NA, but a small number of semiskilled laborers at the port and 3,000 railway workers; 52% of population of working age (1983)
Language
- Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic (an Eskimo dialect); small German-speaking minority
- French (official); Arabic, Somali, and Afar widely used
Life expectancy at birth
- 73 years male, 79 years female (1990)
- 46 years male, 49 years female (1990)
Literacy
- 99%
- 20%
Nationality
- noun — Danc(s); adjective — Danish
- noun — Djiboutian(s); adjective— Djiboutian
Net migration rate
- NEGL migrants/ 1,000 population (1990)
- 0 migrants/ 1 ,000 population (1990)
Organized labor
- 65% of labor force
- 3,000 railway workers
Population
- 5,131,217 (July 1990), growth rate NEGL% (1990)
- 337,386 (July 1990), growth rate 2.6% (1990)
Religion
- 97% Evangelical Lutheran, 2% other Protestant and Roman Catholic, 1% other
- 94% Muslim, 6% Christian
Total fertility rate
- 1 .6 children born/ woman (1990)
- 6.4 children born/ woman (1990)
Government
Administrative divisions
- metropolitan Denmark — 14 counties (amter, singular — amt) and 1 city* (stad); Arhus, Bornholm, Frederiksborg, Fyn, Kebenhavn, Nordjylland, Ribe, Ringkebing, Roskilde, S0nderjylland, Staden Kebenhavn*, Storstrem, Vejle, Vestsjaelland, Viborg; note — see separate entries for the Faroe Islands and Greenland which are part of the Danish realm and self-governing administrative divisions
- 5 districts (cercles, singular — cercle); 'Ali Sahih, Dikhil, Djibouti, Obock, Tadjoura
Capital
- Copenhagen
- Djibouti
Communists
NA
Constitution
- 5 June 1953
- partial constitution ratified January 1981 by the Chamber of Deputies
Diplomatic representation
- Ambassador Peter Pedersen DYVIG; Chancery at 3200 Whitehaven Street NW, Washington DC 20008; telephone (202) 234-4300; there are Danish Consulates General at Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, and New York; US— Ambassador Keith L. BROWN; Embassy at Dag Hammarskjolds Alle 24, 2100 Copenhagen O (mailing address is APO New York 09170); telephone [45] (31) 42 31 44
- Ambassador Roble OLHAYE; Chancery (temporary) at the Djiboutian Permanent Mission to the UN; 866 United Nations Plaza, Suite 4011, New York, NY 10017; telephone (212) 753-3163; US— Ambassador Robert S. BARRETT IV; Embassy at Villa Plateau du Serpent Boulevard, Marechal Joffre, Djibouti (mailing address is B. P. 185, Djibouti); telephone [253] 35-38-49 or 35-39-95, 35-29-16, 35-29-17
Elections
- Parliament — last held 10 May 1988 (next to be held by May 1992); results— Social Democratic 29.9%, Conservative 19.3%, Socialist People's 13.0%, Liberal 11.8%, Radical Liberal 9.0%, Center Democratic 5.6%, Christian People's 2.0%, Common Course 2.7%, other 6.7%; seats — (175 total; includes 2 from Greenland and 2 from the Faroe Islands) Social Democratic 55, Conservative 35, Socialist People's 24, Liberal 22, Progress 16, Radical Liberal 10, Center Democratic 9, Christian People's 4
- President — last held 24 April 1987 (next to be held April 1993); results — President Hassan Gouled Aptidon was reelected without opposition; Chamber of Deputies — last held 24 April 1987 (next to be held April 1992); results — RPP is the only party; seats — (65 total) RPP 65
Executive branch
- monarch, heir apparent, prime minister, Cabinet
- president, prime minister, Council of Ministers
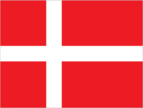
Flag
- red with a white cross that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side and that design element of the Dannebrog (Danish flag) was subsequently adopted by the other Nordic countries of Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden
- two equal horizontal bands of light blue (top) and light green with a white isosceles triangle based on the hoist side bearing a red five-pointed star in the center
Independence
- became a constitutional monarchy in 1 849
- 27 June 1977 (from France; formerly French Territory of the Afars and Issas)
Judicial branch
- Supreme Court
- Supreme Court (Cour Supreme)
Leaders
