2022 Edition
CIA World Factbook 2022 (factbook.json @ 61dadec0c9c9)
Introduction
Background
Madagascar was one of the last major habitable landmasses on earth settled by humans. While there is some evidence of human presence on the island in the millennia B.C., large-scale settlement began between A.D. 350 and 550 with settlers from present-day Indonesia. The island attracted Arab and Persian traders as early as the 7th century, and migrants from Africa arrived around A.D. 1000. Madagascar was a pirate stronghold during the late 17th and early 18th centuries, and served as a slave trading center into the 19th century. From the 16th to the late 19th century, a native Merina Kingdom dominated much of Madagascar. The island was conquered by the French in 1896 who made it a colony; independence was regained in 1960. During 1992-93, free presidential and National Assembly elections were held ending 17 years of single-party rule. In 1997, in the second presidential race, Didier RATSIRAKA, the leader during the 1970s and 1980s, returned to the presidency. The 2001 presidential election was contested between the followers of Didier RATSIRAKA and Marc RAVALOMANANA, nearly causing secession of half of the country. In 2002, the High Constitutional Court announced RAVALOMANANA the winner. RAVALOMANANA won a second term in 2006 but, following protests in 2009, handed over power to the military, which then conferred the presidency on the mayor of Antananarivo, Andry RAJOELINA, in what amounted to a coup d'etat. Following a lengthy mediation process led by the Southern African Development Community, Madagascar held UN-supported presidential and parliamentary elections in 2013. Former de facto finance minister Hery RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA won a runoff election in December 2013 and was inaugurated in January 2014. In January 2019, RAJOELINA was declared the winner of a runoff election against RAVALOMANANA; both RATSIRAKA and RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA also ran in the first round of the election, which took place in November 2018.
Geography
Area
- land
- 581,540 sq km
- total
- 587,041 sq km
- water
- 5,501 sq km
Area - comparative
almost four times the size of Georgia; slightly less than twice the size of Arizona
Climate
tropical along coast, temperate inland, arid in south
Coastline
4,828 km
Elevation
- highest point
- Maromokotro 2,876 m
- lowest point
- Indian Ocean 0 m
- mean elevation
- 615 m
Geographic coordinates
20 00 S, 47 00 E
Geography - note
world's fourth-largest island; strategic location along Mozambique Channel; despite Madagascar’s close proximity to the African continent, ocean currents isolate the island resulting in high rates of endemic plant and animal species; approximately 90% of the flora and fauna on the island are found nowhere else
Irrigated land
10,860 sq km (2012)
Land boundaries
- total
- 0 km
Land use
- agricultural land
- 71.1% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: arable land
- arable land: 6% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent crops
- permanent crops: 1% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent pasture
- permanent pasture: 64.1% (2018 est.)
- forest
- 21.5% (2018 est.)
- other
- 7.4% (2018 est.)
Location
Southern Africa, island in the Indian Ocean, east of Mozambique
Map references
Africa
Maritime claims
- contiguous zone
- 24 nm
- continental shelf
- 200 nm or 100 nm from the 2,500-m isobath
- exclusive economic zone
- 200 nm
- territorial sea
- 12 nm
Natural hazards
periodic cyclones; drought; and locust infestationvolcanism: Madagascar's volcanoes have not erupted in historical times
Natural resources
graphite, chromite, coal, bauxite, rare earth elements, salt, quartz, tar sands, semiprecious stones, mica, fish, hydropower
Population distribution
most of population lives on the eastern half of the island; significant clustering is found in the central highlands and eastern coastline as shown in this population distribution map
Terrain
narrow coastal plain, high plateau and mountains in center
People and Society
Age structure
- 0-14 years
- 38.86% (male 5,278,838/female 5,196,036)
- 15-24 years
- 20.06% (male 2,717,399/female 2,689,874)
- 25-54 years
- 33.02% (male 4,443,147/female 4,456,691)
- 55-64 years
- 4.6% (male 611,364/female 627,315)
- 65 years and over
- 3.47% (male 425,122/female 509,951) (2020 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
- beer
- 0.5 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- other alcohols
- 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- spirits
- 0.32 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- total
- 0.89 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- wine
- 0.07 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Birth rate
28.68 births/1,000 population (2022 est.)
