1993 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1993 (Project Gutenberg)
Geography
Area
total area: 324,220 km2 land area: 307,860 km2 comparative area: slightly larger than New Mexico
Climate
temperate along coast, modified by North Atlantic Current; colder interior; rainy year-round on west coast
Coastline
21,925 km (includes mainland 3,419 km, large islands 2,413 km, long fjords, numerous small islands, and minor indentations 16,093 km)
Environment
air and water pollution; acid rain; note - strategic location adjacent to sea lanes and air routes in North Atlantic; one of most rugged and longest coastlines in world; Norway and Turkey only NATO members having a land boundary with Russia
International disputes
territorial claim in Antarctica (Queen Maud Land); dispute between Denmark and Norway over maritime boundary in Arctic Ocean between Greenland and Jan Mayen is before the Interntional Court of Justice; maritime boundary dispute with Russia over portion of Barents Sea
Irrigated land
950 km2 (1989)
Land boundaries
total 2,515 km, Finland 729 km, Sweden 1,619 km, Russia 167 km
Land use
arable land: 3% permanent crops: 0% meadows and pastures: 0% forest and woodland: 27% other: 70%
Location
Northern Europe, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Sweden
Map references
Arctic Region, Europe, Standard Time Zones of the World
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 10 nm continental shelf: to depth of exploitation exclusive economic zone: 200 nm territorial sea: 4 nm
Natural resources
petroleum, copper, natural gas, pyrites, nickel, iron ore, zinc, lead, fish, timber, hydropower
Note
about two-thirds mountains; some 50,000 islands off its much indented coastline
Terrain
glaciated; mostly high plateaus and rugged mountains broken by fertile valleys; small, scattered plains; coastline deeply indented by fjords; arctic tundra in north
People and Society
Birth rate
13.75 births/1,000 population (1993 est.)
Death rate
10.54 deaths/1,000 population (1993 est.)
Ethnic divisions
Germanic (Nordic, Alpine, Baltic), Lapps 20,000
Infant mortality rate
6.4 deaths/1,000 live births (1993 est.)
Labor force
2.004 million (1992) by occupation: services 39.1%, commerce 17.6%, mining, oil, and manufacturing 16.0%, banking and financial services 7.6%, transportation and communications 7.8%, construction 6.1%, agriculture, forestry, and fishing 5.5% (1989)
Languages
Norwegian (official) note: small Lapp- and Finnish-speaking minorities
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 77.16 years male: 73.79 years female: 80.73 years (1993 est.)
Literacy
age 15 and over can read and write (1976) total population: 99% male: NA% female: NA%
Nationality
noun: Norwegian(s) adjective: Norwegian
Net migration rate
0.87 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1993 est.)
Population
4,297,436 (July 1993 est.)
Population growth rate
0.41% (1993 est.)
Religions
Evangelical Lutheran 87.8% (state church), other Protestant and Roman Catholic 3.8%, none 3.2%, unknown 5.2% (1980)
Total fertility rate
1.86 children born/woman (1993 est.)
