2022 Edition
CIA World Factbook 2022 (factbook.json @ 61dadec0c9c9)
Introduction
Background
Settled by Norwegian and Celtic (Scottish and Irish) immigrants during the late 9th and 10th centuries A.D., Iceland boasts the world's oldest functioning legislative assembly, the Althingi, established in 930. Independent for over 300 years, Iceland was subsequently ruled by Norway and Denmark. Fallout from the Askja volcano of 1875 devastated the Icelandic economy and caused widespread famine. Over the next quarter century, 20% of the island's population emigrated, mostly to Canada and the US. Denmark granted limited home rule in 1874 and complete independence in 1944. The second half of the 20th century saw substantial economic growth driven primarily by the fishing industry. The economy diversified greatly after the country joined the European Economic Area in 1994, but Iceland was especially hard hit by the global financial crisis in the years following 2008. The economy is now on an upward trajectory, fueled primarily by a tourism and construction boom. Literacy, longevity, and social cohesion are first rate by world standards.
Geography
Area
- land
- 100,250 sq km
- total
- 103,000 sq km
- water
- 2,750 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly smaller than Pennsylvania; about the same size as Kentucky
Climate
temperate; moderated by North Atlantic Current; mild, windy winters; damp, cool summers
Coastline
4,970 km
Elevation
- highest point
- Hvannadalshnukur (at Vatnajokull Glacier) 2,110 m
- lowest point
- Atlantic Ocean 0 m
- mean elevation
- 557 m
Geographic coordinates
65 00 N, 18 00 W
Geography - note
strategic location between Greenland and Europe; westernmost European country; Reykjavik is the northernmost national capital in the world; more land covered by glaciers than in all of continental Europe
Irrigated land
0.5 sq km (2020)
Land boundaries
- total
- 0 km
Land use
- agricultural land
- 18.7% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: arable land
- arable land: 1.2% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent crops
- permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent pasture
- permanent pasture: 17.5% (2018 est.)
- forest
- 0.3% (2018 est.)
- other
- 81% (2018 est.)
Location
Northern Europe, island between the Greenland Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, northwest of the United Kingdom
Map references
Arctic Region
Maritime claims
- continental shelf
- 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
- exclusive economic zone
- 200 nm
- territorial sea
- 12 nm
Natural hazards
earthquakes and volcanic activityvolcanism: Iceland, situated on top of a hotspot, experiences severe volcanic activity; Eyjafjallajokull (1,666 m) erupted in 2010, sending ash high into the atmosphere and seriously disrupting European air traffic; scientists continue to monitor nearby Katla (1,512 m), which has a high probability of eruption in the very near future, potentially disrupting air traffic; Grimsvoetn and Hekla are Iceland's most active volcanoes; other historically active volcanoes include Askja, Bardarbunga, Brennisteinsfjoll, Esjufjoll, Hengill, Krafla, Krisuvik, Kverkfjoll, Oraefajokull, Reykjanes, Torfajokull, and Vestmannaeyjar
Natural resources
fish, hydropower, geothermal power, diatomite
Population distribution
Iceland is almost entirely urban with half of the population located in and around the capital of Reykjavik; smaller clusters are primarily found along the coast in the north and west
Terrain
mostly plateau interspersed with mountain peaks, icefields; coast deeply indented by bays and fiords
People and Society
Age structure
- 0-14 years
- 20.31% (male 36,394/female 34,837)
- 15-24 years
- 12.85% (male 22,748/female 22,317)
- 25-54 years
- 39.44% (male 70,227/female 68,095)
- 55-64 years
- 11.94% (male 20,762/female 21,111)
- 65 years and over
- 15.47% (male 25,546/female 28,697) (2020 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
- beer
- 4.39 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- other alcohols
- 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- spirits
- 1.22 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- total
- 7.72 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
- wine
- 2.11 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Birth rate
12.96 births/1,000 population (2022 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
NA
Contraceptive prevalence rate
NA
Current health expenditure
8.6% of GDP (2019)
Death rate
6.56 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.)
