2023 Edition
CIA World Factbook 2023 (factbook.json @ 0d4fa4984ecb)
Introduction
Background
A military power during the 17th century, Sweden maintained a policy of military non-alignment until it applied to join NATO in May 2022. Stockholm preserved and armed neutrality in both World Wars. Since then, Sweden has pursued a successful economic formula consisting of a capitalist system intermixed with substantial welfare elements. Sweden joined the EU in 1995, but the public rejected the introduction of the euro in a 2003 referendum. The share of Sweden’s population born abroad increased from 11.3% in 2000 to 20% in 2021.
Geography
Area
- land
- 410,335 sq km
- total
- 450,295 sq km
- water
- 39,960 sq km
Area - comparative
almost three times the size of Georgia; slightly larger than California
Climate
temperate in south with cold, cloudy winters and cool, partly cloudy summers; subarctic in north
Coastline
3,218 km
Elevation
- highest point
- Kebnekaise South 2,100 m
- lowest point
- reclaimed bay of Lake Hammarsjon, near Kristianstad -2.4 m
- mean elevation
- 320 m
Geographic coordinates
62 00 N, 15 00 E
Geography - note
strategic location along Danish Straits linking Baltic and North Seas; Sweden has almost 100,000 lakes, the largest of which, Vanern, is the third largest in Europe
Irrigated land
519 sq km (2013)
Land boundaries
- border countries
- Finland 545 km; Norway 1,666 km
- total
- 2,211 km
Land use
- agricultural land
- 7.5% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: arable land
- arable land: 6.4% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent crops
- permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent pasture
- permanent pasture: 1.1% (2018 est.)
- forest
- 68.7% (2018 est.)
- other
- 23.8% (2018 est.)
Location
Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, Kattegat, and Skagerrak, between Finland and Norway
Major lakes (area sq km)
- fresh water lake(s)
- Vanern - 5,580 sq km; Vattern - 1,910 sq km; Malaren - 1,140 sq km
Map references
Europe
Maritime claims
- continental shelf
- 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
- exclusive economic zone
- agreed boundaries or midlines
- territorial sea
- 12 nm (adjustments made to return a portion of straits to high seas)
Natural hazards
ice floes in the surrounding waters, especially in the Gulf of Bothnia, can interfere with maritime traffic
Natural resources
iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, gold, silver, tungsten, uranium, arsenic, feldspar, timber, hydropower
Population distribution
most Swedes live in the south where the climate is milder and there is better connectivity to mainland Europe; population clusters are found all along the Baltic coast in the east; the interior areas of the north remain sparsely populated
Terrain
mostly flat or gently rolling lowlands; mountains in west
People and Society
Age structure
- 0-14 years
- 17.26% (male 936,274/female 882,347)
- 15-64 years
- 62.05% (male 3,346,891/female 3,190,608)
- 65 years and over
- 20.69% (2023 est.) (male 1,021,707/female 1,158,511)
Alcohol consumption per capita
- beer
- 2.6 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- other alcohols
- 0.1 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- spirits
- 1 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- total
- 7.1 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- wine
- 3.4 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Birth rate
10.8 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
NA
Contraceptive prevalence rate
- 70.3% (2017)
- note
- note: percent of women aged 16-49
Current health expenditure
11.4% of GDP (2020)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
53.4% (2023 est.)
Death rate
9.5 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
Demographic profile
Sweden, the largest Nordic country in terms of size and population, is also Europe’s most sparsely populated. Most Swedish men and women agree that both partners should contribute to household income. Swedish society is very gender equal, which is reflected in the country’s public policies. A generous leave policy and high-quality subsidized childcare allows mothers and fathers to balance work and family life. Sweden’s income-replacement-based parental leave policy encourages women to establish themselves in the workforce before having children. In fact, Swedish women have one of the highest labor participation rates in Europe and one of its highest total fertility rates (TFR), the number of children women have in their lifetime. Postponement of parenthood has increased steadily. Since the late 1960s, marriage and divorce rates have declined, while non-marital cohabitation and births out of wedlock have increased rapidly. Sweden’s TFR has hovered for decades around 2, which is close to replacement level and among Europe’s highest. Sweden experienced “the great emigration” between 1850 and the 1930s when, faced with famines, approximately 1.5 million Swedes sought a better life in the Americas and Australia. However, since World War II, Sweden has been a country of immigration. During World War II, thousands of refugees from neighboring countries worked in Swedish factories, agriculture, and forestry, replacing Swedish men who were called up for military service. During the 1950s and 1960s, Sweden joined the Geneva Convention and granted permanent residence to refugees from the USSR and the Warsaw Pact countries. During this period, Sweden also welcomed labor migrants, mainly from Finland and other Nordic countries, who bolstered the tax base needed to fund the country’s welfare programs. Until 1971, labor migrants, particularly from Finland, southern Europe (including then Yugoslavia, Italy, and Greece) the Baltics, and Turkey, came to Sweden as its industries flourished. Companies recruited many of the workers, but others came on their own. Sweden’s labor demand eventually decreased, and the job market became saturated. The government restricted the flow of labor migrants, putting an end to labor migration from non-Nordic countries in 1972. From then until the 1990s, inflows consisted largely of asylum seekers from the Middle East, the Balkans, and South America, as well as persons looking to reunite with family members already in Sweden. The country began a new era of labor immigration in 2008, as companies were encouraged to hire non-EU workers. Among the largest source countries have been India, Thailand, and China. As of 2020, over a quarter of Sweden’s population had a migrant background.
