2000 Edition
CIA World Factbook 2000 (Project Gutenberg)
Introduction
Background
A military power during the 17th century, Sweden has not participated in any war in almost two centuries. An armed neutrality was preserved in both World Wars. Sweden's long-successful economic formula of a capitalist system interlarded with substantial welfare elements has recently been undermined by high unemployment, rising maintenance costs, and a declining position in world markets. Indecision over the country's role in the political and economic integration of Europe caused Sweden not to join the EU until 1995, and to forgo the introduction of the euro in 1999.
Geography
Area
- land
- 410,934 sq km
- total
- 449,964 sq km
- water
- 39,030 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly larger than California
Climate
temperate in south with cold, cloudy winters and cool, partly cloudy summers; subarctic in north
Coastline
3,218 km
Elevation extremes
- highest point
- Kebnekaise 2,111 m
- lowest point
- Baltic Sea 0 m
Environment - current issues
acid rain damaging soils and lakes; pollution of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea
Environment - international agreements
- party to
- Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
Geographic coordinates
62 00 N, 15 00 E
Geography - note
strategic location along Danish Straits linking Baltic and North Seas
Irrigated land
1,150 sq km (1993 est.)
Land boundaries
- border countries
- Finland 586 km, Norway 1,619 km
- total
- 2,205 km
Land use
- arable land
- 7%
- forests and woodland
- 68%
- other
- 24% (1993 est.)
- permanent crops
- 0%
- permanent pastures
- 1%
Location
Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, Kattegat, and Skagerrak, between Finland and Norway
Map references
Europe
Maritime claims
- continental shelf
- 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
- exclusive economic zone
- agreed boundaries or midlines
- territorial sea
- 12 nm (adjustments made to return a portion of straits to high seas)
Natural hazards
ice floes in the surrounding waters, especially in the Gulf of Bothnia, can interfere with maritime traffic
Natural resources
zinc, iron ore, lead, copper, silver, timber, uranium, hydropower
Terrain
mostly flat or gently rolling lowlands; mountains in west
People and Society
Age structure
0-14 years: 18% (male 837,358; female 794,774) 15-64 years: 64% (male 2,901,809; female 2,805,138) 65 years and over: 18% (male 648,865; female 885,108) (2000 est.)
Birth rate
10.01 births/1,000 population (2000 est.)
Death rate
10.62 deaths/1,000 population (2000 est.)
Ethnic groups
indigenous population: Swedes and Finnish and Lapp (Sami) minorities; foreign-born or first-generation immigrants: Finns, Yugoslavs, Danes, Norwegians, Greeks, Turks
Infant mortality rate
3.49 deaths/1,000 live births (2000 est.)
Languages
- Swedish
- note
- small Lapp- and Finnish-speaking minorities
Life expectancy at birth
- female
- 82.37 years (2000 est.)
- male
- 76.95 years
- total population
- 79.58 years
Literacy
- definition
- age 15 and over can read and write
- female
- NA%
- male
- NA%
- total population
- 99% (1979 est.)
Nationality
- adjective
- Swedish
- noun
- Swede(s)
Net migration rate
0.86 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2000 est.)
Population
8,873,052 (July 2000 est.)
Population growth rate
0.02% (2000 est.)
Religions
Lutheran 87%, Roman Catholic, Orthodox, Baptist, Muslim, Jewish, Buddhist
Sex ratio
- at birth
- 1.05 male(s)/female under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.73 male(s)/female
- total population
- 0.98 male(s)/female (2000 est.)
Total fertility rate
1.53 children born/woman (2000 est.)
Government
Administrative divisions
21 counties (lan, singular and plural); Blekinge, Dalarnas, Gavleborgs, Gotlands, Hallands, Jamtlands, Jonkopings, Kalmar, Kronobergs, Norrbottens, Orebro, Ostergotlands, Skane, Sodermanlands, Stockholms, Uppsala, Varmlands, Vasterbottens, Vasternorrlands, Vastmanlands, Vastra Gotalands
Capital
Stockholm
Constitution
1 January 1975
Country name
- conventional long form
- Kingdom of Sweden
- conventional short form
- Sweden
- local long form
- Konungariket Sverige
- local short form
- Sverige
Data code
SW
Diplomatic representation from the US
- chief of mission
- Ambassador Lyndon Lowell OLSON, Jr.
