2023 Edition
CIA World Factbook 2023 (factbook.json @ 0d4fa4984ecb)
Introduction
Background
Two centuries of Viking raids into Europe tapered off following the adoption of Christianity by King Olav TRYGGVASON in 994; conversion of the Norwegian kingdom occurred over the next several decades. In 1397, Norway was absorbed into a union with Denmark that lasted more than four centuries. In 1814, Norwegians resisted the cession of their country to Sweden and adopted a new constitution. Sweden then invaded Norway but agreed to let Norway keep its constitution in return for accepting the union under a Swedish king. Rising nationalism throughout the 19th century led to a 1905 referendum granting Norway independence. Norway remained neutral in World War I and proclaimed its neutrality at the outset of World War II but was nonetheless occupied for five years by Nazi Germany (1940-45) and suffered heavy losses to its shipping fleet. In 1949, Norway abandoned neutrality and became a member of NATO. Discovery of oil and gas in adjacent waters in the late 1960s boosted Norway's economic fortunes. In referenda held in 1972 and 1994, Norway rejected joining the EU. Key domestic issues include immigration and integration of ethnic minorities, maintaining the country's extensive social safety net with an aging population, and preserving economic competitiveness.
Geography
Area
- land
- 304,282 sq km
- total
- 323,802 sq km
- water
- 19,520 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly larger than twice the size of Georgia; slightly larger than New Mexico
Climate
temperate along coast, modified by North Atlantic Current; colder interior with increased precipitation and colder summers; rainy year-round on west coast
Coastline
25,148 km (includes mainland 2,650 km, as well as long fjords, numerous small islands, and minor indentations 22,498 km; length of island coastlines 58,133 km)
Elevation
- highest point
- Galdhopiggen 2,469 m
- lowest point
- Norwegian Sea 0 m
- mean elevation
- 460 m
Geographic coordinates
62 00 N, 10 00 E
Geography - note
about two-thirds mountains; some 50,000 islands off its much-indented coastline; strategic location adjacent to sea lanes and air routes in North Atlantic; one of the most rugged and longest coastlines in the world
Irrigated land
337 sq km (2016)
Land boundaries
- border countries
- Finland 709 km; Sweden 1,666 km; Russia 191 km
- total
- 2,566 km
Land use
- agricultural land
- 2.7% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: arable land
- arable land: 2.2% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent crops
- permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent pasture
- permanent pasture: 0.5% (2018 est.)
- forest
- 27.8% (2018 est.)
- other
- 69.5% (2018 est.)
Location
Northern Europe, bordering the North Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Sweden
Map references
Europe
Maritime claims
- contiguous zone
- 10 nm
- continental shelf
- 200 nm
- exclusive economic zone
- 200 nm
- territorial sea
- 12 nm
Natural hazards
rockslides, avalanchesvolcanism: Beerenberg (2,227 m) on Jan Mayen Island in the Norwegian Sea is the country's only active volcano
Natural resources
petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, titanium, pyrites, nickel, fish, timber, hydropower
Population distribution
most Norwegians live in the south where the climate is milder and there is better connectivity to mainland Europe; population clusters are found all along the North Sea coast in the southwest, and Skaggerak in the southeast; the interior areas of the north remain sparsely populated
Terrain
glaciated; mostly high plateaus and rugged mountains broken by fertile valleys; small, scattered plains; coastline deeply indented by fjords; arctic tundra in north
People and Society
Age structure
- 0-14 years
- 17.83% (male 510,835/female 487,126)
- 15-64 years
- 64% (male 1,842,794/female 1,739,688)
- 65 years and over
- 18.18% (2023 est.) (male 474,878/female 542,603)
Alcohol consumption per capita
- beer
- 2.63 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- other alcohols
- 0.19 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- spirits
- 1 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- total
- 6.05 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- wine
- 2.23 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Birth rate
10.4 births/1,000 population (2023 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
NA
Contraceptive prevalence rate
NA
Current health expenditure
11.4% of GDP (2020)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
50.2% (2023 est.)
Death rate
8.2 deaths/1,000 population (2023 est.)