Dependency ratios
- elderly dependency ratio
- 32.3
- potential support ratio
- 3.1 (2021 est.)
- total dependency ratio
- 60.8
- youth dependency ratio
- 28.5
Drinking water source
- improved: rural
- rural: 99.7% of population
- improved: total
- total: 99.8% of population
- improved: urban
- urban: 99.8% of population
- unimproved: rural
- rural: 0.3% of population
- unimproved: total
- total: 0.2% of population (2020 est.)
- unimproved: urban
- urban: 0.2% of population
Education expenditures
7.2% of GDP (2020 est.)
Ethnic groups
- Swedish 80.3%, Syrian 1.9%, Iraqi 1.4%, Finnish 1.4%, other 15% (2020 est.)
- note
- note: data represent the population by country of birth; the indigenous Sami people are estimated to number between 20,000 and 40,000
Gross reproduction rate
0.8 (2023 est.)
Hospital bed density
2.1 beds/1,000 population (2018)
Infant mortality rate
- female
- 2.1 deaths/1,000 live births
- male
- 2.5 deaths/1,000 live births
- total
- 2.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
Languages
- Languages
- Swedish (official)
- major-language sample(s)
- The World Factbook, den obestridliga källan för grundläggande information. (Swedish)The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
- note
- note: Finnish, Sami, Romani, Yiddish, and Meankieli are official minority languages
Life expectancy at birth
- female
- 84.7 years
- male
- 81.1 years
- total population
- 82.8 years (2023 est.)
Literacy
- female
- NA
- male
- NA
- total population
- NA
Major urban areas - population
1.700 million STOCKHOLM (capital) (2023)
Maternal mortality ratio
5 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
Median age
- female
- 42 years
- male
- 40 years
- total
- 41 years (2023 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
29.7 years (2020 est.)
Nationality
- adjective
- Swedish
- noun
- Swede(s)
Net migration rate
3.8 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
20.6% (2016)
Physicians density
7.09 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
Population
10,536,338 (2023 est.)
Population distribution
most Swedes live in the south where the climate is milder and there is better connectivity to mainland Europe; population clusters are found all along the Baltic coast in the east; the interior areas of the north remain sparsely populated
Population growth rate
0.51% (2023 est.)
Religions
- Church of Sweden (Lutheran) 57.6%, other (includes Roman Catholic, Orthodox, Baptist, Muslim, Jewish, and Buddhist) 8.9%, none or unspecified 33.5% (2019 est.)
- note
- note: estimates reflect registered members of faith communities eligible for state funding (not all religions are state-funded and not all people who identify with a particular religion are registered members) and the Church of Sweden
Sanitation facility access
- improved: rural
- rural: 100% of population
- improved: total
- total: 100% of population
- improved: urban
- urban: 100% of population
- unimproved: rural
- rural: 0% of population
- unimproved: total
- total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
- unimproved: urban
- urban: 0% of population
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- female
- 21 years (2020)
- male
- 18 years
- total
- 20 years
Sex ratio
- 0-14 years
- 1.06 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years
- 1.05 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over
- 0.88 male(s)/female
- at birth
- 1.06 male(s)/female
- total population
- 1.01 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
- female
- 18.2% (2020 est.)
- male
- 29.8% (2020 est.)
- total
- 24% (2020 est.)
Total fertility rate
1.67 children born/woman (2023 est.)