Government
Administrative divisions
19 provinces (fylker, singular - fylke); Akershus, Aust-Agder, Buskerud, Finnmark, Hedmark, Hordaland, More og Romsdal, Nordland, Nord-Trondelag, Oppland, Oslo, Ostfold, Rogaland, Sogn og Fjordane, Sor-Trondelag, Telemark, Troms, Vest-Agder, Vestfold
Capital
Oslo
Chief of State
King HARALD V (since 17 January 1991); Heir Apparent Crown Prince HAAKON MAGNUS (born 20 July 1973)
Constitution
17 May 1814, modified in 1884
Dependent areas
Bouvet Island, Jan Mayen, Svalbard
Digraph
NO
Diplomatic representation in US
chief of mission: Ambassador Kjeld VIBE chancery: 2720 34th Street NW, Washington DC 20008 telephone: (202) 333-6000
Executive branch
monarch, prime minister, State Council (cabinet)
FAX
- (202) 337-0870 consulates general: Houston, Los Angeles, Minneapolis, New York, and San Francisco consulate: Miami
- [47] (2) 43-07-77
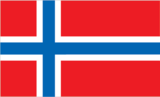
Flag
red with a blue cross outlined in white that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag)
Head of Government
Prime Minister Gro Harlem BRUNDTLAND (since 3 November 1990)
Independence
26 October 1905 (from Sweden)
Judicial branch
Supreme Court (Hoyesterett)
Legal system
mixture of customary law, civil law system, and common law traditions; Supreme Court renders advisory opinions to legislature when asked; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations
Legislative branch
unicameral Parliament (Storting) with an Upper Chamber (Lagting) and a Lower Chamber (Odelsting)
Member of
AfDB, AsDB, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CCC, CE, CERN, COCOM, CSCE, EBRD, ECE, EFTA, ESA, FAO, GATT, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, ILO, IMF, IMO, INMARSAT, INTELSAT, INTERPOL, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, LORCS, MTCR, NACC, NAM (guest), NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OECD, PCA, UN, UNAVEM II, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNIKOM, UNMOGIP, UNOSOM, UNPROFOR, UNTSO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ZC
Names
conventional long form: Kingdom of Norway conventional short form: Norway local long form: Kongeriket Norge local short form: Norge
National holiday
Constitution Day, 17 May (1814)
Political parties and leaders
Labor Party, Gro Harlem BRUNDTLAND; Conservative Party, Kaci Kullmann FIVE; Center Party, Anne ENGER LAHNSTEIN; Christian People's Party, Kjell Magne BONDEVIK; Socialist Left, Eric SOLHEIM; Norwegian Communist, Ingre IVERSEN; Progress Party, Carl I. HAGEN; Liberal, Odd Einar DORUM; Finnmark List, leader NA
Storting
last held on 11 September 1989 (next to be held 6 September 1993); results - Labor 34.3%, Conservative 22.2%, Progress 13.0%, Socialist Left 10.1%, Christian People's 8.5%, Center Party 6.6%, Finnmark List 0.3%, other 5%; seats - (165 total) Labor 63, Conservative 37, Progress 22, Socialist Left 17, Christian People's 14, Center Party 11, Finnmark List 1
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Type
constitutional monarchy
US diplomatic representation
chief of mission: (vacant) embassy: Drammensveien 18, 0244 Oslo 2 mailing address: PSC 69, Box 1000, APO AE 09707 telephone: [47] (2) 44-85-50
Economy
Agriculture
accounts for 2.6% of GDP and 5.5% of labor force; among world's top 10 fishing nations; livestock output exceeds value of crops; over half of food needs imported; fish catch of 1.76 million metric tons in 1989
Budget
revenues $50.6 billion; expenditures $57.0 billion, including capital expenditures of $NA (1992)
Currency
1 Norwegian krone (NKr) = 100 re
Economic aid
donor - ODA and OOF commitments (1970-89), $4.4 billion
Electricity
26,900,000 kW capacity; 111,000 million kWh produced, 25,850 kWh per capita (1992)
Exchange rates
Norwegian kroner (NKr) per US$1 - 6.8774 (January 1993), 6.2145 (1992), 6.4829 (1991), 6.2597 (1990), 6.9045 (1989), 6.5170 (1988)
Exports
$35.3 billion (f.o.b., 1992) commodities: petroleum and petroleum products 37.8%, metals and products 10.7%, natural gas 7.3%, fish 6.6%, chemicals 6.3%, ships 5.4% partners: EC 67%, Nordic countries 18.2%, developing countries 7.9%, US 5.1%, Japan 1.6% (1992)
External debt
$6.5 billion (1992 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Illicit drugs
increasingly used as transshipment point for Latin American cocaine to Europe and gateway for Asian heroin shipped via the CIS and Baltic states for the European market
Imports