Child marriage
- men married by age 18
- 11.8% (2018 est.)
- women married by age 15
- 12.7%
- women married by age 18
- 40.3%
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
26.4% (2018)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
49.7% (2020)
Current health expenditure
3.7% of GDP (2019)
Death rate
6 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.)
Demographic profile
Madagascar’s youthful population – nearly 60% are under the age of 25 as of 2022 – and moderately high total fertility rate of more than 3.6 children per woman ensures that the Malagasy population will continue its rapid growth trajectory for the foreseeable future. The population is predominantly rural and poor; chronic malnutrition is prevalent, and large families are the norm. Many young Malagasy girls are withdrawn from school, marry early (often pressured to do so by their parents), and soon begin having children. Early childbearing, coupled with Madagascar’s widespread poverty and lack of access to skilled health care providers during delivery, increases the risk of death and serious health problems for young mothers and their babies. Child marriage perpetuates gender inequality and is prevalent among the poor, the uneducated, and rural households – as of 2018, 40% of Malagasy women aged 20 to 24 were married. Although the legal age for marriage is 18, parental consent is often given for earlier marriages or the law is flouted, especially in rural areas that make up approximately 60% of the country. Forms of arranged marriage whereby young girls are married to older men in exchange for oxen or money are traditional. If a union does not work out, a girl can be placed in another marriage, but the dowry paid to her family diminishes with each unsuccessful marriage. Madagascar’s population consists of 18 main ethnic groups, all of whom speak the same Malagasy language. Most Malagasy are multi-ethnic, however, reflecting the island’s diversity of settlers and historical contacts (see Background). Madagascar’s legacy of hierarchical societies practicing domestic slavery (most notably the Merina Kingdom of the 16th to the 19th century) is evident today in persistent class tension, with some ethnic groups maintaining a caste system. Slave descendants are vulnerable to unequal access to education and jobs, despite Madagascar’s constitutional guarantee of free compulsory primary education and its being party to several international conventions on human rights. Historical distinctions also remain between central highlanders and coastal people.
Dependency ratios
- elderly dependency ratio
- 5.8
- potential support ratio
- 17.4 (2021 est.)
- total dependency ratio
- 74.5
- youth dependency ratio
- 68.8
Drinking water source
- improved: rural
- rural: 38% of population
- improved: total
- total: 56.1% of population
- improved: urban
- urban: 85% of population
- unimproved: rural
- rural: 62% of population
- unimproved: total
- total: 43.9% of population (2020 est.)
- unimproved: urban
- urban: 15% of population
Education expenditures
3.1% of GDP (2020 est.)
Ethnic groups
Malayo-Indonesian (Merina and related Betsileo), Cotiers (mixed African, Malayo-Indonesian, and Arab ancestry - Betsimisaraka, Tsimihety, Antaisaka, Sakalava), French, Indian, Creole, Comoran
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
0.4% (2021 est.)
Hospital bed density
0.2 beds/1,000 population
Infant mortality rate
- female
- 35.65 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
- male
- 42.33 deaths/1,000 live births
- total
- 39.04 deaths/1,000 live births
Languages
- Malagasy (official) 99.9%, French (official) 23.6%, English 8.2%, other 0.6% (2018 est.)
- note
- note: shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
Life expectancy at birth
- female
- 69.57 years (2022 est.)
- male
- 66.8 years
- total population
- 68.17 years
Literacy
- definition
- age 15 and over can read and write
- female
- 75.1% (2018)
- male
- 78.4%
- total population
- 76.7%
Major infectious diseases
- animal contact diseases
- rabies
- degree of risk
- very high (2020)
- food or waterborne diseases
- bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
- note
- note: on 21 March 2022, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a Travel Alert for polio in Africa; Madagascar is currently considered a high risk to travelers for circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV); vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV) is a strain of the weakened poliovirus that was initially included in oral polio vaccine (OPV) and that has changed over time and behaves more like the wild or naturally occurring virus; this means it can be spread more easily to people who are unvaccinated against polio and who come in contact with the stool or respiratory secretions, such as from a sneeze, of an “infected” person who received oral polio vaccine; the CDC recommends that before any international travel, anyone unvaccinated, incompletely vaccinated, or with an unknown polio vaccination status should complete the routine polio vaccine series; before travel to any high-risk destination, the CDC recommends that adults who previously completed the full, routine polio vaccine series receive a single, lifetime booster dose of polio vaccine
- vectorborne diseases
- malaria and dengue fever
- water contact diseases
- schistosomiasis
Major urban areas - population
3.872 million ANTANANARIVO (capital) (2023)
Maternal mortality ratio
335 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
Median age
- female
- 20.5 years (2020 est.)