Urbanization
- rate of urbanization
- 0.89% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population
- 88.7% of total population (2023)
Government
Administrative divisions
21 counties (lan, singular and plural); Blekinge, Dalarna, Gavleborg, Gotland, Halland, Jamtland, Jonkoping, Kalmar, Kronoberg, Norrbotten, Orebro, Ostergotland, Skane, Sodermanland, Stockholm, Uppsala, Varmland, Vasterbotten, Vasternorrland, Vastmanland, Vastra Gotaland
Capital
- daylight saving time
- +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
- etymology
- stock and holm literally mean "log" and "islet" in Swedish, but there is no consensus as to what the words refer to
- geographic coordinates
- 59 20 N, 18 03 E
- name
- Stockholm
- time difference
- UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Citizenship
- citizenship by birth
- no
- citizenship by descent only
- the father must be a citizen of Sweden; in the case of a child born out of wedlock, the mother must be a citizen of Sweden and the father unknown
- dual citizenship recognized
- no, unless the other citizenship was acquired involuntarily
- residency requirement for naturalization
- 5 years
Constitution
- amendments
- proposed by Parliament; passage requires simple majority vote in two consecutive parliamentary terms with an intervening general election; passage also requires approval by simple majority vote in a referendum if Parliament approves a motion for a referendum by one third of its members; The Instrument of Government - amended several times, last in 2018; The Act of Succession - changed in 1937, 1980; The Freedom of the Press Act - amended several times, last in 2019; The Fundamental Law on Freedom of Expression - amended several times, last in 2018
- history
- Sweden has four fundamental laws which together make up the Constitution: The Instrument of Government (several previous; latest 1974); The Act of Succession (enacted 1810; changed in 1937 and 1980); The Freedom of the Press Act (many previous; latest in 1949); The Fundamental Law on Freedom of Expression (adopted 1991)
Country name
- conventional long form
- Kingdom of Sweden
- conventional short form
- Sweden
- etymology
- name ultimately derives from the North Germanic Svear tribe, which inhabited central Sweden and is first mentioned in the first centuries A.D.
- local long form
- Konungariket Sverige
- local short form
- Sverige
Diplomatic representation from the US
- chief of mission
- Ambassador Erik D. RAMANATHAN (since 20 January 2022)
- email address and website
- STKACSinfo@state.govhttps://se.usembassy.gov/
- embassy
- Dag Hammarskjolds Vag 31, SE-115 89 Stockholm
- FAX
- [46] (08) 661-19-64
- mailing address
- 5750 Stockholm Place, Washington, DC 20521-5750
- telephone
- [46] (08) 783-53-00
Diplomatic representation in the US
- chancery
- 2900 K Street NW, Washington, DC 20007
- chief of mission
- Ambassador Urban AHLIN (since 15 September 2023)
- consulate(s) general
- New York
- email address and website
- ambassaden.washington@gov.sehttps://www.swedenabroad.se/en/embassies/usa-washington/
- FAX
- [1] (202) 467-2699
- telephone
- [1] (202) 467-2600
Executive branch
- cabinet
- Cabinet appointed by the prime minister
- chief of state
- King CARL XVI GUSTAF (since 15 September 1973); Heir Apparent Princess VICTORIA Ingrid Alice Desiree (daughter of the monarch, born 14 July 1977)
- elections/appointments
- the monarchy is hereditary; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually becomes the prime minister
- head of government
- Prime Minister Ulf KRISTERSSON (since 18 October 2022); Deputy Prime Minister Ebba BUSCH (since 18 October 2022)
Flag description
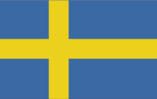
blue with a golden yellow cross extending to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag); the colors reflect those of the Swedish coat of arms - three gold crowns on a blue field
Government type
parliamentary constitutional monarchy
Independence
6 June 1523 (Gustav VASA elected king of Sweden, marking the abolishment of the Kalmar Union between Denmark, Norway, and Sweden)
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
International organization participation
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EITI (implementing country), EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-9, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNMOGIP, UNOOSA, UNRWA, UN Security Council (temporary), UNSOM, UNTSO, UPU, Wassenaar Arrangement, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Judicial branch
- highest court(s)
- Supreme Court of Sweden (consists of 16 justices, including the court chairman); Supreme Administrative Court (consists of 18 justices, including the court president)
- judge selection and term of office