Dependency ratios
- elderly dependency ratio
- 22.5
- potential support ratio
- 4.5 (2021 est.)
- total dependency ratio
- 50.5
- youth dependency ratio
- 28
Drinking water source
- improved: rural
- rural: 100% of population
- improved: total
- total: 100% of population
- improved: urban
- urban: 100% of population
- unimproved: rural
- rural: 0% of population
- unimproved: total
- total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
- unimproved: urban
- urban: 0% of population
Education expenditures
7.7% of GDP (2020 est.)
Ethnic groups
- Icelandic 81.3%, Polish 5.6%, Danish 1%, other 12.1% (2021 est.)
- note
- note: data represent population by country of birth
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
0.1% (2021)
Hospital bed density
2.8 beds/1,000 population (2019)
Infant mortality rate
- female
- 1.46 deaths/1,000 live births (2022 est.)
- male
- 1.83 deaths/1,000 live births
- total
- 1.65 deaths/1,000 live births
Languages
Icelandic, English, Nordic languages, German
Life expectancy at birth
- female
- 85.97 years (2022 est.)
- male
- 81.41 years
- total population
- 83.64 years
Literacy
- female
- NA
- male
- NA
- total population
- NA
Major urban areas - population
216,000 REYKJAVIK (capital) (2018)
Maternal mortality ratio
4 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
Median age
- female
- 37.7 years (2020 est.)
- male
- 36.6 years
- total
- 37.1 years
Mother's mean age at first birth
28.7 years (2020 est.)
Nationality
- adjective
- Icelandic
- noun
- Icelander(s)
Net migration rate
2.89 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
21.9% (2016)
Physicians density
4.14 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
Population
357,603 (2022 est.)
Population distribution
Iceland is almost entirely urban with half of the population located in and around the capital of Reykjavik; smaller clusters are primarily found along the coast in the north and west
Population growth rate
0.93% (2022 est.)
Religions
Evangelical Lutheran Church of Iceland (official) 62.3%, Roman Catholic 4%, Independent Congregation of Reykjavik 2.7%, Independent Congregation of Hafnarfjordur 2%, pagan worship 1.4%, Icelandic Ethical Humanist Association 1.1%, other (includes Zuist and Pentecostal) or unspecified 19%, none 7.6% (2021 est.)
Sanitation facility access
- improved: rural
- rural: 100% of population
- improved: total
- total: 100% of population
- improved: urban
- urban: 100% of population
- unimproved: rural
- rural: 0% of population
- unimproved: total
- total: 0% of population (2020 est.)
- unimproved: urban
- urban: 0% of population
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- female
- 21 years (2020)
- male
- 18 years
- total
- 19 years
Sex ratio
- 0-14 years
- 1.04 male(s)/female
- 15-24 years
- 1.02 male(s)/female
- 25-54 years
- 1.03 male(s)/female
- 55-64 years
- 0.98 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over
- 0.76 male(s)/female
- at birth
- 1.05 male(s)/female
- total population
- 1 male(s)/female (2022 est.)
Tobacco use
- female
- 12% (2020 est.)
- male
- 11.9% (2020 est.)
- total
- 12% (2020 est.)
Total fertility rate
1.95 children born/woman (2022 est.)
Urbanization
- rate of urbanization
- 0.74% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population
- 94% of total population (2023)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
- female
- 10.7% (2021 est.)
