1992 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1992 (Project Gutenberg)
Geography
Climate
temperate; cold, cloudy winters with frequent snow and fog; sunny summers with frequent showers and thunderstorms
Coastline
225 km
Comparative area
slightly smaller than Oregon
Continental shelf
200 m (depth) or to depth of exploitation
Disputes
none
Environment
frequent earthquakes most severe in south and southwest; geologic structure and climate promote landslides; air pollution in south
Exclusive economic zone
200 nm
Land area
230,340 km2
Land boundaries
2,508 km total; Bulgaria 608 km, Hungary 443 km, Moldova 450 km, Serbia and Montenegro 476 km, Ukraine (north) 362 km, Ukraine (south) 169 km
Land use
arable land 43%; permanent crops 3%; meadows and pastures 19%; forest and woodland 28%; other 7%; includes irrigated 11%
Natural resources
crude oil (reserves being exhausted), timber, natural gas, coal, iron ore, salt
Note
controls most easily traversable land route between the Balkans, Moldova, and the Ukraine
Terrain
central Transylvanian Basin is separated from the plain of Moldavia on the east by the Carpathian Mountains and separated from the Walachian Plain on the south by the Transylvanian Alps
Territorial sea
12 nm
Total area
237,500 km2
People and Society
Birth rate
14 births/1,000 population (1992)
Death rate
10 deaths/1,000 population (1992)
Ethnic divisions
Romanian 89.1%, Hungarian 8.9%, German 0.4%, Ukrainian, Serb, Croat, Russian, Turk, and Gypsy 1.6%
Infant mortality rate
22 deaths/1,000 live births (1992)
Labor force
10,945,700; industry 38%, agriculture 28%, other 34% (1989)
Languages
Romanian, Hungarian, German
Life expectancy at birth
68 years male, 74 years female (1992)
Literacy
96% (male NA%, female NA%) age 15 and over can read and write (1970 est.)
Nationality
noun - Romanian(s); adjective - Romanian
Net migration rate
-3 migrants/1,000 population (1992)
Organized labor
until December 1989, a single trade union system organized by the General Confederation of Romanian Trade Unions (UGSR) under control of the Communist Party; since CEAUSESCU'S overthrow, newly created trade and professional trade unions are joining umbrella organizations, including the Organization of Free Trade Unions, Fratia (Brotherhood), and the Alfa Cartel; many other trade unions have been formed
Population
23,169,914 (July 1992), growth rate 0.0% (1992)
Religions
Romanian Orthodox 70%, Roman Catholic 6%, Greek Catholic (Uniate) 3%, Protestant 6%, unaffiliated 15%
Total fertility rate
1.8 children born/woman (1992)
Government
Administrative divisions
40 counties (judete, singular - judet) and 1 municipality* (municipiu); Alba, Arad, Arges, Bacau, Bihor, Bistrita-Nasaud, Botosani, Braila, Brasov, Bucuresti*, Buzau, Calarasi, Caras-Severin, Cluj, Constanta, Covasna, Dimbovita, Dolj, Galati, Gorj, Giurgiu, Harghita, Hunedoara, Ialomita, Iasi, Maramures, Mehedinti, Mures, Neamt, Olt, Prahova, Salaj, Satu Mare, Sibiu, Suceava, Teleorman, Timis, Tulcea, Vaslui, Vilcea, Vrancea
Capital
Bucharest
Constitution
8 December 1991
Diplomatic representation
Ambassador Aurel MUNTEANU; Chancery at 1607 23rd Street NW, Washington, DC 20008; telephone (202) 232-4747 US: Ambassador John R. DAVIS; Embassy at Strada Tudor Arghezi 7-9, Bucharest (mailing address is APO AE 09213-5260); telephone [40] (0) 10-40-40; FAX [40] (0) 12-03-95
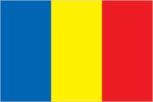
Flag
three equal vertical bands of blue (hoist side), yellow, and red; the national coat of arms that used to be centered in the yellow band has been removed; now similar to the flags of Andorra and Chad
Independence
1881 (from Turkey); republic proclaimed 30 December 1947
Legal system
former mixture of civil law system and Communist legal theory that increasingly reflected Romanian traditions is being revised
Long-form name
none
Member of
BIS, CCC, CSCE, ECE, FAO, G-9, G-77, GATT, IAEA, IBEC, IBRD, ICAO, IFAD, IFC, IIB, ILO, IMF, IMO, INTERPOL, IOC, ITU, LORCS, NAM (guest), PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
National holiday
National Day of Romania, 1 December (1990)
Type
republic
Economy
Agriculture
accounts for 15% of GDP and 28% of labor force; major wheat and corn producer; other products - sugar beets, sunflower seed, potatoes, milk, eggs, meat, grapes
Budget
revenues $19 billion; expenditures $20 billion, including capital expenditures of $2.1 billion (1991 est.)