- male
- 20.1 years
- total
- 20.3 years
Mother's mean age at first birth
- 19.5 years (2021 est.)
- note
- note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-29
Nationality
- adjective
- Malagasy
- noun
- Malagasy (singular and plural)
Net migration rate
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
5.3% (2016)
Physicians density
0.2 physicians/1,000 population (2018)
Population
28,172,462 (2022 est.)
Population distribution
most of population lives on the eastern half of the island; significant clustering is found in the central highlands and eastern coastline as shown in this population distribution map
Population growth rate
2.27% (2022 est.)
Religions
Church of Jesus Christ in Madagascar/Malagasy Lutheran Church/Anglican Church 34%, Roman Catholic 32.3%, other Christian 8.1%, traditional/Animist 1.7%, Muslim 1.4%, other 0.6%, none 21.9% (2021 est.)
Sanitation facility access
- improved: rural
- rural: 22.1% of population
- improved: total
- total: 32.6% of population
- improved: urban
- urban: 49.2% of population
- unimproved: rural
- rural: 77.9% of population
- unimproved: total
- total: 67.4% of population (2020 est.)
- unimproved: urban
- urban: 50.8% of population
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- female
- 10 years (2018)
- male
- 10 years
- total
- 10 years
Sex ratio
- 0-14 years
- 1.02 male(s)/female
- 15-24 years
- 1.02 male(s)/female
- 25-54 years
- 1 male(s)/female
- 55-64 years
- 0.98 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over
- 0.78 male(s)/female
- at birth
- 1.03 male(s)/female
- total population
- 1 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Tobacco use
- female
- 12.8% (2020 est.)
- male
- 42.7% (2020 est.)
- total
- 27.8% (2020 est.)
Total fertility rate
3.62 children born/woman (2022 est.)
Urbanization
- rate of urbanization
- 4.26% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population
- 40.6% of total population (2023)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
- female
- 3% (2015 est.)
- male
- 3.9%
- total
- 3.4%
Government
Administrative divisions
6 provinces (faritany); Antananarivo, Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga, Toamasina, Toliara
Capital
- etymology
- the name, which means "City of the Thousand," was bestowed by 17th century King ADRIANJAKAKING to honor the soldiers assigned to guard the city
- geographic coordinates
- 18 55 S, 47 31 E
- name
- Antananarivo
- time difference
- UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Citizenship
- citizenship by birth
- no
- citizenship by descent only
- the father must be a citizen of Madagascar; in the case of a child born out of wedlock, the mother must be a citizen
- dual citizenship recognized
- no
- residency requirement for naturalization
- unknown
Constitution
- amendments
- proposed by the president of the republic in consultation with the cabinet or supported by a least two thirds of both the Senate and National Assembly membership; passage requires at least three-fourths approval of both the Senate and National Assembly and approval in a referendum; constitutional articles, including the form and powers of government, the sovereignty of the state, and the autonomy of Madagascar’s collectivities, cannot be amended
- history
- previous 1992; latest passed by referendum 17 November 2010, promulgated 11 December 2010
Country name
- conventional long form
- Republic of Madagascar
- conventional short form
- Madagascar
- etymology
- the name "Madageiscar" was first used by the 13th-century Venetian explorer Marco POLO, as a corrupted transliteration of Mogadishu, the Somali port with which POLO confused the island
- former
- Malagasy Republic
- local long form
- Republique de Madagascar/Repoblikan'i Madagasikara
- local short form
- Madagascar/Madagasikara
Diplomatic representation from the US
- chief of mission
- Ambassador Claire PIERANGELO (since 2 May 2022)
- email address and website
- antanACS@state.govhttps://mg.usembassy.gov/
- embassy
- Lot 207A, Andranoro, Antehiroka, 105 Antananarivo
- FAX
- [261] 20-23-480-35
- mailing address
- 2040 Antananarivo Place, Washington DC 20521-2040