- Supreme Court and Supreme Administrative Court justices nominated by the Judges Proposal Board, a 9-member nominating body consisting of high-level judges, prosecutors, and members of Parliament; justices appointed by the Government; following a probationary period, justices' appointments are permanent
- subordinate courts
- first instance, appellate, general, and administrative courts; specialized courts that handle cases such as land and environment, immigration, labor, markets, and patents
Legal system
civil law system influenced by Roman-Germanic law and customary law
Legislative branch
- description
- unicameral Parliament or Riksdag (349 seats; 310 members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by open party-list proportional representation vote and 39 members in "at-large" seats directly elected by open party-list proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
- election results
- percent of vote by party - S/SAP 30.3%, M 19.1%, SD 20.5%, C 6.7%, V 6.7%, KD 5.3%, L 4.6%, MP 5.1%, other 1.7%; seats by party - S/SAP 107, M 68, SD 73, C 24, V 24, KD 19, L 16, MP 18; composition as of mid-2022 - men 188, women 161, percent of women 46%
- elections
- last held on 11 September 2022 (next to beheld on 13 September 2026)
National anthem
- lyrics/music
- Richard DYBECK/traditional
- name
- "Du Gamla, Du Fria" (Thou Ancient, Thou Free)
- note
- note: in use since 1844; also known as "Sang till Norden" (Song of the North), is based on a Swedish folk tune; it has never been officially adopted by the government; "Kungssangen" (The King's Song) serves as the royal anthem and is played in the presence of the royal family and during certain state ceremonies
National heritage
- selected World Heritage Site locales
- Royal Domain of Drottningholm (c); Laponian Area (m); High Coast/Kvarken Archipelago (n); Birka and Hovgården (c); Hanseatic Town of Visby (c); Church Town of Gammelstad, Luleå (c); Naval Port of Karlskrona (c); Rock Carvings in Tanum (c); Engelsberg Ironworks (c); Mining Area of the Great Copper Mountain in Falun (c)
- total World Heritage Sites
- 15 (13 cultural, 1 natural, 1 mixed)
National holiday
National Day, 6 June (1983); note - from 1916 to 1982 this date was celebrated as Swedish Flag Day
National symbol(s)
three crowns, lion; national colors: blue, yellow
Political parties and leaders
Center Party (Centerpartiet) or C [Muharrem DEMIROK]Christian Democrats (Kristdemokraterna) or KD [Ebba BUSCH]Green Party (Miljopartiet de Grona) or MP [Marta STEVENI and Per BOLUND]Left Party (Vansterpartiet) or V [Nooshi DADGOSTAR]Moderate Party (Moderaterna) or M [Ulf KRISTERSSON]Sweden Democrats (Sverigedemokraterna) or SD [Jimmie AKESSON]Swedish Social Democratic Party (Socialdemokraterna) or S/SAP [Magdalena ANDERSSON]The Liberals (Liberalerna) or L [Johan PEHRSON]
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Economy
Agricultural products
wheat, milk, sugar beets, barley, potatoes, oats, rapeseed, pork, rye, triticale
Average household expenditures
- on alcohol and tobacco
- 3.4% of household expenditures (2018 est.)
- on food
- 12.4% of household expenditures (2018 est.)
Budget
- expenditures
- $256.454 billion (2019 est.)
- revenues
- $259.17 billion (2019 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)
1.3% (of GDP) (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
- Fitch rating
- AAA (2004)
- Moody's rating
- Aaa (2002)
- note
- note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
- Standard & Poors rating
- AAA (2004)
Current account balance
- Current account balance 2019
- $29.361 billion (2019 est.)
- Current account balance 2020
- $32.372 billion (2020 est.)
- Current account balance 2021
- $34.075 billion (2021 est.)
Debt - external
- Debt - external 2018
- $1,012,171,000,000 (2018 est.)
- Debt - external 2019
- $911.317 billion (2019 est.)
Economic overview
small, open, competitive, and thriving economy that remains outside of the euro zone; has achieved an enviable standard of living, with its combination of free-market capitalism and extensive welfare benefits
Exchange rates
- Currency
- Swedish kronor (SEK) per US dollar -
- Exchange rates 2017
- 8.549 (2017 est.)
- Exchange rates 2018
- 8.693 (2018 est.)
- Exchange rates 2019
- 9.458 (2019 est.)
- Exchange rates 2020
- 9.21 (2020 est.)
- Exchange rates 2021
- 8.577 (2021 est.)
Exports
- Exports 2019
- $257.293 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Exports 2020
- $241.94 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Exports 2021
- $290.793 billion (2021 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Exports - commodities
cars and vehicle parts, refined petroleum, packaged medicines, lumber, iron, broadcasting equipment (2021)
Exports - partners
Germany 10%, Norway 9%, United States 8%, Denmark 8%, Finland 6% (2021)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP - composition, by end use
- exports of goods and services
- 45.3% (2017 est.)