Currency
leu (plural - lei); 1 leu (L) = 100 bani
Economic aid
donor - $4.4 billion in bilateral aid to non-Communist less developed countries (1956-89)
Electricity
22,700,000 kW capacity; 64,200 million kWh produced, 2,760 kWh per capita (1990)
Exchange rates
lei (L) per US$1 - 198.00 (March 1992), 76.39 (1991), 22.432 (1990), 14.922 (1989), 14.277 (1988), 14.557 (1987)
Exports
$4.0 billion (f.o.b., 1991 est.) commodities: machinery and equipment 29.3%, fuels, minerals and metals 32.1%, manufactured consumer goods 18.1%, agricultural materials and forestry products 9.0%, other 11.5% (1989) partners: USSR 27%, Eastern Europe 23%, EC 15%, US 5%, China 4% (1987)
External debt
$2 billion (1991)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP
purchasing power equivalent - $71.9 billion, per capita $3,100; real growth rate - 12% (1991 est.)
Illicit drugs
transshipment point for southwest Asian heroin transiting the Balkan route
Imports
$5.4 billion (f.o.b., 1991 est.) commodities: fuels, minerals, and metals 56.0%, machinery and equipment 25.5%, agricultural and forestry products 8.6%, manufactured consumer goods 3.4%, other 6.5% (1989) partners: Communist countries 60%, non-Communist countries 40% (1987)
Industrial production
growth rate -17% (1991 est.)
Industries
mining, timber, construction materials, metallurgy, chemicals, machine building, food processing, petroleum
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
215% (1991 est.)
Overview
Industry, which accounts for about one-third of the labor force and generates over half the GDP, suffers from an aging capital plant and persistent shortages of energy. The year 1991 witnessed about a 17% drop in industrial production because of energy and input shortages and labor unrest. In recent years the agricultural sector has had to contend with flooding, mismanagement, shortages of inputs, and disarray caused by the dismantling of cooperatives. A shortage of fuel and equipment in 1991 contributed to a lackluster harvest, a problem compounded by corruption and a poor distribution system. The new government is loosening the tight central controls of CEAUSESCU'S command economy. It has instituted moderate land reforms, with more than one-half of cropland now in private hands, and it has liberalized private agricultural output. Also, the new regime is permitting the establishment of private enterprises, largely in services, handicrafts, and small-scale industry. A law providing for the privatization of large state firms has been passed. Most of the large state firms have been converted into joint-stock companies, but the selling of shares and assets to private owners has been delayed. While the government has halted the old policy of diverting food from domestic consumption to hard currency export markets, supplies remain scarce in some areas. Furthermore, real wages in Romania fell about 20% in 1991, contributing to the unrest which forced the resignation of ROMAN in September. The new government continues to impose price ceilings on key consumer items.
Unemployment rate
4% (1991 est.)
Communications
Airports
165 total, 165 usable; 25 with permanent-surface runways; 15 with runways 2,440-3,659 m; 15 with runways 1,220-2,439 m
Civil air
59 major transport aircraft
Highways
72,799 km total; 35,970 km paved; 27,729 km gravel, crushed stone, and other stabilized surfaces; 9,100 km unsurfaced roads (1985)
Inland waterways
1,724 km (1984)
Merchant marine
262 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 3,320,373 GRT/5,207,580 DWT; includes 1 passenger-cargo, 174 cargo, 2 container, 1 rail-car carrier, 9 roll-on/roll-off cargo, 13 petroleum tanker, 60 bulk, 2 combination ore/oil
Pipelines
crude oil 2,800 km, petroleum products 1,429 km, natural gas 6,400 km
Ports
Constanta, Galati, Braila, Mangalia; inland ports are Giurgiu, Drobeta-Turnu Severin, Orsova
Railroads
11,275 km total; 10,860 km 1.435-meter gauge, 370 km narrow gauge, 45 km broad gauge; 3,411 km electrified, 3,060 km double track; government owned (1987)
Telecommunications
poor service; about 2.3 million telephone customers; 89% of phone network is automatic; cable and open wire; trunk network is microwave; present phone density is 9.85 per 100 residents; roughly 3,300 villages with no service (February 1990); broadcast stations - 12 AM, 5 FM, 13 TV (1990); 1 satellite ground station using INTELSAT
Military and Security
Branches
Army, Navy, Air and Air Defense Forces, Paramilitary Forces, Civil Defense
Defense expenditures
exchange rate conversion - 50 billion lei (unofficial), NA% of GDP (1991); note - conversion of defense expenditures into US dollars using the current exchange rate could produce misleading results
Manpower availability
males 15-49, 5,799,837; 4,909,642 fit for military service; 184,913 reach military age (20) annually