- telephone
- [261] 20-23-480-00
Diplomatic representation in the US
- chancery
- 2374 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
- chief of mission
- Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Amielle Pelenne NIRINIAVISOA MARCEDA (since 31 October 2019)
- consulate(s) general
- New York
- email address and website
- contact@us-madagascar-embassy.orghttps://us-madagascar-embassy.org/
- FAX
- [1] (202) 265-3034
- telephone
- [1] (202) 265-5525
Executive branch
- cabinet
- Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister
- chief of state
- President Andry RAJOELINA (since 21 January 2019)
- election results
- 2018: Andry RAJOELINA elected President in second round; percent of vote in first round - Andry RAJOELINA (TGV) 39.2%, Marc RAVALOMANANA (TIM) 35.4%, other 25.4%; percent of vote in second round - Andry RAJOELINA (TGV) 55.7%, Marc RAVALOMANANA (TIM) 44.3% 2013: Hery Martial RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Hery Martial RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA (HVM) 15.9%, Jean Louis ROBINSON (AVANA) 21.1%, other 63%; percent of vote in second round - Hery Martial RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA (HVM) 53.5%, Jean Louis ROBINSON (AVANA) 46.5%
- elections/appointments
- president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 7 November and 19 December 2018 (next to be held in 2023); prime minister nominated by the National Assembly, appointed by the president
- head of government
- Prime Minister Christian NTSAY (since 6 June 2018)
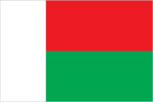
Flag description
two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and green with a vertical white band of the same width on hoist side; by tradition, red stands for sovereignty, green for hope, white for purity
Government type
semi-presidential republic
Independence
26 June 1960 (from France)
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, CD, COMESA, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, InOC, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Judicial branch
- highest court(s)
- Supreme Court or Cour Supreme (consists of 11 members; addresses judicial administration issues only); High Constitutional Court or Haute Cour Constitutionnelle (consists of 9 members); note - the judiciary includes a High Court of Justice responsible for adjudicating crimes and misdemeanors by government officials, including the president
- judge selection and term of office
- Supreme Court heads elected by the president and judiciary officials to serve 3-year, single renewable terms; High Constitutional Court members appointed - 3 each by the president, by both legislative bodies, and by the Council of Magistrates; members serve single, 7-year terms
- subordinate courts
- Courts of Appeal; Courts of First Instance
Legal system
civil law system based on the old French civil code and customary law in matters of marriage, family, and obligation
Legislative branch
- description
- bicameral Parliament consists of:Senate or Antenimieran-Doholona (18 seats; 12 members indirectly elected by an electoral college of municipal, communal, regional, and provincial leaders and 6 appointed by the president; members serve 5-year terms)National Assembly or Antenimierampirenena (151 seats; 87 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 64 directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by closed-list proportional representation vote; members serve 5-year terms)
- election results
- 2020:Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; elected seats by party - Irmar 10, Malagasy Miara Miainga 2; composition - men 16, women 2, percent of women 11%2019:National Assembly - percent of vote by party - TGV 30.9%, TIM 9.7%, MATITA 1.1%, MTS 0.4%, GJMP 0.3%, MDM 0.2%, RPSD Vaovao 0.1%, Independents 50%, Other 7.3%; composition - men 123, women 28, percent of women 18.5%; note - total Parliament percent of women 17.8%
- elections
- Senate - last held on 11 December 2020 (next to be held in December 2025)National Assembly - last held on 27 May 2019 (next to be held in May 2024)
National anthem
