1990 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1990 (Project Gutenberg)
Geography
Climate
tropical along coast, temperate inland, arid in south
Coastline
4,828 km
Comparative area
slightly less than twice the size of Arizona
Disputes
claims Bassas da India, Europa Island, Glorioso Islands, Juan de Nova Island, and Tromelin Island (all administered by France)
Environment
subject to periodic cyclones; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification
Exclusive fishing zone
150 nm;
Extended economic zone
200 nm;
Land boundaries
none
Land use
4% arable land; 1% permanent crops; 58% meadows and pastures; 26% forest and woodland; 11% other; includes 2% irrigated
Natural resources
graphite, chromite, coal, bauxite, salt, quartz, tar sands, semiprecious stones, mica, fish
Note
world's fourth-largest island; strategic location along Mozambique Channel
Terrain
narrow coastal plain, high plateau and mountains in center
Territorial sea
12 nm
Total area
587,040 km2; land area: 581,540 km2
People and Society
Birth rate
47 births/1,000 population (1990)
Death rate
15 deaths/1,000 population (1990)
Ethnic divisions
basic split between highlanders of predominantly Malayo-Indonesian origin (Merina 1,643,000 and related Betsileo 760,000) on the one hand and coastal tribes, collectively termed the Cotiers, with mixed African, Malayo-Indonesian, and Arab ancestry (Betsimisaraka 941,000, Tsimihety 442,000, Antaisaka 415,000, Sakalava 375,000), on the other; there are also 11,000 European French, 5,000 Indians of French nationality, and 5,000 Creoles
Infant mortality rate
97 deaths/1,000 live births (1990)
Labor force
4,900,000; 90% nonsalaried family workers engaged in subsistence agriculture; 175,000 wage earners--26% agriculture, 17% domestic service, 15% industry, 14% commerce, 11% construction, 9% services, 6% transportation, 2% other; 51% of population of working age (1985)
Language
French and Malagasy (official)
Life expectancy at birth
50 years male, 54 years female (1990)
Literacy
67.5%
Nationality
noun--Malagasy (sing. and pl.); adjective--Malagasy
Net migration rate
0 migrants/1,000 population (1990)
Organized labor
4% of labor force
Population
11,800,524 (July 1990), growth rate 3.2% (1990)
Religion
52% indigenous beliefs; about 41% Christian, 7% Muslim
Total fertility rate
6.9 children born/woman (1990)
Government
Administrative divisions
6 provinces (plural--NA, singular--faritanin); Antananarivo, Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga, Toamasina, Toliara
Capital
Antananarivo
Communists
Communist party of virtually no importance; small and vocal group of Communists has gained strong position in leadership of AKFM, the rank and file of which is non-Communist
Constitution
21 December 1975
Diplomatic representation
Ambassador Pierrot Jocelyn RAJAONARIVELO; Chancery at 2374 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington DC 20008; telephone (202) 265-5525 or 5526; there is a Malagasy Consulate General in New York; US--Ambassador Howard K. WALKER; Embassy at 14 and 16 Rue Rainitovo, Antsahavola, Antananarivo (mailing address is B. P. 620, Antananarivo); telephone 212-57, 209-56, 200-89, 207-18
Elections
President--last held on 12 March 1989 (next to be held March 1996); results--Didier Ratsiraka (AREMA) 62%, Manandafy Rakotonirina (MFM/MFT) 20%, Dr. Jerome Marojama Razanabahiny (VONJY) 15%, Monja Jaona (MONIMA) 3%; People's National Assembly--last held on 28 May 1989 (next to be held May 1994); results--AREMA 88.2%, MFM 5.1%, AKFM 3.7%, VONJY 2.2%, others 0.8%; seats--(137 total) AREMA 120, MFM 7, AKFM 5, VONJY 4, MONIMA 1, independent 1
Executive branch
president, Supreme Council of the Revolution, prime minister, Council of Ministers
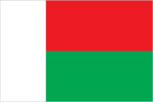
Flag
two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and green with a vertical white band of the same width on hoist side
Independence
26 June 1960 (from France; formerly Malagasy Republic)
Judicial branch
Supreme Court (Cour Supreme), High Constitutional Court (Haute Cour Constitutionnelle)
Leaders
Chief of State--President Adm. Didier RATSIRAKA (since 15 June 1975); Head of Government--Prime Minister Lt. Col. Victor RAMAHATRA (since 12 February 1988)
Legal system
based on French civil law system and traditional Malagasy law; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Legislative branch
unicameral Popular National Assembly (Assemblee Nationale Populaire)
Long-form name
Democratic Republic of Madagascar
Member of
ACP, AfDB, CCC, EAMA, FAO, G-77, GATT, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICO, IDA, IFAD, IFC, ILO, IMF, IMO, INTELSAT, INTERPOL, IRC, ISO, ITU, NAM, OAU, OCAM, UN, UNESCO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WMO, WTO
National holiday
Independence Day, 26 June (1960)