- government consumption
- 26% (2017 est.)
- household consumption
- 44.1% (2017 est.)
- imports of goods and services
- -41.1% (2017 est.)
- investment in fixed capital
- 24.9% (2017 est.)
- investment in inventories
- 0.8% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
- agriculture
- 1.6% (2017 est.)
- industry
- 33% (2017 est.)
- services
- 65.4% (2017 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$531.35 billion (2019 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
- Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income 2019
- 29.3 (2019 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
- highest 10%
- 24% (2012)
- lowest 10%
- 3.4%
Imports
- Imports 2019
- $233.648 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Imports 2020
- $217.165 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Imports 2021
- $263.269 billion (2021 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - commodities
cars and vehicle parts, crude petroleum, refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, computers (2021)
Imports - partners
Germany 18%, Netherlands 9%, Norway 8%, China 7%, Denmark 7% (2021)
Industrial production growth rate
5.72% (2021 est.)
Industries
iron and steel, precision equipment (bearings, radio and telephone parts, armaments), wood pulp and paper products, processed foods, motor vehicles
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2019
- 1.78% (2019 est.)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2020
- 0.5% (2020 est.)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2021
- 2.16% (2021 est.)
Labor force
5.556 million (2021 est.)
Population below poverty line
17.1% (2018 est.)
Public debt
- note
- note: data cover general government debt and include debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intragovernmental debt; intragovernmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions
- Public debt 2018
- 42.28% of GDP (2018 est.)
- Public debt 2019
- 38.69% of GDP (2019 est.)
- Public debt 2020
- 44% of GDP (2020 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
- note
- note: data are in 2017 dollars
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2020
- $531.455 billion (2020 est.)
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2021
- $558.427 billion (2021 est.)
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022
- $574.877 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
- Real GDP growth rate 2020
- -2.17% (2020 est.)
- Real GDP growth rate 2021
- 5.08% (2021 est.)
- Real GDP growth rate 2022
- 2.6% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
- note
- note: data are in 2017 dollars
- Real GDP per capita 2020
- $51,300 (2020 est.)
- Real GDP per capita 2021
- $53,600 (2021 est.)
- Real GDP per capita 2022
- $54,800 (2022 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2019
- $55.51 billion (31 December 2019 est.)
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2020
- $58.26 billion (31 December 2020 est.)
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2021
- $62.053 billion (31 December 2021 est.)
Taxes and other revenues
26.58% (of GDP) (2020 est.)
Unemployment rate
- Unemployment rate 2019
- 6.83% (2019 est.)
- Unemployment rate 2020
- 8.29% (2020 est.)
- Unemployment rate 2021
- 8.66% (2021 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
- female
- 23%
- male
- 26.1%
- total
- 24.5% (2021 est.)
Energy
Carbon dioxide emissions
- from coal and metallurgical coke
- 7.38 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- from consumed natural gas
- 2.359 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- from petroleum and other liquids
- 38.406 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- total emissions
- 48.144 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Coal
- consumption
- 3.328 million metric tons (2020 est.)
- exports
- 24,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
- imports
- 2.144 million metric tons (2020 est.)
- production
- 1.07 million metric tons (2020 est.)
- proven reserves
- 1 million metric tons (2019 est.)
Electricity
- consumption
- 124.609 billion kWh (2020 est.)
- exports
- 36.824 billion kWh (2020 est.)
- imports
- 11.827 billion kWh (2020 est.)
- installed generating capacity
- 43.499 million kW (2020 est.)
- transmission/distribution losses
- 10.434 billion kWh (2020 est.)
Electricity access
- electrification - total population
- 100% (2021)
Electricity generation sources
- biomass and waste
- 6.9% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- fossil fuels
- 1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- geothermal
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- hydroelectricity
- 44.7% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- nuclear
- 29.5% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- solar
- 0.7% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- tide and wave
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- wind
- 17.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
- Total energy consumption per capita 2019
- 210.882 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
Natural gas
- consumption
- 1,275,785,000 cubic meters (2020 est.)
- exports
- 34.886 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
- imports
- 1,310,671,000 cubic meters (2020 est.)
- production
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
- proven reserves
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Nuclear energy
- Net capacity of operational nuclear reactors
- 6.94GW (2023)
- Number of nuclear reactors permanently shut down
- 4
- Number of operational nuclear reactors
- 6 (2023)
- Percent of total electricity production
- 30.8% (2021)
- Percent of total energy produced
- 34% (2021)
Petroleum
- crude oil and lease condensate exports
- 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
- crude oil and lease condensate imports
- 403,200 bbl/day (2018 est.)