Demographic profile
Norway is a trendsetter country in gender equality, especially in workforce participation. Of particular value to families are the child and parental leave benefits. This supplement is a monthly allowance paid to families from a month after birth until the child reaches 18 to defray some of the costs of raising children. This is helpful to families with young children where the mother works limited hours. The parental leave benefit is available to qualified mothers in a child’s first year, enabling parents to share at-home childcare for up to 49 weeks at full salary (or 59 weeks with 80% of their salary). Afterward, parents can put their child in high-quality subsidized daycare or receive funding toward private child care or as compensation for one parent staying home to care for their child. Norway was originally a country of emigration with almost 850,000 Norwegians going abroad between 1825 and 1945. At the turn of the 20th century, most Norwegians emigrated temporarily to work in the US. Immigrants to Norway in the 1960s were mostly from neighboring Nordic countries, with whom they shared a common labor market. By the end of the 1960s, with a strong economy and population shortage, Norway admitted guest workers from Pakistan, Morocco, then Yugoslavia, and Turkey. The labor migrants were expected to be temporary, but many settled in Norway. Eventually, Norway imposed immigration restrictions and the majority of migrants came in as refugees or for family reunification. Beginning in the 1990s, Norway’s migration policy aimed at achieving integration – including language instruction and integration into the job market – as well as combatting racism and xenophobia.
Dependency ratios
- elderly dependency ratio
- 27.9
- note
- note: data include Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands
- potential support ratio
- 3.6 (2021 est.)
- total dependency ratio
- 54
- youth dependency ratio
- 26.1
Drinking water source
- improved: rural
- rural: 100% of population
- improved: total
- total: 100% of population
- improved: urban
- urban: 100% of population
- unimproved: rural
- rural: 0% of population
- unimproved: total
- total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
- unimproved: urban
- urban: 0% of population
Education expenditures
5.9% of GDP (2020 est.)
Ethnic groups
Norwegian 81.5% (includes about 60,000 Sami), other European 8.9%, other 9.6% (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.76 (2023 est.)
Hospital bed density
3.5 beds/1,000 population (2018)
Infant mortality rate
- female
- 1.5 deaths/1,000 live births
- male
- 2.1 deaths/1,000 live births
- total
- 1.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2023 est.)
Languages
- Languages
- Bokmal Norwegian (official), Nynorsk Norwegian (official), small Sami- and Finnish-speaking minorities; note - Sami has three dialects: Lule, North Sami, and South Sami; Sami is an official language in nine municipalities in Norway's three northernmost counties: Finnmark, Nordland, and Troms
- major-language sample(s)
- Verdens Faktabok, den essensielle kilden for grunnleggende informasjon. (Norwegian)The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Life expectancy at birth
- female
- 84.7 years
- male
- 81.4 years
- total population
- 83 years (2023 est.)
Literacy
- female
- NA
- male
- NA
- total population
- NA
Major urban areas - population
1.086 million OSLO (capital) (2023)
Maternal mortality ratio
2 deaths/100,000 live births (2020 est.)
Median age
- female
- 41.4 years
- male
- 39.9 years
- total
- 40.6 years (2023 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
- 29.8 years (2020 est.)
- note
- note: data is calculated based on actual age at first births
Nationality
- adjective
- Norwegian
- noun
- Norwegian(s)
Net migration rate
3.8 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2023 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
23.1% (2016)
Physicians density
5.04 physicians/1,000 population (2020)
Population
5,597,924 (2023 est.)
Population distribution
most Norwegians live in the south where the climate is milder and there is better connectivity to mainland Europe; population clusters are found all along the North Sea coast in the southwest, and Skaggerak in the southeast; the interior areas of the north remain sparsely populated
Population growth rate
0.6% (2023 est.)
Religions
Church of Norway (Evangelical Lutheran - official) 67.5%, Muslim 3.1%, Roman Catholic 3.1%, other Christian 3.8%, other 2.6%, unspecified 19.9% (2021 est.)
Sanitation facility access
- improved: rural
- rural: 100% of population
- improved: total
- total: 100% of population
- improved: urban
- urban: 100% of population
- unimproved: rural
- rural: 0% of population
- unimproved: total
- total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
- unimproved: urban
- urban: 0% of population
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- female
- 19 years (2020)
- male
- 18 years
- total
- 18 years
Sex ratio
- 0-14 years
- 1.05 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years
- 1.06 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over
- 0.88 male(s)/female
- at birth
- 1.05 male(s)/female
- total population
- 1.02 male(s)/female (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
- female
- 15.4% (2020 est.)
- male
- 17% (2020 est.)
- total
- 16.2% (2020 est.)
Total fertility rate
1.57 children born/woman (2023 est.)