- lyrics/music
- Pasteur RAHAJASON/Norbert RAHARISOA
- name
- "Ry Tanindraza nay malala o" (Oh, Our Beloved Fatherland)
- note
- note: adopted 1959
National heritage
- selected World Heritage Site locales
- Tsingy de Bemaraha Strict Nature Reserve (n); Ambohimanga Royal Hill (c); Atsinanana Rainforests (n)
- total World Heritage Sites
- 3 (1 cultural, 2 natural)
National holiday
Independence Day, 26 June (1960)
National symbol(s)
traveller's palm, zebu; national colors: red, green, white
Political parties and leaders
Group of Young Malagasy Patriots (Groupe des Jeunes Malgaches Patriotes) or GJMPI Love Madagascar (Tiako I Madagasikara) or TIM [Marc RAVALOMANANA]Malagasy Aware (Malagasy Tonga Saina) or MTS [Roland RATSIRAKA]Malagasy Tia Tanindrazana or MATITA or ANGADY [Hyacinthe Befeno TODIMANANA]Movement for Democracy in Madagascar (Mouvement pour la Démocratie à Madagascar) or MDM [Pierrot RAJAONARIVELO]Rally for Democratic Socialism (Rassemblement pour Socialisme Démocratique - Nauveau) or RPSD Vaovao [Evariste MARSON]Young Malagasies Determined (Tanora Malagasy Vonona) or TGV [Andry RAJOELINA]Note: Only parties with seats in the National Assembly included
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Economy
Agricultural products
rice, sugar cane, cassava, sweet potatoes, milk, vegetables, bananas, mangoes/guavas, tropical fruit, potatoes
Budget
- expenditures
- 2.136 billion (2017 est.)
- revenues
- 1.828 billion (2017 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)
-2.7% (of GDP) (2017 est.)
Current account balance
- Current account balance 2016
- $57 million (2016 est.)
- Current account balance 2017
- -$35 million (2017 est.)
Debt - external
- Debt - external 2018
- $4.107 billion (2018 est.)
- Debt - external 2019
- $3.085 billion (2019 est.)
Economic overview
Madagascar is a mostly unregulated economy with many untapped natural resources, but no capital markets, a weak judicial system, poorly enforced contracts, and rampant government corruption. The country faces challenges to improve education, healthcare, and the environment to boost long-term economic growth. Agriculture, including fishing and forestry, is a mainstay of the economy, accounting for more than one-fourth of GDP and employing roughly 80% of the population. Deforestation and erosion, aggravated by bushfires, slash-and-burn clearing techniques, and the use of firewood as the primary source of fuel, are serious concerns to the agriculture dependent economy. After discarding socialist economic policies in the mid-1990s, Madagascar followed a World Bank- and IMF-led policy of privatization and liberalization until a 2009 coup d’état led many nations, including the United States, to suspend non-humanitarian aid until a democratically-elected president was inaugurated in 2014. The pre-coup strategy had placed the country on a slow and steady growth path from an extremely low starting point. Exports of apparel boomed after gaining duty-free access to the US market in 2000 under the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA); however, Madagascar's failure to comply with the requirements of the AGOA led to the termination of the country's duty-free access in January 2010, a sharp fall in textile production, a loss of more than 100,000 jobs, and a GDP drop of nearly 11%. Madagascar regained AGOA access in January 2015 and ensuing growth has been slow and fragile. Madagascar produces around 80% of the world’s vanilla and its reliance on this commodity for most of its foreign exchange is a significant source of vulnerability. Economic reforms have been modest and the country’s financial sector remains weak, limiting the use of monetary policy to control inflation. An ongoing IMF program aims to strengthen financial and investment management capacity.
Exchange rates
- Currency
- Malagasy ariary (MGA) per US dollar -
- Exchange rates 2013
- 2,414.8 (2013 est.)
- Exchange rates 2014
- 2,933.5 (2014 est.)
- Exchange rates 2015
- 3,176.5 (2015 est.)
- Exchange rates 2016
- 3,176.5 (2016 est.)
- Exchange rates 2017
- 3,116.1 (2017 est.)
Exports
- Exports 2017
- $4.839 billion (2017 est.)