- crude oil estimated reserves
- 0 barrels (2021 est.)
- refined petroleum consumption
- 295,800 bbl/day (2019 est.)
- total petroleum production
- 10,600 bbl/day (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - exports
371,100 bbl/day (2017 est.)
Refined petroleum products - imports
229,600 bbl/day (2017 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
413,200 bbl/day (2017 est.)
Communications
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 41 (2020 est.)
- total
- 4,179,574 (2020 est.)
Broadcast media
publicly owned TV broadcaster operates 2 terrestrial networks plus regional stations; multiple privately owned TV broadcasters operating nationally, regionally, and locally; about 50 local TV stations; widespread access to pan-Nordic and international broadcasters through multi-channel cable and satellite TV; publicly owned radio broadcaster operates 3 national stations and a network of 25 regional channels; roughly 100 privately owned local radio stations with some consolidating into near national networks; an estimated 900 community and neighborhood radio stations broadcast intermittently
Internet country code
.se
Internet users
- percent of population
- 88% (2021 est.)
- total
- 8.8 million (2021 est.)
Telecommunication systems
- domestic
- fixed-line is 13 per 100 and mobile-cellular is 123 per 100 (2021)
- general assessment
- Sweden’s telecom market includes mature mobile and broadband sectors which have been stimulated by the progressive investment of the main telcos in developing new technologies; the country retains one of the best developed LTE infrastructures in the region, while its MNOs have benefited from the January 2021 auction of spectrum in the 3.5GHz band which will enable them to expand services nationally; the country also has one of the highest fiber broadband penetration rates in Europe; the focus of FttP is aimed at fulfilling the government’s target of providing a 1Gb/s service to 98% of the population by 2025; the methodology to achieve this has rested on regulatory measures supported by public funds, as well as on the auction of spectrum in different bands; in the fixed-line broadband segment, the number of DSL subscribers is falling steadily as customers continue to migrate to fiber networks; there is also competition from HFC infrastructure, offering fiber-based broadband and investing in services based on the DOCSIS3.1 standard; this report assesses key aspects of the Swedish telecom market, providing data on fixed network services and profiling the main players; it also reviews the key regulatory issues, including interconnection, local loop unbundling, number portability, carrier preselection and NGN open access; the report also analyses the mobile market, providing data on network operators and their strategies in a highly competitive environment; in addition, the report considers the fixed and fixed-wireless broadband markets, including analyses of market dynamics and the main operators, as well as providing subscriber forecasts (2021)
- international
- country code - 46; landing points for Botina, SFL, SFS-4, Baltic Sea Submarine Cable, Eastern Light, Sweden-Latvia, BCS North-Phase1, EE-S1, LV-SE1, BCS East-West Interlink, NordBalt, Baltica, Denmark-Sweden-15,-17,-18, Scandinavian Ring -North,-South, IP-Only Denmark-Sweden, Donica North, Kattegate-1,-2, Energinet Laeso-Varberg and GC2 submarine cables providing links to other Nordic countries and Europe; satellite earth stations - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean), 1 Eutelsat, and 1 Inmarsat (Atlantic and Indian Ocean regions); note - Sweden shares the Inmarsat earth station with the other Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, and Norway) (2019)
Telephones - fixed lines
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 13 (2021 est.)
- total subscriptions
- 1,382,146 (2021 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 123 (2021 est.)
- total subscriptions
- 12,843,683 (2021 est.)
Transportation
Airports
231 (2021)
Airports - with paved runways
- civil airports
- 26
- joint use (civil-military) airports
- 3
- military airports
- 4
- note
- note: paved runways have a concrete or asphalt surface but not all have facilities for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control; the length of a runway required for aircraft to safely operate depends on a number of factors including the type of aircraft, the takeoff weight (including passengers, cargo, and fuel), engine types, flap settings, landing speed, elevation of the airport, and average maximum daily air temperature; paved runways can reach a length of 5,000 m (16,000 ft.), but the “typical” length of a commercial airline runway is between 2,500-4,000 m (8,000-13,000 ft.)