$26.8 billion (c.i.f., 1992) commodities: machinery, fuels and lubricants, transportation equipment, chemicals, foodstuffs, clothing, ships partners: EC 48.7%, Nordic countries 26.8%, developing countries 9.3%, US 8.6%, Japan 6.3% (1992)
Industrial production
growth rate 7.3% (1992)
Industries
petroleum and gas, food processing, shipbuilding, pulp and paper products, metals, chemicals, timber, mining, textiles, fishing
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.3% (1992)
National product
GDP - purchasing power equivalent - $76.1 billion (1992)
National product per capita
$17,700 (1992)
National product real growth rate
2.9% (1992)
Overview
Norway has a mixed economy involving a combination of free market activity and government intervention. The government controls key areas, such as the vital petroleum sector (through large-scale state enterprises) and extensively subsidizes agriculture, fishing, and areas with sparse resources. Norway also maintains an extensive welfare system that helps propel public sector expenditures to slightly more than 50% of the GDP and results in one of the highest average tax burdens in the world (54%). A small country with a high dependence on international trade, Norway is basically an exporter of raw materials and semiprocessed goods, with an abundance of small- and medium-sized firms, and is ranked among the major shipping nations. The country is richly endowed with natural resources - petroleum, hydropower, fish, forests, and minerals - and is highly dependent on its oil sector to keep its economy afloat. Although one of the government's main priorities is to reduce this dependency, this situation is not likely to improve for years to come. The government also hopes to reduce unemployment and strengthen and diversify the economy through tax reform and a series of expansionary budgets. The budget deficit is expected to hit a record 8% of GDP because of welfare spending and bail-outs of the banking system. Unemployment continues at record levels of over 10% - including those in job programs - because of the weakness of the economy outside the oil sector. Overall economic growth is expected to be around 2% in 1993 while inflation is likely to rise slightly to 4%. Oslo, a member of the European Free Trade Area, has applied for EC membership and continues to deregulate and harmonize with EC regulations to prepare for the European Economic Area (EEA) - which creates an EC/EFTA market with free movement of capital, goods, services, and labor - to take effect in late 1993 and its EC bid.
Unemployment rate
5.9% (excluding people in job-training programs) (1992)
Communications
Airports
total: 103 usable: 102 with permanent-surface runways: 63 with runways over 3,659 m: with runways 2,440-3,659 m: 12 with runways 1,220-2,439 m: 16
Highways
79,540 km total; 38,580 km paved; 40,960 km gravel, crushed stone, and earth
Inland waterways
1,577 km along west coast; 2.4 m draft vessels maximum
Merchant marine
829 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 22,312,412 GRT/38,532,109 DWT; includes 13 passenger, 20 short-sea passenger, 106 cargo, 2 passenger-cargo, 19 refrigerated cargo, 15 container, 49 roll-on/roll-off, 23 vehicle carrier, 1 railcar carrier, 174 oil tanker, 91 chemical tanker, 82 liquefied gas, 25 combination ore/oil, 201 bulk, 8 combination bulk; note - the government has created a captive register, the Norwegian International Ship Register (NIS), as a subset of the Norwegian register; ships on the NIS enjoy many benefits of flags of convenience and do not have to be crewed by Norwegians; the majority of ships (777) under the Norwegian flag are now registered with the NIS
Pipelines
refined products 53 km
Ports
Oslo, Bergen, Fredrikstad, Kristiansand, Stavanger, Trondheim
Railroads
4,223 km 1.435-meter standard gauge; Norwegian State Railways (NSB) operates 4,219 km (2,450 km electrified and 96 km double track); 4 km other
Telecommunications
high-quality domestic and international telephone, telegraph, and telex services; 2 buried coaxial cable systems; 3,102,000 telephones; broadcast stations - 46 AM, 350 private and 143 government FM, 54 (2,100 repeaters) TV; 4 coaxial submarine cables; 3 communications satellite earth stations operating in the EUTELSAT, INTELSAT (1 Atlantic Ocean), MARISAT, and domestic systems
Military and Security
Branches
Norwegian Army, Royal Norwegian Navy, Royal Norwegian Air Force, Home Guard
Defense expenditures
exchange rate conversion - $3.8 billion, 3.4% of GDP (1992)
Manpower availability
males age 15-49 1,120,744; fit for military service 934,968; reach military age (20) annually 31,903 (1993 est.)