- male
- 13.2%
- total
- 12%
Government
Administrative divisions
64 municipalities (sveitarfelog, singular - sveitarfelagidh); Akranes, Akureyri, Arneshreppur, Asahreppur, Blaskogabyggdh, Bolungarvik, Borgarbyggdh, Dalabyggdh, Dalvikurbyggdh, Eyjafjardharsveit, Eyja-og Miklaholtshreppur, Fjallabyggdh, Fjardhabyggdh, Fljotsdalshreppur, Floahreppur, Gardhabaer, Grimsnes-og Grafningshreppur, Grindavikurbaer, Grundarfjardharbaer, Grytubakkahreppur, Hafnarfjordhur, Horgarsveit, Hrunamannahreppur, Hunathing Vestra, Hunabyggdh, Hvalfjardharsveit, Hveragerdhi, Isafjardharbaer, Kaldrananeshreppur, Kjosarhreppur, Kopavogur, Langanesbyggdh, Mosfellsbaer, Mulathing, Myrdalshreppur, Nordhurthing, Rangarthing Eystra, Rangarthing Ytra, Reykholahreppur, Reykjanesbaer, Reykjavik, Seltjarnarnes, Skaftarhreppur, Skagabyggdh, Skagafjordhur, Skeidha-og Gnupverjahreppur, Skorradalshreppur, Snaefellsbaer, Strandabyggdh, Stykkisholmur, Sudhavikurhreppur, Sudhurnesjabaer, Svalbardhsstrandarhreppur, Sveitarfelagidh Arborg, Sveitarfelagidh Hornafjordhur, Sveitarfelagidh Olfus, Sveitarfelagidh Skagastrond, Sveitarfelagidh Vogar, Talknafjardharhreppur, Thingeyjarsveit, Tjorneshreppur, Vestmannaeyjar, Vesturbyggdh, Vopnafjardharhreppur
Capital
- etymology
- the name means "smoky bay" in Icelandic and refers to the steamy, smoke-like vapors discharged by hot springs in the area
- geographic coordinates
- 64 09 N, 21 57 W
- name
- Reykjavik
- time difference
- UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Citizenship
- citizenship by birth
- no
- citizenship by descent only
- at least one parent must be a citizen of Iceland
- dual citizenship recognized
- yes
- residency requirement for naturalization
- 3 to 7 years
Constitution
- amendments
- proposed by the Althingi; passage requires approval by the Althingi and by the next elected Althingi, and confirmation by the president of the republic; proposed amendments to Article 62 of the constitution – that the Evangelical Lutheran Church shall be the state church of Iceland – also require passage by referendum; amended many times, last in 2013
- history
- several previous; latest ratified 16 June 1944, effective 17 June 1944 (at independence)
Country name
- conventional long form
- none
- conventional short form
- Iceland
- etymology
- Floki VILGERDARSON, an early Norse explorer of the island (9th century), applied the name "Land of Ice" after spotting a fjord full of drift ice to the north and spending a bitter winter on the island; he eventually settled on the island, however, after he saw how it greened up in the summer and that it was, in fact, habitable
- local long form
- none
- local short form
- Island
Diplomatic representation from the US
- chief of mission
- Ambassador Carrin F. PATMAN (since 6 October 2022)
- email address and website
- ReykjavikConsular@state.govhttps://is.usembassy.gov/
- embassy
- Engjateigur 7, 105 Reykjavik
- FAX
- [354] 562-9118
- mailing address
- 5640 Reykjavik Place, Washington, D.C. 20521-5640
- telephone
- [354] 595-2200
Diplomatic representation in the US
- chancery
- House of Sweden, 2900 K Street NW, #509, Washington, DC 20007
- chief of mission
- Ambassador Bergdis ELLERTSDOTTIR (since 16 September 2019)
- consulate(s) general
- New York
- email address and website
- washington@mfa.ishttps://www.government.is/diplomatic-missions/embassy-of-iceland-in-washington-d.c/
- FAX
- [1] (202) 265-6656
- telephone
- [1] (202) 265-6653
Executive branch
- cabinet
- Cabinet appointed by the president upon the recommendation of the prime minister
- chief of state
- President Gudni Thorlacius JOHANNESSON (since 1 August 2016)
- election results