Urbanization
- note
- note: data include Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands
- rate of urbanization
- 1.32% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population
- 84% of total population (2023)
Government
Administrative divisions
11 counties (fylker, singular - fylke); Agder, Innlandet, More og Romsdal, Nordland, Oslo, Rogaland, Troms og Finnmark, Trondelag, Vestfold og Telemark, Vestland, Viken
Capital
- daylight saving time
- +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
- etymology
- the medieval name was spelt "Aslo"; the as component refered either to the Ekeberg ridge southeast of the town ("as" in modern Norwegian), or to the Aesir (Norse gods); lo refered to "meadow," so the most likely interpretations would have been either "the meadow beneath the ridge" or "the meadow of the gods"; both explanations are considered equally plausible
- geographic coordinates
- 59 55 N, 10 45 E
- name
- Oslo
- time difference
- UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Citizenship
- citizenship by birth
- no
- citizenship by descent only
- at least one parent must be a citizen of Norway
- dual citizenship recognized
- no
- residency requirement for naturalization
- 7 years
Constitution
- amendments
- proposals submitted by members of Parliament or by the government within the first three years of Parliament's four-year term; passage requires two-thirds majority vote of a two-thirds quorum in the next elected Parliament; amended over 400 times, last in 2020
- history
- drafted spring 1814, adopted 16 May 1814, signed by Constituent Assembly 17 May 1814
Country name
- conventional long form
- Kingdom of Norway
- conventional short form
- Norway
- etymology
- derives from the Old Norse words "nordr" and "vegr" meaning "northern way" and refers to the long coastline of western Norway
- local long form
- Kongeriket Norge
- local short form
- Norge
Dependent areas
Bouvet Island, Jan Mayen, Svalbard (3)
Diplomatic representation from the US
- chief of mission
- Ambassador Marc NATHANSON (since 16 June 2022)
- email address and website
- OsloACS@state.govhttps://no.usembassy.gov/
- embassy
- Morgedalsvegen 36, 0378 Oslo
- FAX
- [47] 22-56-27-51
- mailing address
- 5460 Oslo Place, Washington DC 20521-5460
- telephone
- [47] 21-30-85-40
Diplomatic representation in the US
- chancery
- 2720 34th Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
- chief of mission
- Ambassador Anniken Ramberg KRUTNES (since 17 September 2020)
- consulate(s) general
- Houston, New York, San Francisco
- email address and website
- emb.washington@mfa.nohttps://www.norway.no/en/usa/
- FAX
- [1] (202) 469-3990
- telephone
- [1] (202) 333-6000
Executive branch
- cabinet
- Council of State appointed by the monarch, approved by Parliament
- chief of state
- King HARALD V (since 17 January 1991); Heir Apparent Crown Prince HAAKON MAGNUS (son of the monarch, born 20 July 1973)
- elections/appointments
- the monarchy is hereditary; following parliamentary elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the monarch with the approval of the parliament
- head of government
- Prime Minister Jonas Gahr STORE (since 14 October 2021)
Flag description
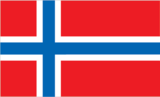
red with a blue cross outlined in white that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag); the colors recall Norway's past political unions with Denmark (red and white) and Sweden (blue)
Government type
parliamentary constitutional monarchy
Independence
7 June 1905 (union with Sweden declared dissolved); 26 October 1905 (Sweden agreed to the repeal of the union); notable earlier dates: ca. 872 (traditional unification of petty Norwegian kingdoms by HARALD Fairhair); 1397 (Kalmar Union of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden); 1524 (Denmark-Norway); 17 May 1814 (Norwegian constitution adopted); 4 November 1814 (Sweden-Norway union confirmed)
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
International organization participation
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EFTA, EITI (implementing country), ESA, FAO, FATF, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNMISS, UNOOSA, UNRWA, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, Wassenaar Arrangement, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Judicial branch
- highest court(s)
- Supreme Court or Hoyesterett (consists of the chief justice and 18 associate justices)
- judge selection and term of office
- justices appointed by the monarch (King in Council) upon the recommendation of the Judicial Appointments Board; justices can serve until mandatory retirement at age 70
- subordinate courts