- other airports
- 116
- total
- 149
Airports - with unpaved runways
- 82
- note
- note: unpaved runways have a surface composition such as grass or packed earth and are most suited to the operation of light aircraft; unpaved runways are usually short, often less than 1,000 m (3,280 ft.) in length; airports with unpaved runways often lack facilities for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
SE
Heliports
2 (2021)
Merchant marine
- by type
- general cargo 46, oil tanker 21, other 301
- total
- 368 (2022)
National air transport system
- inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers
- 316
- number of registered air carriers
- 11 (2020)
Pipelines
1626 km gas (2013)
Ports and terminals
- LNG terminal(s) (import)
- Brunnsviksholme, Lysekil
- major seaport(s)
- Brofjorden, Goteborg, Helsingborg, Karlshamn, Lulea, Malmo, Stockholm, Trelleborg, Visby
Railways
- narrow gauge
- 65 km
- total
- 10,910 km (2020) 8,184 km electrified
Roadways
- note
- note: includes 98,500 km of state roads, 433,034 km of private roads, and 41,600 km of municipal roads
- paved
- 140,100 km (2016)
- total
- 573,134 km (2016) (includes 2,050 km of expressways)
- unpaved
- 433,034 km (2016)
Transportation - note
Sweden operates four PC 3 or 4 class medium icebreakers in the Baltic Seanote - PC indicates a Polar Class vessel: PC 3 - year-round operation in second-year ice which may include multi-year ice inclusions (ice thickness up to 2.5 m); PC 4 - year-round operation in thick first-year ice which may include old ice inclusions (ice thickness up to 120 cm)
Waterways
2,052 km (2010)
Military and Security
Military - note
the Swedish military is responsible for the defense of the country and its territories against armed attack, supporting Sweden’s national security interests, providing societal support, such as humanitarian aid, and contributing to international peacekeeping and peacemaking operations; it has a relatively small active duty force that is designed to be rapidly mobilized in a crisis; it is equipped with modern, mostly Swedish-made weapons, exercises regularly, and is backed up by a trained reserve and a large Home Guard; the military’s main focus is maintaining itself as a credible and visible deterrent through training and exercises, sustaining high levels of readiness, cooperating and collaborating with both domestic and foreign partnersSweden maintained a policy of military non-alignment for over 200 years before applying for NATO membership in May 2022 following Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine; before then, Stockholm joined NATO’s Partnership for Peace program in 1994 and contributed to NATO-led missions, including those in Afghanistan, Iraq, and Kosovo; the military cooperates closely with the forces of other Nordic countries through the Nordic Defense Cooperation (NORDEFCO; established 2009), which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden; areas of cooperation include armaments, education, human resources, training and exercises, and operations; Sweden is a signatory of the EU’s Common Security and Defense Policy (CSDP) and contributes to CSDP missions and operations, including EU battlegroups; it also participates in UN-led missions; Sweden has close bilateral security relations with some NATO member states, particularly Finland, the UK, and the USthe military is headed by the Supreme Commander, who leads and supervises the force through Armed Forces Headquarters, which is the highest level of command and control of the military; the Army’s principal active combat arms units are approximately 14 battalions of armor, artillery, reconnaissance, security, and infantry forces, which include airborne/rangers, light, mechanized, and motorized infantry; in a crisis, the battalions would be filled out by reservists and formed into battlegroups/task forces and brigades; they are backed up by 40 Home Guard battalions comprised of locally based rapid-response units with mostly part-time but experienced soldiers; the Navy is organized into flotillas and an amphibious/naval infantry battalion; its principal warships are seven corvettes and four attack submarines; other combat vessels include patrol boats, fast attack craft, and minesweepers; all of the Navy’s warships are produced by Sweden; the Swedish Air Force has about 70 Swedish-made multirole fighter aircraft organized into wings with an additional 60 on order; the military also has a joint service special operations group directly under the Supreme Commander (2023)
Military and security forces
Swedish Armed Forces (Försvarsmakten or "the Defense Force"): Army, Navy, Air Force, Home Guard (2023)
Military and security service personnel strengths
- the SAF has about 25,000 active-duty personnel: approximately 14,000 continuous service/full-time and approximately 11,000 temporary service; approximately 21,000 Home Guard (some on active duty) (2023)
- note
- note 1: SAF personnel are divided into continuously serving (full-time) and temporary service troops (part-timers who serve periodically and have another main employer or attend school); additional personnel have signed service agreements with the SAF and mostly serve in the Home Guard; the SAF also has about 9,000 civilian employeesnote 2: in 2021, Sweden announced plans that increase the total size of the armed forces to about 100,000 personnel by 2030
Military deployments