- 2020: Gudni Thorlacius JOHANNESSON reelected president; percent of vote - Gudni Thorlacius JOHANNESSON (independent) 92.2%, Gudmundur Franklin JONSSON (independent) 7.8%2016: Gudni Thorlacius JOHANNESSON elected president; Gudni Thorlacius JOHANNESSON (independent) 39.1%, Halla TOMASDOTTIR (independent) 27.9%, Andri Snær MAGNASON (Democracy Movement) 14.3%, Davíd ODDSSON (independent) 13.7%, other 5%
- elections/appointments
- president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 4-year term (no term limits); election last held on 27 June 2020 (next to be held in 2024); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition becomes prime minister
- head of government
- Prime Minister Katrin JAKOBSDOTTIR (since 30 November 2017)
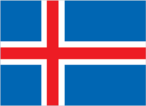
Flag description
blue with a red cross outlined in white extending to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag); the colors represent three of the elements that make up the island: red is for the island's volcanic fires, white recalls the snow and ice fields of the island, and blue is for the surrounding ocean
Government type
unitary parliamentary republic
Independence
1 December 1918 (became a sovereign state under the Danish Crown); 17 June 1944 (from Denmark; birthday of Jon SIGURDSSON, leader of Iceland's 19th Century independence movement)
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
International organization participation
Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, EFTA, FAO, FATF, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Judicial branch
- highest court(s)
- Supreme Court or Haestirettur (consists of 9 judges)
- judge selection and term of office
- judges proposed by Ministry of Interior selection committee and appointed by the president; judges appointed for an indefinite period
- subordinate courts
- Appellate Court or Landsrettur; 8 district courts; Labor Court
Legal system
civil law system influenced by the Danish model
Legislative branch
- description
- unicameral Althingi or Parliament (63 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by closed-list proportional representation vote using the D'Hondt method; members serve 4-year terms)
- election results
- percent of vote by party - IP 25.4%, PP 20.6%, LGM 12.7%, SDA 9.5%, People's Party 9.5%, Pirate Party 9.5%, Reform Party 7.9%. CP 4.8%; seats by party - IP 16, PP 13, LGM 8, SDA 6, People's Party 6, Pirate Party 6, Reform Party 5, CP 3; composition - men 33, women 30; percent of women 47.6%
- elections
- last held on 25 September 2021 (next to be held in 2025)
National anthem
- lyrics/music
- Matthias JOCHUMSSON/Sveinbjorn SVEINBJORNSSON
- name
- "Lofsongur" (Song of Praise)
- note
- note: adopted 1944; also known as "O, Gud vors lands" (O, God of Our Land), the anthem was originally written and performed in 1874
National heritage
- selected World Heritage Site locales
- Thingvellir National Park (c); Surtsey (n); Vatnajökull National Park - Dynamic Nature of Fire and Ice (n)
- total World Heritage Sites
- 3 (1 cultural, 2 natural)
National holiday
Independence Day, 17 June (1944)
National symbol(s)
gyrfalcon; national colors: blue, white, red
Political parties and leaders
Centrist Party (Midflokkurinn) or CP [Sigmundur David GUNNLAUGSSON] Independence Party (Sjalfstaedisflokkurinn) or IP [Bjarni BENEDIKTSSON] Left-Green Movement (Vinstrihreyfingin-graent frambod) or LGM [Katrin JAKOBSDOTTIR] People's Party (Flokkur Folksins) [Inga SAELAND] Pirate Party (Piratar) [Halldora MOGENSEN] Progressive Party (Framsoknarflokkurinn) or PP [Sigurdur Ingi JOHANNSSON]Reform Party (Vidreisn) [Thorgerdur Katrin GUNNARSDOTTIR] Social Democratic Alliance (Samfylkingin) or SDA [Logi Mar EINARSSON]
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Economy
Agricultural products
milk, mutton, poultry, potatoes, barley, pork, eggs, beef, other meat, sheep skins
Budget
- expenditures
- 10.02 billion (2017 est.)