- Courts of Appeal or Lagmennsrett; regional and district courts; Conciliation Boards; ordinary and special courts; note - in addition to professionally trained judges, elected lay judges sit on the bench with professional judges in the Courts of Appeal and district courts
Legal system
mixed legal system of civil, common, and customary law; Supreme Court can advise on legislative acts
Legislative branch
- description
- unicameral Parliament or Storting (169 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by list proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
- election results
- percent of vote by party - Ap 26.3%, H 20.5%, SP 13.6%, FrP 11.7%, SV 7.6%, R 4.7%, V 4.6%, MDG 3.9%, KrF 3.8%, PF 0.2%, other 3.1%; seats by party - Ap 48, H 36, SP 28, FrP 21, SV 13, R 8, V 8, , KrF 3, MDG 3, PF 1; composition (as of October 2021) men 93, women 76, percent of women 45%
- elections
- last held on 13 September 2021 (next to be held on 30 September 2025)
National anthem
- lyrics/music
- lyrics/music: Bjornstjerne BJORNSON/Rikard NORDRAAK
- name
- "Ja, vi elsker dette landet" (Yes, We Love This Country)
- note
- note: adopted 1864; in addition to the national anthem, "Kongesangen" (Song of the King), which uses the tune of "God Save the King," serves as the royal anthem
National heritage
- selected World Heritage Site locales
- Bryggen (c); Urnes Stave Church (c); Røros Mining Town and the Circumference (c); Rock Art of Alta (c); Vegaøyan – The Vega Archipelago (c); Struve Geodetic Arc (c); West Norwegian Fjords – Geirangerfjord and Nærøyfjord (n); Rjukan-Notodden Industrial Heritage Site (c)
- total World Heritage Sites
- 8 (7 cultural, 1 natural)
National holiday
Constitution Day, 17 May (1814)
National symbol(s)
lion; national colors: red, white, blue
Political parties and leaders
Center Party or Sp [Trygve Slagsvold VEDUM]Christian Democratic Party or KrF [Olaug Vervik BOLLESTAD] Conservative Party or H [Erna SOLBERG] Green Party or MDG [Arild HERMSTAD] Labor Party or Ap [Jonas Gahr STORE] Liberal Party or V [Guri MELBY]Patient Focus or PF [Irene OJALA]Progress Party or FrP [Sylvi LISTHAUG] Red Party or R [Bjonar MOXNES]Socialist Left Party or SV [Kristi BERGSTO]
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Economy
Agricultural products
milk, barley, wheat, potatoes, oats, pork, poultry, beef, eggs, rye
Average household expenditures
- on alcohol and tobacco
- 4.1% of household expenditures (2018 est.)
- on food
- 11.7% of household expenditures (2018 est.)
Budget
- expenditures
- $210.522 billion (2020 est.)
- revenues
- $185.338 billion (2020 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)
4.4% (of GDP) (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
- Fitch rating
- AAA (1995)
- Moody's rating
- Aaa (1997)
- note
- note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
- Standard & Poors rating
- AAA (1975)
Current account balance
- Current account balance 2019
- $11.919 billion (2019 est.)
- Current account balance 2020
- $4.223 billion (2020 est.)
- Current account balance 2021
- $71.551 billion (2021 est.)
Debt - external
- Debt - external 2018
- $648.878 billion (2018 est.)
- Debt - external 2019
- $651.04 billion (2019 est.)
- note
- note: Norway is a net external creditor
Economic overview
high-income non-EU European economy; aging labor force; large state-owned energy company constrains budget and spending; largest oil sovereign wealth fund; major fishing, forestry, and extraction industries; large welfare system
Exchange rates
- Currency
- Norwegian kroner (NOK) per US dollar -
- Exchange rates 2017
- 8.272 (2017 est.)
- Exchange rates 2018
- 8.133 (2018 est.)
- Exchange rates 2019
- 8.8 (2019 est.)
- Exchange rates 2020
- 9.416 (2020 est.)
- Exchange rates 2021
- 8.59 (2021 est.)
Exports
- Exports 2019
- $146.28 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Exports 2020
- $116.718 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Exports 2021
- $199.074 billion (2021 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Exports - commodities
natural gas, crude petroleum, salmon, refined petroleum, aluminum (2021)
Exports - partners
United Kingdom 21%, Germany 19%, Sweden 8%, Netherlands 7%, China 6% (2021)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP - composition, by end use
- exports of goods and services
- 35.5% (2017 est.)
- government consumption
- 24% (2017 est.)
- household consumption
- 44.8% (2017 est.)
- imports of goods and services
- -33.2% (2017 est.)
- investment in fixed capital
- 24.1% (2017 est.)
- investment in inventories
- 4.8% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
- agriculture
- 2.3% (2017 est.)