- Chief of State— Queen MARGRETHE II (since January 1972); Heir Apparent Crown Prince FREDERIK, elder son of the Queen (born 26 May 1968); Head of Government — Prime Minister Poul SCHLUTER (since 10 September 1982) Political parties and leaders: Social Democratic, Svend Auken; Liberal, Uffe EllemannJensen; Conservative, Poul Schluter; Radical Liberal, Niels Helveg Petersen; Socialist People's, Gert Petersen; Communist, Ole Sohn; Left Socialist, Elizabeth Brun Olesen; Center Democratic, Mimi Stilling Jakobsen; Christian People's, Flemming Kofoed-Svendsen; Justice, Poul Gerhard Kristiansen; Progress Party, Aage Brusgaard; Socialist Workers Party, leader NA; Communist Workers' Party (KAP); Common Course, Preben Mailer Hansen; Green Party, Inger Borlehmann
- Chief of State — President Hassan GOULED Aptidon (since 24 June 1977); Head of Government — Prime Minister Barkat GOURAD Hamadou (since 30 September 1978) Political parties and leaders: only party — People's Progress Assembly (RPP), Hassan Gouled Aptidon
Legal system
- civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations
- based on French civil law system, traditional practices, and Islamic law
Legislative branch
- unicameral Parliament (Folketing)
- Chamber of Deputies (Chambre des Deputes)
Long-form name
- Kingdom of Denmark
- Republic of Djibouti
Member of
- ADB, CCC, Council of Europe, DAC, EC, EMS, ESA, FAO, GATT, IAEA, IBRD, ICAC, ICAO, ICES, ICO, IDA, IDB, Inter-American Development Bank, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IHO, ILO, ILZSG, IMF, IMO, INTELSAT, INTERPOL, IPU, ISO, ITC, ITU, IWC— International Wheat Council, NATO, Nordic Council, OECD, UN, UNESCO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WSG
- ACP, AfDB, Arab League, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IDB— Islamic Development Bank, IFAD, IFC, ILO, IMF, IMO, INTERPOL, ITU, NAM, OAU, QIC, UN, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WMO
National holiday
- Birthday of the Queen, 16 April (1940)
- Independence Day, 27 June (1977)
Suffrage
- universal at age 21
- universal adult at age NA
Type
- constitutional monarchy
- republic
Economy
Agriculture
- accounts for 7% of GNP and employs 1 .8% of labor force (includes fishing); farm products account for nearly 16% of export revenues; principal products— meat, dairy, grain, potatoes, rape, sugar beets, fish; self-sufficient in food production
- accounts for 30% of GDP; scanty rainfall limits crop production to mostly fruit and vegetables; half of population pastoral nomads herding goats, sheep, and camels; imports bulk of food needs
Aid
- donor — ODA and OOF commitments (1970-87) $4.8 billion
- US commitments, including Ex-Im (FY78-88), $36 million; Western (non-US) countries, including ODA and OOF bilateral commitments (1970-87), $962 million; OPEC bilateral aid (1979-89), $149 million; Communist countries (1970-88), $35 million
Budget
- revenues S34 billion; expenditures S34 billion, including capital expenditures of $19 billion (1988)
- revenues $117 million; expenditures $163 billion, including capital expenditures of $52 million (1987 est.)
Currency
- Danish krone (plural — kroner); 1 Danish krone (DKr) = 100 ere
- Djiboutian franc (plural — francs); 1 Djiboutian franc (DF) = 100 centimes
Electricity
- 1 1,215,000 kW capacity; 30,910 million kWh produced, 6,030 kWh per capita (1989)
- 110,000 kW capacity; 190 million kWh produced, 580 kWh per capita (1989)
Exchange rates
- Danish kroner (DKr) per US$1— 6.560 (January 1990), 7.310 (1989), 6.732 (1988), 6.840 (1987), 8.091 (1986), 10.596 (1985) Fiscal yean calendar year
- Djiboutian francs (DF) per US$1— 177.721 (fixed rate since 1973)
Exports
- $27.7 billion (f.o.b., 1989 est.); commodities — meat and meat products, dairy products, transport equipment, fish, chemicals, industrial machinery; partners— US 6.0%, FRG, Norway, Sweden, UK, other EC, Japan
- $128 million (f.o.b., 1986); commodities— hides and skins, coffee (in transit); partners — Middle East 50%, Africa 43%, Western Europe 7%
External debt
- $41.1 billion (1989 est.)