- revenues
- 10.39 billion (2017 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)
1.5% (of GDP) (2017 est.)
Credit ratings
- Fitch rating
- A (2017)
- Moody's rating
- A2 (2019)
- note
- note: The year refers to the year in which the current credit rating was first obtained.
- Standard & Poors rating
- A (2017)
Current account balance
- Current account balance 2018
- $814 million (2018 est.)
- Current account balance 2019
- $1.496 billion (2019 est.)
Debt - external
- Debt - external 2018
- $22.055 billion (2018 est.)
- Debt - external 2019
- $19.422 billion (2019 est.)
Economic overview
Iceland's economy combines a capitalist structure and free-market principles with an extensive welfare system. Except for a brief period during the 2008 crisis, Iceland has in recent years achieved high growth, low unemployment, and a remarkably even distribution of income. Iceland's economy has been diversifying into manufacturing and service industries in the last decade, particularly within the fields of tourism, software production, and biotechnology. Abundant geothermal and hydropower sources have attracted substantial foreign investment in the aluminum sector, boosted economic growth, and sparked some interest from high-tech firms looking to establish data centers using cheap green energy. Tourism, aluminum smelting, and fishing are the pillars of the economy. For decades the Icelandic economy depended heavily on fisheries, but tourism has now surpassed fishing and aluminum as Iceland’s main export industry. Tourism accounted for 8.6% of Iceland’s GDP in 2016, and 39% of total exports of merchandise and services. From 2010 to 2017, the number of tourists visiting Iceland increased by nearly 400%. Since 2010, tourism has become a main driver of Icelandic economic growth, with the number of tourists reaching 4.5 times the Icelandic population in 2016. Iceland remains sensitive to fluctuations in world prices for its main exports, and to fluctuations in the exchange rate of the Icelandic Krona. Following the privatization of the banking sector in the early 2000s, domestic banks expanded aggressively in foreign markets, and consumers and businesses borrowed heavily in foreign currencies. Worsening global financial conditions throughout 2008 resulted in a sharp depreciation of the krona vis-a-vis other major currencies. The foreign exposure of Icelandic banks, whose loans and other assets totaled nearly nine times the country's GDP, became unsustainable. Iceland's three largest banks collapsed in late 2008. GDP fell 6.8% in 2009, and unemployment peaked at 9.4% in February 2009. Three new banks were established to take over the domestic assets of the collapsed banks. Two of them have majority ownership by the state, which intends to re-privatize them. Since the collapse of Iceland's financial sector, government economic priorities have included stabilizing the krona, implementing capital controls, reducing Iceland's high budget deficit, containing inflation, addressing high household debt, restructuring the financial sector, and diversifying the economy. Capital controls were lifted in March 2017, but some financial protections, such as reserve requirements for specified investments connected to new inflows of foreign currency, remain in place.
Exchange rates
- Currency
- Icelandic kronur (ISK) per US dollar -
- Exchange rates 2013
- 116.77 (2013 est.)
- Exchange rates 2014
- 131.92 (2014 est.)
- Exchange rates 2018
- 121.86 (2018 est.)
- Exchange rates 2019
- 121.68 (2019 est.)
- Exchange rates 2020
- 127.05 (2020 est.)
Exports
- Exports 2018
- $12.26 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Exports 2019
- $11.01 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Exports 2020
- $7.43 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Exports - commodities
aluminum and aluminum products, fish products, aircraft, iron alloys, animal meal (2019)
Exports - partners
Netherlands 23%, United Kingdom 9%, Germany 9%, Spain 8%, United States 7%, France 7%, Canada 5% (2019)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP - composition, by end use
- exports of goods and services
- 47% (2017 est.)
- government consumption
- 23.3% (2017 est.)
- household consumption
- 50.4% (2017 est.)
- imports of goods and services
- -42.8% (2017 est.)
- investment in fixed capital
- 22.1% (2017 est.)