- industry
- 33.7% (2017 est.)
- services
- 64% (2017 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$405.695 billion (2019 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
- Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income 2019
- 27.7 (2019 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
- highest 10%
- 21.2% (2014)
- lowest 10%
- 3.8%
Imports
- Imports 2019
- $140.211 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Imports 2020
- $119.632 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Imports 2021
- $140.444 billion (2021 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - commodities
cars, refined petroleum, broadcasting equipment, computers, ships, nickel (2021)
Imports - partners
Sweden 18%, Germany 12%, China 10%, Denmark 6%, United States 5% (2021)
Industrial production growth rate
2.19% (2021 est.)
Industries
petroleum and gas, shipping, fishing, aquaculture, food processing, shipbuilding, pulp and paper products, metals, chemicals, timber, mining, textiles
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2019
- 2.17% (2019 est.)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2020
- 1.29% (2020 est.)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2021
- 3.48% (2021 est.)
Labor force
2.971 million (2021 est.)
Population below poverty line
12.7% (2018 est.)
Public debt
- note
- note: data cover general government debt and include debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data exclude treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data exclude debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intragovernmental debt; intragovernmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions
- Public debt 2016
- 36.4% of GDP (2016 est.)
- Public debt 2017
- 36.5% of GDP (2017 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
- note
- note: data are in 2017 dollars
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2020
- $341.855 billion (2020 est.)
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2021
- $355.122 billion (2021 est.)
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022
- $368.151 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
- Real GDP growth rate 2020
- -0.72% (2020 est.)
- Real GDP growth rate 2021
- 3.88% (2021 est.)
- Real GDP growth rate 2022
- 3.3% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
- note
- note: data are in 2017 dollars
- Real GDP per capita 2020
- $63,500 (2020 est.)
- Real GDP per capita 2021
- $65,700 (2021 est.)
- Real GDP per capita 2022
- $67,500 (2022 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2019
- $66.946 billion (31 December 2019 est.)
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2020
- $75.259 billion (31 December 2020 est.)
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2021
- $84.271 billion (31 December 2021 est.)
Taxes and other revenues
21.09% (of GDP) (2020 est.)
Unemployment rate
- Unemployment rate 2019
- 3.69% (2019 est.)
- Unemployment rate 2020
- 4.42% (2020 est.)
- Unemployment rate 2021
- 4.99% (2021 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
- female
- 12.5%
- male
- 13.5%
- total
- 13% (2021 est.)
Energy
Carbon dioxide emissions
- from coal and metallurgical coke
- 3.182 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- from consumed natural gas
- 8.294 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- from petroleum and other liquids
- 25.256 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- total emissions
- 36.731 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Coal
- consumption
- 1.13 million metric tons (2020 est.)
- exports
- 46,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
- imports
- 1.172 million metric tons (2020 est.)
- production
- 69,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
- proven reserves
- 2 million metric tons (2019 est.)
Electricity
- consumption
- 124.288 billion kWh (2020 est.)
- exports
- 24.968 billion kWh (2020 est.)
- imports
- 4.496 billion kWh (2020 est.)
- installed generating capacity
- 38.36 million kW (2020 est.)
- transmission/distribution losses
- 8.909 billion kWh (2020 est.)
Electricity access
- electrification - total population
- 100% (2021)
Electricity generation sources
- biomass and waste
- 0.3% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- fossil fuels
- 1.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- geothermal
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- hydroelectricity
- 92.1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- nuclear
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- solar
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- tide and wave
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- wind
- 6.4% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
- Total energy consumption per capita 2019
- 333.833 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
Natural gas
- consumption
- 3,980,351,000 cubic meters (2020 est.)
- exports
- 107,337,690,000 cubic meters (2020 est.)
- imports
- 32.196 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
- production
- 112,052,523,000 cubic meters (2020 est.)
- proven reserves
- 1,544,455,000,000 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
- crude oil and lease condensate exports
- 1,242,500 bbl/day (2018 est.)
- crude oil and lease condensate imports
- 66,300 bbl/day (2018 est.)
- crude oil estimated reserves
- 8,122,200,000 barrels (2021 est.)
- refined petroleum consumption
- 215,900 bbl/day (2019 est.)
- total petroleum production
- 2.026 million bbl/day (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - exports
432,800 bbl/day (2017 est.)
Refined petroleum products - imports
135,300 bbl/day (2017 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
371,600 bbl/day (2017 est.)