- Exports 2018
- $4.41 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Exports 2019
- $4.09 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Exports - commodities
vanilla, nickel, gold, clothing and apparel, gemstones (2019)
Exports - partners
United States 19%, France 18%, United Arab Emirates 7%, China 6%, Japan 6%, Germany 5%, India 5% (2019)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP - composition, by end use
- exports of goods and services
- 31.5% (2017 est.)
- government consumption
- 11.2% (2017 est.)
- household consumption
- 67.1% (2017 est.)
- imports of goods and services
- -33.7% (2017 est.)
- investment in fixed capital
- 15.1% (2017 est.)
- investment in inventories
- 8.8% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
- agriculture
- 24% (2017 est.)
- industry
- 19.5% (2017 est.)
- services
- 56.4% (2017 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$13.964 billion (2019 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
- Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income 2010
- 42.7 (2010)
- Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income 2012
- 42.6 (2012 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
- highest 10%
- 34.7% (2010 est.)
- lowest 10%
- 2.2%
Imports
- Imports 2017
- $5.796 billion (2017 est.)
- Imports 2018
- $4.82 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Imports 2019
- $4.7 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, rice, cars, packaged medicines, clothing and apparel (2019)
Imports - partners
China 24%, France 11%, United Arab Emirates 9%, India 7%, South Africa 5% (2019)
Industrial production growth rate
5.2% (2017 est.)
Industries
meat processing, seafood, soap, beer, leather, sugar, textiles, glassware, cement, automobile assembly plant, paper, petroleum, tourism, mining
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2017
- 8.5% (2017 est.)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2018
- 8.6% (2018 est.)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2019
- 5.6% (2019 est.)
Labor force
13.4 million (2017 est.)
Population below poverty line
70.7% (2012 est.)
Public debt
- Public debt 2016
- 38.4% of GDP (2016 est.)
- Public debt 2017
- 36% of GDP (2017 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
- note
- note: data are in 2017 dollars
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2018
- $41.81 billion (2018 est.)
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2019
- $43.65 billion (2019 est.)
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2020
- $41.82 billion (2020 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
- Real GDP growth rate 2015
- 3.1% (2015 est.)
- Real GDP growth rate 2016
- 4.2% (2016 est.)
- Real GDP growth rate 2017
- 4.2% (2017 est.)
Real GDP per capita
- note
- note: data are in 2017 dollars
- Real GDP per capita 2018
- $1,600 (2018 est.)
- Real GDP per capita 2019
- $1,600 (2019 est.)
- Real GDP per capita 2020
- $1,500 (2020 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2016
- $1.076 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2017
- $1.6 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
Taxes and other revenues
15.9% (of GDP) (2017 est.)
Unemployment rate
- Unemployment rate 2016
- 1.8% (2016 est.)
- Unemployment rate 2017
- 1.8% (2017 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
- female
- 3% (2015 est.)
- male
- 3.9%
- total
- 3.4%
Energy
Carbon dioxide emissions
- from coal and metallurgical coke
- 1.044 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- from consumed natural gas
- 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- from petroleum and other liquids
- 3.175 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- total emissions
- 4.218 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Coal
- consumption
- 107,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
- exports
- 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
- imports
- 115,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
- production
- 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
- proven reserves
- 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Electricity
- consumption
- 1,720,140,000 kWh (2019 est.)
- exports
- 0 kWh (2020 est.)
- imports
- 0 kWh (2020 est.)
- installed generating capacity
- 587,000 kW (2020 est.)
- transmission/distribution losses
- 131 million kWh (2019 est.)
Electricity access
- electrification - rural areas
- 23% (2019)
- electrification - total population
- 39% (2019)
- electrification - urban areas
- 64% (2019)
Electricity generation sources
- biomass and waste
- 1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- fossil fuels
- 59.8% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- geothermal
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- hydroelectricity
- 38.2% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- nuclear
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- solar
- 1.1% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- tide and wave
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- wind
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
- Total energy consumption per capita 2019
- 2.307 million Btu/person (2019 est.)
Natural gas
- consumption
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
- exports
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
- imports
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
- production
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
- proven reserves
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
- crude oil and lease condensate exports
- 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
- crude oil and lease condensate imports
- 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
- crude oil estimated reserves
- 0 barrels (2021 est.)