- investment in inventories
- 0% (2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
- agriculture
- 5.8% (2017 est.)
- industry
- 19.7% (2017 est.)
- services
- 74.6% (2017 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$24.614 billion (2019 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
- Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income 2005
- 25 (2005)
- Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income 2015
- 26.8 (2015 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
- highest 10%
- NA
- lowest 10%
- NA
Imports
- Imports 2018
- $11.34 billion (2018 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Imports 2019
- $9.76 billion (2019 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
- Imports 2020
- $7.55 billion (2020 est.) note: data are in current year dollars
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, aluminum oxide, carbon/graphite electronics, cars, packaged medicines (2019)
Imports - partners
Norway 11%, Netherlands 10%, Germany 8%, Denmark 8%, United States 7%, United Kingdom 6%, China 6%, Sweden 5% (2019)
Industrial production growth rate
2.4% (2017 est.)
Industries
tourism, fish processing; aluminum smelting; geothermal power, hydropower; medical/pharmaceutical products
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2017
- 1.7% (2017 est.)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2018
- 2.6% (2018 est.)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2019
- 3% (2019 est.)
Labor force
200,000 (2020 est.)
Labor force - by occupation
- agriculture
- 4.8%
- industry
- 22.2%
- services
- 73% (2008)
Population below poverty line
8.8% (2017 est.)
Public debt
- Public debt 2016
- 51.7% of GDP (2016 est.)
- Public debt 2017
- 40% of GDP (2017 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
- note
- note: data are in 2017 dollars
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2018
- $20.01 billion (2018 est.)
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2019
- $20.52 billion (2019 est.)
- Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2020
- $19.16 billion (2020 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
- Real GDP growth rate 2017
- 4.57% (2017 est.)
- Real GDP growth rate 2018
- 3.88% (2018 est.)
- Real GDP growth rate 2019
- 1.94% (2019 est.)
Real GDP per capita
- note
- note: data are in 2017 dollars
- Real GDP per capita 2018
- $56,700 (2018 est.)
- Real GDP per capita 2019
- $56,900 (2019 est.)
- Real GDP per capita 2020
- $52,300 (2020 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2016
- $7.226 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 31 December 2017
- $6.567 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
Taxes and other revenues
42.4% (of GDP) (2017 est.)
Unemployment rate
- Unemployment rate 2018
- 2.73% (2018 est.)
- Unemployment rate 2019
- 3.62% (2019 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
- female
- 10.7% (2021 est.)
- male
- 13.2%
- total
- 12%
Energy
Carbon dioxide emissions
- from coal and metallurgical coke
- 459,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- from consumed natural gas
- 0 metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- from petroleum and other liquids
- 2.879 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
- total emissions
- 3.337 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2019 est.)
Coal
- consumption
- 142,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
- exports
- 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
- imports
- 136,000 metric tons (2020 est.)
- production
- 0 metric tons (2020 est.)
- proven reserves
- 0 metric tons (2019 est.)
Electricity
- consumption
- 17,912,066,000 kWh (2020 est.)
- exports
- 0 kWh (2020 est.)
- imports
- 0 kWh (2020 est.)
- installed generating capacity
- 2.967 million kW (2020 est.)
- transmission/distribution losses
- 519 million kWh (2020 est.)
Electricity access
- electrification - total population
- 100% (2020)
Electricity generation sources
- biomass and waste
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- fossil fuels
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- geothermal
- 32.3% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- hydroelectricity
- 67.6% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- nuclear
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- solar
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- tide and wave
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
- wind
- 0% of total installed capacity (2020 est.)
Natural gas
- consumption
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
- exports
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
- imports
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
- production
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
- proven reserves
- 0 cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
- crude oil and lease condensate exports
- 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
- crude oil and lease condensate imports
- 0 bbl/day (2018 est.)
- crude oil estimated reserves
- 0 barrels (2021 est.)
- refined petroleum consumption
- 19,700 bbl/day (2019 est.)