Communications
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 44 (2020 est.)
- total
- 2,387,661 (2020 est.)
Broadcast media
state-owned public radio-TV broadcaster operates 3 nationwide TV stations, 3 nationwide radio stations, and 16 regional radio stations; roughly a dozen privately owned TV stations broadcast nationally and roughly another 25 local TV stations broadcasting; nearly 75% of households have access to multi-channel cable or satellite TV; 2 privately owned radio stations broadcast nationwide and another 240 stations operate locally; Norway is the first country in the world to phase out FM radio in favor of Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB), a process scheduled for completion in late 2017 (2019)
Internet country code
.no
Internet users
- percent of population
- 99% (2021 est.)
- total
- 5.346 million (2021 est.)
Telecommunication systems
- domestic
- fixed-line is 7 per 100 and mobile-cellular nearly 110 per 100 (2021)
- general assessment
- Norway has a sophisticated telecom market with high broadband and mobile penetration rates and a highly developed digital media sector. Although not a member of the European Union, the country’s telecoms sector is synchronized with relevant EC legislation; Norway enjoys near comprehensive LTE coverage with upgrades to 5G technologies in the future (2023)
- international
- country code - 47; landing points for the Svalbard Undersea Cable System, Polar Circle Cable, Bodo-Rost Cable, NOR5KE Viking, Celtic Norse, Tempnet Offshore FOC Network, England Cable, Denmark-Norwary6, Havfrue/AEC-2, Skagerrak 4, and the Skagenfiber West & East submarine cables providing links to other Nordic countries, Europe and the US; satellite earth stations - Eutelsat, Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean), and 1 Inmarsat (Atlantic and Indian Ocean regions); note - Norway shares the Inmarsat earth station with the other Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, and Sweden) (2019)
Telephones - fixed lines
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 7 (2021 est.)
- total subscriptions
- 350,000 (2021 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 110 (2021 est.)
- total subscriptions
- 5.8 million (2021 est.)
Transportation
Airports
95 (2021)
Airports - with paved runways
- civil airports
- 25
- joint use (civil-military) airports
- 6
- military airports
- 1
- note
- note: paved runways have a concrete or asphalt surface but not all have facilities for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control; the length of a runway required for aircraft to safely operate depends on a number of factors including the type of aircraft, the takeoff weight (including passengers, cargo, and fuel), engine types, flap settings, landing speed, elevation of the airport, and average maximum daily air temperature; paved runways can reach a length of 5,000 m (16,000 ft.), but the “typical” length of a commercial airline runway is between 2,500-4,000 m (8,000-13,000 ft.)
- other airports
- 35
- total
- 67
Airports - with unpaved runways
- 28
- note
- note: unpaved runways have a surface composition such as grass or packed earth and are most suited to the operation of light aircraft; unpaved runways are usually short, often less than 1,000 m (3,280 ft.) in length; airports with unpaved runways often lack facilities for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
LN
Heliports
1 (2021)
Merchant marine
- by type
- bulk carrier 105, container ship 1, general cargo 273, oil tanker 95, other 1,236
- total
- 1,710 (2022)
National air transport system
- inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers
- 125
- number of registered air carriers
- 8 (2020)
Pipelines
8,520 km gas, 1,304 km oil/condensate (2017)
Ports and terminals
- LNG terminal(s) (export)
- Kamoy, Kollsnes, Melkoya Island, Tjeldbergodden
- LNG terminal(s) (import)
- Fredrikstad, Mosjoen
- major seaport(s)
- Bergen, Haugesund, Maaloy, Mongstad, Narvik, Sture
Railways
- total
- 3,848 km (2020) 2,482 km electrified
Roadways
- total
- 94,902 km (2018) (includes 455 km of expressways)
Transportation - note
Norway operates one PC 3 or 4 class icebreaker and one PC 5 or 6 class icebreaker in the Arctic Oceannote - PC indicates a Polar Class vessel: PC 3 - year-round operation in second-year ice which may include multi-year ice inclusions (ice thickness up to 2.5 m); PC 4 - year-round operation in thick first-year ice which may include old ice inclusions (ice thickness up to 120 cm); PC 5 - year-round operation in medium first-year ice which may include old ice inclusions (ice thickness up to 70-120 cm); PC 6 - summer/autumn operation in medium first-year ice which may include old ice inclusions (ice thickness up to 30-70 cm)
Waterways
1,577 km (2010)
Military and Security
Military - note