- embassy
- Strandvagen 101, S-115 89 Stockholm
- mailing address
- American Embassy Stockholm, Department of State, Washington, DC 20521-5750 (pouch)
- telephone
- (8) 783 53 00
Diplomatic representation in the US
- chancery
- 1501 M Street NW, Washington, DC 20005-1702
- chief of mission
- Ambassador Rolf EKEUS
- telephone
- (202) 467-2600
Executive branch
- cabinet
- Cabinet appointed by the prime minister
- chief of state
- King CARL XVI GUSTAF (since 19 September 1973); Heir Apparent Princess VICTORIA Ingrid Alice Desiree, daughter of the monarch (born 14 July 1977)
- election results
- Goran PERSSON reelected prime minister with 131 out of 349 votes
- elections
- the monarch is hereditary; prime minister elected by the Parliament; election last held NA September 1998 (next to be held NA 2002)
- head of government
- Prime Minister Goran PERSSON (since 21 March 1996)
FAX
- (202) 467-2699
- (8) 661 19 64
- consulate(s) general
- Los Angeles and New York
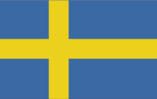
Flag description
blue with a yellow cross that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag)
Government type
constitutional monarchy
Independence
6 June 1523 (Gustav VASA elected king)
International organization participation
AfDB, AsDB, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CCC, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECE, EIB, ESA, EU, FAO, G- 6, G- 9, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Inmarsat, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, MINURSO, MONUC, NAM (guest), NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIKOM, UNMIBH, UNMIK, UNMOGIP, UNMOP, UNOMIG, UNTAET, UNTSO, UPU, WEU (observer), WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTrO, ZC
Judicial branch
Supreme Court or Hogsta Domstolen, judges are appointed by the government (prime minister and cabinet)
Legal system
civil law system influenced by customary law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations
Legislative branch
- unicameral Parliament or Riksdag (349 seats; members are elected by popular vote on a proportional representation basis to serve four-year terms)
- election results
- percent of vote by party - Social Democrats 36.5%, Moderates 22.7%, Left Party 12%, Christian Democrats 11.8%, Center Party 5.1%, Liberal Party 4.7%, Greens 4.5%; seats by party - Social Democrats 131, Moderates 82, Left Party 43, Christian Democrats 42, Center Party 18, Liberal Party 17, Greens 16
- elections
- last held 20 September 1998 (next to be held NA September 2002)
National holiday
Day of the Swedish Flag, 6 June
Political parties and leaders
Center Party ; Christian Democratic Party ; Communist Workers' Party ; Green Party [no formal leader but party spokesperson is Briger SCHLAUG]; Left Party or VP (formerly Communist) [Gudrun SCHYMAN]; Liberal People's Party ; Moderate Party (conservative) ; New Democracy Party ; Social Democratic Party
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Economy
Agriculture - products
grains, sugar beets, potatoes; meat, milk
Budget
- expenditures
- $146.1 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (FY95/96)
- revenues
- $109.4 billion
Currency
1 Swedish krona (SKr) = 100 oere
Debt - external
$66.5 billion (1994)
Economic aid - donor
ODA, $1.7 billion (1997)
Economy - overview
Aided by peace and neutrality for the whole twentieth century, Sweden has achieved an enviable standard of living under a mixed system of high-tech capitalism and extensive welfare benefits. It has a modern distribution system, excellent internal and external communications, and a skilled labor force. Timber, hydropower, and iron ore constitute the resource base of an economy heavily oriented toward foreign trade. Privately owned firms account for about 90% of industrial output, of which the engineering sector accounts for 50% of output and exports. Agriculture accounts for only 2% of GDP and 2% of the jobs. In recent years, however, this extraordinarily favorable picture has been clouded by budgetary difficulties, inflation, high unemployment, and a gradual loss of competitiveness in international markets. Sweden has harmonized its economic policies with those of the EU, which it joined at the start of 1995. Sweden decided not to join the euro system at its outset in January 1999 but plans to hold a referendum in 2000 on whether to join. GDP growth is forecast for 4% in 2000, buttressed by solid consumer confidence.