- refined petroleum consumption
- 21,100 bbl/day (2019 est.)
- total petroleum production
- 0 bbl/day (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - exports
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)
Refined petroleum products - imports
18,880 bbl/day (2015 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)
Communications
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 0.1 (2020 est.)
- total
- 32,000 (2020 est.)
Broadcast media
state-owned Radio Nationale Malagasy (RNM) and Television Malagasy (TVM) have an extensive national network reach; privately owned radio and TV broadcasters in cities and major towns; state-run radio dominates in rural areas; relays of 2 international broadcasters are available in Antananarivo (2019)
Internet country code
.mg
Internet users
- percent of population
- 10% (2019 est.)
- total
- 2,696,931 (2019 est.)
Telecommunication systems
- domestic
- less than 1 per 100 for fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity about 57 per 100 persons (2020)
- general assessment
- telecom services in Madagascar have benefited from intensifying competition between the main operators; there have been positive developments with the country’s link to international submarine cables, particularly the METISS cable connecting to South Africa and Mauritius; in addition, the country’s connection to the Africa-1 cable, expected in late 2023, will provide it with links to Kenya, Djibouti, countries in north and south Africa, as well Pakistan, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and France; a national fiber backbone has been implemented connecting the major cities; in addition, the government has progressed with its five-year plan to develop a digital platform running to 2024; various schemes within the program have been managed by a unit within the President’s office; penetration rates in all market sectors remain below the average for the African region, and so there remains considerable growth potential; much progress was made in 2020, stimulated by the particular conditions related to the pandemic, which encouraged greater use of voice and data services (2022)
- international
- country code - 261; landing points for the EASSy, METISS, and LION fiber-optic submarine cable systems connecting to numerous Indian Ocean Islands, South Africa, and Eastern African countries; satellite earth stations - 2 (1 Intelsat - Indian Ocean, 1 Intersputnik - Atlantic Ocean region) (2019)
- note
- note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Telephones - fixed lines
- total subscriptions
- 69,000 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 57 (2020 est.)
- total subscriptions
- 15.869 million (2020 est.)
Transportation
Airports
- total
- 83 (2021)
Airports - with paved runways
- 1,524 to 2,437 m
- 6
- 2,438 to 3,047 m
- 2
- 914 to 1,523 m
- 16
- over 3,047 m
- 1
- total
- 26
- under 914 m
- 1 (2021)
Airports - with unpaved runways
- 1,524 to 2,437 m
- 1
- 914 to 1,523 m
- 38
- total
- 57
- under 914 m
- 18 (2021)
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
5R
Merchant marine
- by type
- general cargo 14, oil tanker 2, other 11 (2021)
- total
- 27
National air transport system
- annual freight traffic on registered air carriers
- 16.25 million (2018) mt-km
- annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers
- 541,290 (2018)
- inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers
- 18
- number of registered air carriers
- 4 (2020)
Ports and terminals
- major seaport(s)
- Antsiranana (Diego Suarez), Mahajanga, Toamasina, Toliara (Tulear)
Railways
- narrow gauge
- 836 km (2018) 1.000-m gauge
- total
- 836 km (2018)
Roadways
- total
- 31,640 km (2018)
Waterways
600 km (2011) (432 km navigable)
Military and Security
Military - note
one of the military’s duties is assisting the gendarmerie with maintaining law and order in rural areas, particularly in areas affected by banditry, cattle rustling (cattle thieves are known as dahalo), and criminal groups (2022)
Military and security forces
- Madagascar People's Armed Forces (PAF): Army, Navy, Air Force; Ministry of Defense: National Gendarmerie; Ministry of Public Security: National Police (2022)
- note
- note: the National Gendarmerie is separate from the PAF and is responsible for maintaining law and order in rural areas at the village level, protecting government facilities, and operating a maritime police contingent; the National Police is responsible for maintaining law and order in urban areas
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 13,000 personnel (12,000 Army; 500 Navy; 500 Air Force); estimated 10,000 Gendarmerie (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the PAF's inventory consists mostly of aging Soviet-era equipment; since 2010, it has received limited amounts of second-hand equipment from France, South Africa, and the UAE (2022)
Military expenditures
- Military Expenditures 2017
- 0.5% of GDP (2017 est.) (approximately $120 million)
- Military Expenditures 2018
- 0.5% of GDP (2018 est.) (approximately $130 million)
- Military Expenditures 2019
- 0.5% of GDP (2019 est.) (approximately $130 million)
- Military Expenditures 2020
- 0.7% of GDP (2020 est.)