the Swedish military has small numbers of personnel deployed on multiple EU-, NATO-, and UN-led missions (2023)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the SAF's inventory is comprised of domestically produced and imported Western weapons systems; in recent years, the US has been the leading supplier of military hardware to Sweden; Sweden has a large and sophisticated defense industry that produces a range of air, land, and naval systems (2023)
Military expenditures
- Military Expenditures 2019
- 1.1% of GDP (2019)
- Military Expenditures 2020
- 1.2% of GDP (2020)
- Military Expenditures 2021
- 1.3% of GDP (2021)
- Military Expenditures 2022
- 1.3% of GDP (2022)
- Military Expenditures 2023
- 1.5% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military service age and obligation
- 18-47 years of age for male and female voluntary military service; service obligation: 7.5 months (Army), 7-15 months (Navy), 8-12 months (Air Force); after completing initial service, soldiers have a reserve commitment until age 47; compulsory military service, abolished in 2010, was reinstated in January 2018; conscription is selective, includes both men and women (age 18), and requires 9-12 months of service (2023)
- note
- note 1: Sweden conscripts about 5,500 men and women each year; it plans to increase this number to 8,000 by 2025note 2: as of 2023, women made over 20% of the military's personnelnote 3: conscientious objectors in Sweden have the right to choose alternative service (called vapenfri tjänst); after completing alternative service, the conscript then belongs to the civilian reserve
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
none identified
Refugees and internally displaced persons
- refugees (country of origin)
- 113,213 (Syria), 26,857 (Afghanistan), 25,849 (Eritrea), 10,464 (Iraq), 9,315 (Somalia), 7,146 (Iran) (mid-year 2022); 41,520 (Ukraine) (as of 30 November 2023)
- stateless persons
- 46,515 (2022); note - the majority of stateless people are from the Middle East and Somalia
Space
Space agency/agencies
Swedish National Space Agency (SNSA; established 1972; known until 2018 as the Swedish National Space Board) (2023)
Space launch site(s)
Esrange Space Center (Kiruna); Esrange is slated to become a new European launch site for small satellites in 2023; Esrange also accommodates one of the world’s largest civilian satellite ground stations and acts as a hub for Sweden’s satellite station network (2023)
Space program overview
- member of the European Space Agency (ESA) and program is integrated within the framework of the ESA; produces and operates satellites; builds and launches sounding rockets; involved in the research, development, production, and operations of a wide variety of other space-related areas and capabilities, including astronomy, atmospheric monitoring, geographic information systems, infrared imaging, meteorology, propulsion systems, remote sensing, satellite subsystems, spacecraft systems and structures, space physics, scientific research, stratospheric balloons, and telecommunications; conducts extensive bilateral and multilateral international cooperation, in particular through the ESA and EU and their member states, as well as with the US; has a robust commercial space industry with more than 30 companies involved in a broad range of space-related capabilities (2023)
- note
- note: further details about the key activities, programs, and milestones of the country’s space program, as well as government spending estimates on the space sector, appear in Appendix S
Terrorism
Terrorist group(s)
- Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS)
- note
- note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in Appendix-T
Environment
Air pollutants
- carbon dioxide emissions
- 43.25 megatons (2016 est.)
- methane emissions
- 4.42 megatons (2020 est.)
- particulate matter emissions
- 5.96 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Climate
temperate in south with cold, cloudy winters and cool, partly cloudy summers; subarctic in north
Environment - current issues
marine pollution (Baltic Sea and North Sea); acid rain damage to soils and lakes; air pollution; inappropriate timber harvesting practices
Environment - international agreements
- party to
- Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Heavy Metals, Air Pollution-Multi-effect Protocol, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protection, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
- signed, but not ratified
- none of the selected agreements
Land use
- agricultural land
- 7.5% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: arable land
- arable land: 6.4% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent crops
- permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent pasture
- permanent pasture: 1.1% (2018 est.)
- forest
- 68.7% (2018 est.)
- other
- 23.8% (2018 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
- fresh water lake(s)
- Vanern - 5,580 sq km; Vattern - 1,910 sq km; Malaren - 1,140 sq km
Revenue from coal
0% of GDP (2018 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
0.21% of GDP (2018 est.)
Total renewable water resources
174 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
Total water withdrawal
- agricultural
- 100 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
- industrial
- 1.27 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
- municipal
- 700 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
Urbanization
- rate of urbanization
- 0.89% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population
- 88.7% of total population (2023)
Waste and recycling
- municipal solid waste generated annually
- 4.377 million tons (2015 est.)
- municipal solid waste recycled annually
- 1,416,835 tons (2015 est.)
- percent of municipal solid waste recycled
- 32.4% (2015 est.)