the Norwegian Armed Forces (Forsvaret) are responsible for protecting Norway and its allies, including monitoring Norway’s airspace, digital, land, and maritime areas, maintaining the country’s borders and sovereignty, contributing to NATO and UN missions, and providing support to civil society, such as assisting the police, search and rescue, and maritime counterterrorism efforts; the military’s territorial and sovereignty defense missions are complicated by Norway’s vast sea areas, numerous islands, long and winding fjords, and difficult and mountainous terrain; a key area of focus is its far northern border with RussiaNorway is one of the original members of NATO, and the Alliance is a key component of Norway’s defense policy; the Forsvaret participates regularly in NATO exercises, missions, and operations, including air policing of NATO territory, NATO’s Enhanced Forward Presence mission in the Baltic States and Eastern Europe, and standing naval missions, as well as operations in non-NATO areas, such as the Middle East; the Forsvaret also cooperates closely with the militaries of other Nordic countries through the Nordic Defense Cooperation (NORDEFCO; established 2009), which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden; areas of cooperation include armaments, education, human resources, training and exercises, and operations; Norway contributes to the UK-led Joint Expeditionary Force, a pool of high-readiness military forces from 10 Baltic and Scandinavian countries designed to respond to a wide range of contingencies both in peacetime and in times of crisis or conflict with a focus on the High North, North Atlantic, and Baltic Sea regions; the Forsvaret participates in UN missions in such areas as Africa and the Middle East; Norway has close military ties with the US, including rotational US military deployments and an agreement allowing for mutual defense activities and US military forces to access some Norwegian facilities the Forsvaret is a compact and mixed force of conscripts and professionals that trains regularly and is equipped with modern weapons systems; its origins go back to the leidangen, defense forces which were established along the coastline in the 10th century to protect the Norwegian coast; the Army was created in 1628; its principal combat forces are a mechanized infantry brigade, plus a special operations commando (group); the Finnmark Land Command safeguards Norway's northernmost land territories and the land border with Russia; the Army is supplemented by the Home Guard (Heimevernet or HV), a reserve mobilization and national emergency force consisting of some 40,000 part-time soldiers spread over 11 districts where they have territorial responsibility for protecting key civilian and military installations and may assist civil authorities during natural disasters and search and rescue operations; the HV includes several rapid-reaction intervention task forcesthe Navy is comprised of the fleet, the Coast Guard, and several bases; the fleet has a small mix of frigates, corvettes, and attack submarines, as well as mine warfare vessels; it also has a special operations group and the Coastal Hunter Command (Kystjegerkommandoen), which monitors coastal seas and land; the Air Force has about 60 US-made combat aircraft and will have a new fully operational fleet of US F-35 stealth multirole fighters by 2025 (2023)
Military and security forces
- Norwegian Armed Forces (Forsvaret or "the Defense"): Norwegian Army (Haeren), Royal Norwegian Navy (Kongelige Norske Sjoeforsvaret; includes Coastal Rangers and Coast Guard (Kystvakt)), Royal Norwegian Air Force (Kongelige Norske Luftforsvaret), Norwegian Special Forces, Norwegian Cyber Defense Force, Home Guard (Heimevernet, HV) (2023)
- note
- note: the national police have primary responsibility for internal security; the National Police Directorate, an entity under the Ministry of Justice and Public Security, oversees the police force
Military and security service personnel strengths
- approximately 27,000 active personnel (9,000 Army; 4,300 Navy; 4,700 Air Force; 9,000 other, including special operations, cyber, joint staff, intelligence, logistics support, active Home Guard, etc.); approximately 40,000 Home Guard (2023)
- note
- note: active personnel include about 10,000 conscripts
Military deployments
- up to 200 Lithuania (NATO) (2023)
- note
- note: in response to Russia’s 2022 invasion of Ukraine, some NATO countries, including Norway, have sent additional troops and equipment to the battlegroups deployed in NATO territory in eastern Europe
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the military's inventory includes a mix of modern, imported European, US, and domestically produced weapons systems and equipment; in recent years, the US has been the leading supplier of weapons systems to Norway (2023)
Military expenditures
- Military Expenditures 2019
- 1.8% of GDP (2019)
- Military Expenditures 2020
- 2% of GDP (2020)
- Military Expenditures 2021
- 1.7% of GDP (2021)
- Military Expenditures 2022
- 1.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
- Military Expenditures 2023
- 1.7% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military service age and obligation
- 19-35 years of age for selective compulsory military service for men and women; 17 years of age for male volunteers; 18 years of age for women volunteers; 12-19 month service obligation; conscripts first serve 12 months between the ages of 19 and 28, and then up to 4-5 refresher training periods until age 35, 44, 55, or 60 depending on rank and function (2023)
- note