- total petroleum production
- 0 bbl/day (2021 est.)
Refined petroleum products - exports
2,530 bbl/day (2017 est.)
Refined petroleum products - imports
20,220 bbl/day (2017 est.)
Refined petroleum products - production
0 bbl/day (2017 est.)
Communications
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 42 (2020 est.)
- total
- 141,816 (2020 est.)
Broadcast media
state-owned public TV broadcaster (RUV) operates 21 TV channels nationally (RUV and RUV 2, though RUV 2 is used less frequently); RUV broadcasts nationally, every household in Iceland is required to have RUV as it doubles as the emergency broadcast network; RUV also operates stringer offices in the north (Akureyri) and the east (Egilsstadir) but operations are all run out of RUV headquarters in Reykjavik; there are 3 privately owned TV stations; Stod 2 (Channel 2) is owned by Syn, following 365 Media and Vodafone merger, and is headquartered in Reykjavik; Syn also operates 4 sports channels under Stod 2; N4 is the only television station headquartered outside of Reykjavik, in Akureyri, with local programming for the north, south, and east of Iceland; Hringbraut is the newest station and is headquartered in Reykjavik; all of these television stations have nationwide penetration as 100% of households have multi-channel services though digital and/or fiber-optic connections RUV operates 3 radio stations (RAS 1, RAS2, and Rondo) as well as 4 regional stations (but they mostly act as range extenders for RUV radio broadcasts nationwide); there is 1 privately owned radio conglomerate, Syn (4 stations), that broadcasts nationwide, and 3 other radio stations that broadcast to the most densely populated regions of the country. In addition, there are upwards of 20 radio stations that operate regionally (2019)
Internet country code
.is
Internet users
- percent of population
- 99% (2020 est.)
- total
- 362,798 (2020 est.)
Telecommunication systems
- domestic
- 31 per 100 for fixed line and nearing 123 per 100 for mobile-cellular subscriptions (2020)
- general assessment
- Iceland has one of the smallest yet most progressive telecom markets in Europe; the country in 2020 became the top in Europe for fiber penetration; it aims to provide a fixed broadband service of at least 100Mb/s to 99.9% of the population by the end of 2021, an ambitious target by international standards and one which it is likely to achieve given the progress which operators have made in extending the reach of fiber networks; there is effective competition in the mobile and broadband markets, with a number of players having emerged to challenge the dominance of the two leading operators which have interests across the telecom sectors; the telecom market has shown some resilience in recent years following the significant economic downturn a decade ago, supported by continuing investment in mobile and fixed-line broadband infrastructure by operators and well as by the government’s Telecommunications Fund which is supporting Next Generation Access networks, particularly in rural areas (2022)
- international
- country code - 354; landing points for the CANTAT-3, FARICE-1, Greenland Connect and DANICE submarine cable system that provides connectivity to Canada, the Faroe Islands, Greenland, UK, Denmark, and Germany; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean), 1 Inmarsat (Atlantic and Indian Ocean regions); note - Iceland shares the Inmarsat earth station with the other Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Sweden) (2019)
- note
- note: the COVID-19 pandemic continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally; since 2020, some aspects of the telecom sector have experienced a downturn, particularly in mobile device production; progress toward 5G implementation has resumed, as well as upgrades to infrastructure; consumer spending on telecom services has increased due to the surge in demand for capacity and bandwidth; the crucial nature of telecom services as a tool for work and school from home is still evident, and the spike in this area has seen growth opportunities for development of new tools and increased services
Telephones - fixed lines
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 31 (2020 est.)
- total subscriptions
- 107,032 (2020 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
- subscriptions per 100 inhabitants
- 123 (2020 est.)
- total subscriptions
- 421,384 (2020 est.)