Political parties and leaders
seven parties are now allowed limited political activity under the national front and are represented on the Supreme
Revolutionary Council
Advance Guard of the Malagasy Revolution (AREMA), Didier Ratsiraka; Congress Party for Malagasy Independence (AKFM); Congress Party for Malagasy Independence-Revival (AKFM-R), Pastor Richard Andriamanjato; Movement for National Unity (VONJY), Dr. Marojama Razanabahiny; Malagasy Christian Democratic Union (UDECMA), Norbert Andriamorasata; Militants for the Establishment of a Proletarian Regime (MFM), Manandafy Rakotonirina; National Movement for the Independence of Madagascar (MONIMA), Monja Jaona; Socialist Organization Monima (VSM, an offshoot of MONIMA), Tsihozony Maharanga
Suffrage
universal at age 18
Type
republic
Economy
Agriculture
accounts for 40% of GDP; cash crops--coffee, vanilla, sugarcane, cloves, cocoa; food crops--rice, cassava, beans, bananas, peanuts; cattle raising widespread; not self-sufficient in rice and wheat flour
Aid
US commitments, including Ex-Im (FY70-88), $118 million; Western (non-US) countries, ODA and OOF bilateral commitments (1970-87), $2.6 billion; Communist countries (1970-88), $491 million
Budget
revenues $337 million; expenditures $245 million, including capital expenditures of $163 million (1988)
Currency
Malagasy franc (plural--francs); 1 Malagasy franc (FMG) = 100 centimes
Electricity
119,000 kW capacity; 430 million kWh produced, 40 kWh per capita (1989)
Exchange rates
Malagasy francs (FMG) per US$1--1,531.0 (January 1990), 1603.4 (1989), 1,407.1 (1988), 1,069.2 (1987), 676.3 (1986), 662.5 (1985)
Exports
$284 million (f.o.b., 1988); commodities--coffee 45%, vanilla 15%, cloves 11%, sugar, petroleum products; partners--France, Japan, Italy, FRG, US
External debt
$3.6 billion (1989)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP
$1.7 billion, per capita $155; real growth rate 2.2% (1988)
Illicit drugs
illicit producer of cannabis (cultivated and wild varieties) used mostly for domestic consumption
Imports
$319 million (f.o.b., 1988); commodities--intermediate manufactures 30%, capital goods 28%, petroleum 15%, consumer goods 14%, food 13%; partners--France, FRG, UK, other EC, US
Industrial production
growth rate - 3.9 % (1988)
Industries
agricultural processing (meat canneries, soap factories, brewery, tanneries, sugar refining), light consumer goods industries (textiles, glassware), cement, automobile assembly plant, paper, petroleum
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
17.0% (1988)
Overview
Madagascar is one of the poorest countries in the world. During the period 1980-85 it had a population growth of 3% a year and a - 0.4% GDP growth rate. Agriculture, including fishing and forestry, is the mainstay of the economy, accounting for over 40% of GDP, employing about 85% of the labor force, and contributing more than 70% to export earnings. Industry is confined to the processing of agricultural products and textile manufacturing; in 1988 it contributed only 16% to GDP and employed 3% of the labor force. Industrial development has been hampered by government policies that have restricted imports of equipment and spare parts and put strict controls on foreign-owned enterprises. In 1986 the government introduced a five-year development plan that stresses self-sufficiency in food (mainly rice) by 1990, increased production for exports, and reduced energy imports.
Unemployment rate
NA%
Communications
Airports
147 total, 115 usable; 30 with permanent-surface runways; none with runways over 3,659 m; 3 with runways 2,440-3,659 m; 43 with runways 1,220-2,439 m
Civil air
5 major transport aircraft
Highways
40,000 km total; 4,694 km paved, 811 km crushed stone, gravel, or stabilized soil, 34,495 km improved and unimproved earth (est.)
Inland waterways
of local importance only; isolated streams and small portions of Canal des Pangalanes
Merchant marine
13 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 58,126 GRT/79,420 DWT; includes 8 cargo, 2 roll-on/roll-off cargo, 1 petroleum, oils, and lubricants (POL) tanker, 1 chemical tanker, 1 liquefied gas
Ports
Toamasina, Antsiranana, Mahajanga, Toliara
Railroads
1,020 km 1.000-meter gauge
Telecommunications
above average system includes open-wire lines, coaxial cables, radio relay, and troposcatter links; submarine cable to Bahrain; satellite earth stations--1 Indian Ocean INTELSAT and 1 Atlantic Ocean INTELSAT; over 38,200 telephones; stations--14 AM, 1 FM, 7 (30 repeaters) TV
Military and Security
Branches
Popular Army, Aeronaval Forces (includes Navy and Air Force), paramilitary Gendarmerie
Defense expenditures
2.2% of GDP, or $37 million (1989 est.)
Military manpower
males 15-49, 2,550,775; 1,519,084 fit for military service; 116,438 reach military age (20) annually