- note 1: Norway conscripts about 8,000 individuals annually; it has had compulsory military service since 1907note 2: Norway was the first NATO country to allow women to serve in all combat arms branches of the military (1985); it also has an all-female special operations unit known as Jegertroppen (The Hunter Troop), which was established in 2014; as of 2023, women comprised about 20% of the military's full-time personnelnote 3: beginning in 1995, the military began offering Icelandic citizens the opportunity to apply for admission to officer schools in Norway with an associated education and service contract under special reasons and based on recommendations from Icelandic authorities; as early as 1996, Norway and Iceland entered into a cooperation agreement on the voluntary participation of Icelandic personnel in Norwegian force contributions in foreign operations
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Norway-Antarctica: Norway asserts a territorial claim in Antarctica (Queen Maud Land and its continental shelf) Norway-Russia: Russia amended its 2001 CLCS submission in 2015 and 2021, each time delineating the outer limits of its continental shelf further into the Arctic Ocean; Norway and Russia signed a comprehensive maritime boundary agreement in 2010, ending a dispute over an area of the Barents Sea by dividing the territory equally Norway-Sweden: none identified
Refugees and internally displaced persons
- refugees (country of origin)
- 15,901 (Syria), 10,883 (Eritrea) (mid-year 2022); 61,005 (Ukraine) (as of 4 December 2023)
- stateless persons
- 3,901 (2022)
Space
Space agency/agencies
the Norwegian Space Agency (NOSA, aka Norsk Romsenter; established 1987) (2023)
Space launch site(s)
Andøya Space Center (Andøya Island; note - first operational spaceport in continental Europe) (2023)
Space program overview
- has a broad and active space program coordinated with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the EU; jointly designs and builds satellites with foreign partners, including communications, remote sensing (RS), scientific, and navigational/positional; operates satellites; develops and launches sounding rockets; researches and produces a range of other space-related technologies, including satellite/space launch vehicle (SLV) and space station components, telescopes, and robotics; conducts solar and telecommunications research; participates in international space programs, such as the International Space Station; hosts training for Mars landing missions on the island of Svalbard; active member of the ESA and cooperates with a variety of foreign space agencies and industries, including those of Canada, ESA/EU member states, Japan, Russia, and the US; has an active and advanced space industry that cooperates with both the NOSA and foreign space programs and produces a variety of space-related products, from terminals for satellite communications and technologies for RS satellites to sensors for gamma radiation in deep space (2023)
- note
- note: further details about the key activities, programs, and milestones of the country’s space program, as well as government spending estimates on the space sector, appear in Appendix S
Environment
Air pollutants
- carbon dioxide emissions
- 41.02 megatons (2016 est.)
- methane emissions
- 4.81 megatons (2020 est.)
- particulate matter emissions
- 6.3 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Climate
temperate along coast, modified by North Atlantic Current; colder interior with increased precipitation and colder summers; rainy year-round on west coast
Environment - current issues
water pollution; acid rain damaging forests and adversely affecting lakes, threatening fish stocks; air pollution from vehicle emissions
Environment - international agreements
- party to
- Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Heavy Metals, Air Pollution-Multi-effect Protocol, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protection, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
- signed, but not ratified
- none of the selected agreements
Land use
- agricultural land
- 2.7% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: arable land
- arable land: 2.2% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent crops
- permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent pasture
- permanent pasture: 0.5% (2018 est.)
- forest
- 27.8% (2018 est.)
- other
- 69.5% (2018 est.)
Revenue from coal
0% of GDP (2018 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
0.05% of GDP (2018 est.)
Total renewable water resources
393 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
Total water withdrawal
- agricultural
- 840 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
- industrial
- 1.07 billion cubic meters (2020 est.)
- municipal
- 780 million cubic meters (2020 est.)
Urbanization
- note
- note: data include Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands
- rate of urbanization
- 1.32% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population
- 84% of total population (2023)
Waste and recycling
- municipal solid waste generated annually
- 2.187 million tons (2015 est.)
- municipal solid waste recycled annually
- 572,119 tons (2015 est.)
- percent of municipal solid waste recycled
- 26.2% (2015 est.)