Transportation
Airports
- total
- 96 (2021)
Airports - with paved runways
- 1,524 to 2,437 m
- 3
- 914 to 1,523 m
- 3 (2021)
- over 3,047 m
- 1
- total
- 7
Airports - with unpaved runways
- 1,524 to 2,437 m
- 3
- 914 to 1,523 m
- 26
- total
- 89
- under 914 m
- 60 (2021)
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
TF
Merchant marine
- by type
- general cargo 5, oil tanker 2, other 34 (2021)
- total
- 41
National air transport system
- annual freight traffic on registered air carriers
- 163.65 million (2018) mt-km
- annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers
- 7,819,740 (2018)
- inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers
- 63
- number of registered air carriers
- 6 (2020)
Ports and terminals
- major seaport(s)
- Grundartangi, Hafnarfjordur, Reykjavik
Roadways
- paved/oiled gravel
- 5,647 km (2012) (excludes urban roads)
- total
- 12,898 km (2012)
- unpaved
- 7,251 km (2012)
Military and Security
Military - note
Iceland was one of the original 12 countries to sign the North Atlantic Treaty (also known as the Washington Treaty) in 1949; Iceland is the only NATO member that has no standing military force; defense of Iceland remains a NATO commitment and NATO maintains an air policing presence in Icelandic airspace; Iceland participates in international peacekeeping missions with the civilian-manned Icelandic Crisis Response Unit (ICRU)Iceland cooperates with the militaries of other Nordic countries through the Nordic Defense Cooperation (NORDEFCO), which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden; areas of cooperation include armaments, education, human resources, training and exercises, and operations; NORDEFCO was established in 2009in 1951, Iceland and the US concluded an agreement to make arrangements regarding the defense of Iceland and for the use of facilities in Iceland to that end; the agreement, along with NATO membership, is one of the two pillars of Iceland‘s security policy; since 2007 Iceland has concluded cooperation agreements with Canada, Denmark, Norway, and the UK; it also has regular consultations with Germany and France on security and defense (2022)
Military and security forces
no regular military forces; Ministry of Interior: Icelandic Coast Guard (includes both air and maritime elements); Icelandic National Police (2022)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Icelandic Coast Guard has approximately 250 personnel (2022)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the Icelandic Coast Guard's inventory consists of equipment from mostly European suppliers (2022)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
Iceland, the UK, and Ireland dispute Denmark's claim that the Faroe Islands' continental shelf extends beyond 200 nm; the European Free Trade Association Surveillance Authority filed a suit against Iceland, claiming the country violated the Agreement on the European Economic Area in failing to pay minimum compensation to Icesave depositors
Refugees and internally displaced persons
- stateless persons
- 73 (mid-year 2021)
Environment
Air pollutants
- carbon dioxide emissions
- 2.06 megatons (2016 est.)
- methane emissions
- 0.59 megatons (2020 est.)
- particulate matter emissions
- 5.94 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
Climate
temperate; moderated by North Atlantic Current; mild, windy winters; damp, cool summers
Environment - current issues
water pollution from fertilizer runoff
Environment - international agreements
- party to
- Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
- signed, but not ratified
- Air Pollution-Heavy Metals, Environmental Modification, Marine Life Conservation
Land use
- agricultural land
- 18.7% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: arable land
- arable land: 1.2% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent crops
- permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
- agricultural land: permanent pasture
- permanent pasture: 17.5% (2018 est.)
- forest
- 0.3% (2018 est.)
- other
- 81% (2018 est.)
Revenue from coal
- coal revenues
- 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
Revenue from forest resources
- forest revenues
- 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
Total renewable water resources
170 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
Total water withdrawal
- agricultural
- 300,000 cubic meters (2017 est.)
- industrial
- 198 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
- municipal
- 80 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
Urbanization
- rate of urbanization
- 0.74% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population
- 94% of total population (2023)
Waste and recycling
- municipal solid waste generated annually
- 525,000 tons (2015 est.)
- municipal solid waste recycled annually
- 293,003 tons (2013 est.)
- percent of municipal solid waste recycled
- 55.8% (2013 est.)