Electricity - consumption
135.098 billion kWh (1998)
Electricity - exports
16.8 billion kWh (1998)
Electricity - imports
6.1 billion kWh (1998)
Electricity - production
156.772 billion kWh (1998)
Electricity - production by source
- fossil fuel
- 6.09%
- hydro
- 46.49%
- nuclear
- 45.16%
- other
- 2.26% (1998)
Exchange rates
Swedish kronor (SKr) per US$1 - 8.4831 (January 2000), 8.2624 (1999), 7.9499 (1998), 7.6349 (1997), 6.7060 (1996), 7.1333 (1995)
Exports
$85.7 billion (f.o.b., 1999)
Exports - commodities
machinery 35%, motor vehicles, paper products, pulp and wood, iron and steel products, chemicals
Exports - partners
EU 57% (Germany 11%, UK 9%, Denmark 6%, Finland 5%), Norway 9%, US 9% (1998)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP
purchasing power parity - $184 billion (1999 est.)
GDP - composition by sector
- agriculture
- 2.2%
- industry
- 30.5%
- services
- 67.3% (1997)
GDP - per capita
purchasing power parity - $20,700 (1999 est.)
GDP - real growth rate
3.8% (1999 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 3.7% highest 10%: 20.1% (1992)
Imports
$67.9 billion (f.o.b., 1999)
Imports - commodities
machinery, petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, motor vehicles, iron and steel; foodstuffs, clothing
Imports - partners
EU 68% (Germany 19%, UK 10%, Denmark 6%, France 6%), Norway 8%, US 6% (1998)
Industrial production growth rate
3% (1999 est.)
Industries
iron and steel, precision equipment (bearings, radio and telephone parts, armaments), wood pulp and paper products, processed foods, motor vehicles
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
0.4% (1999 est.)
Labor force
4.3 million (1996)
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture 2%, industry 24%, services 74% (1999 est.)
Population below poverty line
NA%
Unemployment rate
5.5% plus about 5% in training programs (1999 est.)
Communications
Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
29 (1999)
Radio broadcast stations
AM 1, FM 265, shortwave 1 (1998)
Radios
8.25 million (1997)
Telephone system
- excellent domestic and international facilities; automatic system
- domestic
- coaxial and multiconductor cable carry most voice traffic; parallel microwave radio relay network carries some additional telephone channels
- international
- 5 submarine coaxial cables; satellite earth stations - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean), 1 Eutelsat, and 1 Inmarsat (Atlantic and Indian Ocean regions); note - Sweden shares the Inmarsat earth station with the other Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, and Norway)
Telephones - main lines in use
6.017 million (December 1998)
Telephones - mobile cellular
3.835 million (October 1998)
Television broadcast stations
163 (1997)
Televisions
4.6 million (1997)
Transportation
Airports
256 (1999 est.)
Airports - with paved runways
- total
- 147 over 3,047 m: 3 2,438 to 3,047 m: 11 1,524 to 2,437 m: 80 914 to 1,523 m: 28 under 914 m: 25 (1999 est.)
Airports - with unpaved runways
- total
- 109 914 to 1,523 m: 5 under 914 m: 104 (1999 est.)
Heliports
1 (1999 est.)
Highways
- paved
- 163,453 km (including 1,439 km of expressways)
- total
- 210,907 km
- unpaved
- 47,454 km (1998 est.)
Merchant marine
- ships by type
- bulk 6, cargo 26, chemical tanker 33, combination ore/oil 4, liquified gas 1, petroleum tanker 23, rail car carrier 1, roll-on/roll-off 43, short-sea passenger 4, specialized tanker 6, vehicle carrier 18 (1999 est.)
- total
- 165 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 2,301,633 GRT/1,726,018 DWT
Pipelines
natural gas 84 km
Ports and harbors
Gavle, Goteborg, Halmstad, Helsingborg, Hudiksvall, Kalmar, Karlshamn, Malmo, Solvesborg, Stockholm, Sundsvall
Railways
- standard gauge
- 12,821 km 1.435-m gauge (7,918 km electrified and 1,152 km double track) (1998)
- total
- 12,821 km (includes 3,594 km of privately-owned railways)
Waterways
2,052 km navigable for small steamers and barges
Military and Security
Military branches
Swedish Army, Royal Swedish Navy, Swedish Air Force
Military expenditures - dollar figure
$5 billion (FY98)
Military expenditures - percent of GDP
2.1% (FY98)
Military manpower - availability
males age 15-49: 2,067,631 (2000 est.)
Military manpower - fit for military service
males age 15-49: 1,809,129 (2000 est.)
Military manpower - military age
19 years of age
Military manpower - reaching military age annually
- males
- 51,962 (2000 est.)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
- none
- SWITZERLAND