- Military Expenditures 2021
- 0.7% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military service age and obligation
18-25 years of age for men and women; service obligation 18 months; no conscription; women are permitted to serve in all branches (2022)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Madagascar-France: claims Bassas da India, Europa Island, Glorioso Islands, and Juan de Nova Island (all administered by France); the vegetated drying cays of Banc du Geyser, which were claimed by Madagascar in 1976, also fall within the EEZ claim of France Madagascar-Comoros: the vegetated drying cays of Banc du Geyser, which were claimed by Madagascar in 1976, also fall within the EEZ claim of the Comoros
Illicit drugs
illicit producer of cannabis (cultivated and wild varieties) used mostly for domestic consumption; transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin
Environment
Air pollutants
- carbon dioxide emissions
- 3.91 megatons (2016 est.)
- methane emissions
- 10.14 megatons (2020 est.)
- particulate matter emissions
- 21.44 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
Climate
tropical along coast, temperate inland, arid in south
Environment - current issues
erosion and soil degredation results from deforestation and overgrazing; desertification; agricultural fires; surface water contaminated with raw sewage and other organic wastes; wildlife preservation (endangered species of flora and fauna unique to the island)
Environment - international agreements
- party to
- Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands
- signed, but not ratified
- none of the selected agreements
Food insecurity
- severe localized food insecurity
- due to the effects of extreme weather events and slow economic recovery - according to the latest May 2022 analysis, the prevalence of food insecurity in the southern regions is projected to peak at 2.1 million people by December 2022 until at least March 2023; overall, the number of people requiring humanitarian assistance by the end of 2022 is expected to be about 30 percent higher compared to the peak number in 2021; the poor food security situation is mainly the consequence of six consecutive poor agricultural seasons that culminated in very tight food supplies for rural households and curbed incomes from crop sales; high rates of poverty and increased prices of essential food commodities, combined with a high reliance on market supplies due to low harvests for own consumption, are also contributing to the high rates of food insecurity across the southern regions (2022)
Land use
- agricultural land
- 71.1% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: arable land
- arable land: 6% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent crops
- permanent crops: 1% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent pasture
- permanent pasture: 64.1% (2018 est.)
- forest
- 21.5% (2018 est.)
- other
- 7.4% (2018 est.)
Major infectious diseases
- animal contact diseases
- rabies
- degree of risk
- very high (2020)
- food or waterborne diseases
- bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
- note
- note: on 21 March 2022, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a Travel Alert for polio in Africa; Madagascar is currently considered a high risk to travelers for circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV); vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV) is a strain of the weakened poliovirus that was initially included in oral polio vaccine (OPV) and that has changed over time and behaves more like the wild or naturally occurring virus; this means it can be spread more easily to people who are unvaccinated against polio and who come in contact with the stool or respiratory secretions, such as from a sneeze, of an “infected” person who received oral polio vaccine; the CDC recommends that before any international travel, anyone unvaccinated, incompletely vaccinated, or with an unknown polio vaccination status should complete the routine polio vaccine series; before travel to any high-risk destination, the CDC recommends that adults who previously completed the full, routine polio vaccine series receive a single, lifetime booster dose of polio vaccine
- vectorborne diseases
- malaria and dengue fever
- water contact diseases
- schistosomiasis
Revenue from coal
- coal revenues
- 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
- forest revenues
- 4.34% of GDP (2018 est.)
Total renewable water resources
337 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total water withdrawal
- agricultural
- 13 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
- industrial
- 161.9 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
- municipal
- 395 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Urbanization
- rate of urbanization
- 4.26% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population
- 40.6% of total population (2023)
Waste and recycling
- municipal solid waste generated annually
- 3,768,759 tons (2016 est.)