- $250 million (December 1988)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP
$73.7 billion, per capita $14,300; real growth rate 1.4% (1989 est.) Denmark (continued) Djibouti
GNP
$333 million, $1,070 per capita; real growth rate -0.7% (1986)
Imports
- S26.4 billion (c.i.f., 1989 est.); commodities — petroleum, machinery and equipment, chemicals, grain and foodstuffs, textiles, paper; partners — US 7.0%, FRG, Netherlands, Sweden, UK, other EC
- $198 million (f.o.b., 1986); commodities— foods, beverages, transport equipment, chemicals, petroleum products; partners — EC 36%, Africa 21%, Bahrain 14%, Asia 12%, US 2%
Industrial production
- growth rate 0.9% (1988)
- growth rate — 1 .6% (1986)
Industries
- food processing, machinery and equipment, textiles and clothing, chemical products, electronics, construction, furniture, and other wood products
- limited to a few small-scale enterprises, such as dairy products and mineral-water bottling
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
- 4.25% (1989 est.)
- 8.0% (1987)
Overview
- This modern economy features high-tech agriculture, up-to-date smallscale and corporate industry, extensive government welfare measures, comfortable living standards, and high dependence on foreign trade. Growth in output, however, has been sluggish in 1987-89, and unemployment in early 1989 stood at 9.6% of the labor force. The government is trying to revitalize growth in preparation for the economic integration of Europe in 1992.
- The economy is based on service activities connected with the country's strategic location and status as a free trade zone. Djibouti provides services as both a transit port for the region and an international transshipment and refueling center. It has few natural resources and little industry. The nation is, therefore, heavily dependent on foreign assistance to help support its balance of payments and to finance development projects. An unemployment rate of over 50% continues to be a major problem.
Unemployment rate
- 9.6% (1989)
- over 50% (1987)
Communications
Airports
- 130 total, 114 usable; 27 with permanent-surface runways; none with runways over 3,659 m; 9 with runways 2,440-3,659 m; 6 with runways 1, 220-2,439 m
- 12 total, 9 usable; none with runways over 3,659 m; 1 with permanentsurface runways; 1 with runways 2,4403,659 m; 4 with runways 1,220-2,439 m
Branches
- Royal Danish Army, Royal Danish Navy, Royal Danish Air Force
- Army, Navy, Air Force; paramilitary National Security Force
Civil air
2 major transport aircraft
Defense expenditures
- 2.1% of GDP, or $1.5 billion (1989 est.) Srr regional map VII
- $29.9 million, 23% of central government budget (1986)
Highways
- 66,482 km total; 64,551 km concrete, bitumen, or stone block; 1,931 km gravel, crushed stone, improved earth
- 2,900 km total; 280 km bituminous surface, 2,620 km improved or unimproved earth (1982)
Inland waterways
417 km
Merchant marine
252 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 4,498,61 1 GRT/ 6,711,011 DWT; includes 12 short-sea passenger, 82 cargo, 15 refrigerated cargo, 28 container, 36 roll-on/roll-off cargo, 1 railcar carrier, 37 petroleum, oils, and lubricants (POL) tanker, 1 3 chemical tanker, 1 2 liquefied gas, 4 livestock carrier, 1 2 bulk; note — Denmark has created a captive register called the Danish International Ship Register (DIS) as its own internal register; DIS ships do not have to meet Danish manning regulations, and they amount to a flag of convenience within the Danish register; by the end of 1990, most Danish flag ships will belong to the DIS Civil air. 58 major transport aircraft
Military manpower
- males 15-49, 1,368,013; 1,180,865 fit for military service; 37,228 reach military age (20) annually
- males 15-49, 88,132; 51,260 fit for military service
Pipelines
crude oil, 1 10 km; refined products, 578 km; natural gas, 700 km
Ports
- Alborg, Arhus, Copenhagen, Esbjerg, Fredericia; numerous secondary and minor ports
- Djibouti
Railroads
- 2,675 km 1.435-meter standard gauge; Danish State Railways (DSB) operate 2,025 km (1,999 km rail line and 121 km rail ferry services); 1 88 km electrified, 730 km double tracked; 650 km of standard-gauge lines are privately owned and operated
- the Ethiopian-Djibouti railroad extends for 97 km through Djibouti
Telecommunications
- excellent telephone, telegraph, and broadcast services; 4,237,000 telephones; stations — 2 AM, 1 5 (39 repeaters) FM, 27 (25 repeaters) TV stations; 7 submarine coaxial cables; 1 satellite earth station operating in INTELSAT, 4 Atlantic Ocean, EUTELSAT, and domestic systems Defense Forces
- fair system of urban facilities in Djibouti and radio relay stations at outlying places; 7,300 telephones; stations— 2 AM, 1 FM, 2 TV; 1 Indian Ocean INTELSAT earth station and 1 ARABSAT; 1 submarine cable to Saudi Arabia Defense Forces