1999 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1999 (Internet Archive)
Introduction
Background
Iceland boasts the oldest surviving parliament in the world, the Althing, established in 930. Subsequently this Nordic island, whose small population has largely depended on fishing and sheep-herding for a living, came under the rule of Norway and then Denmark. It gained home rule in 1874 and full independence in 1944. Literacy, longevity, and social cohesion are topnotch by world standards. Tensions continue with Norway, Russia, and other nearby countries over fishing rights in the North Atlantic and adjacent seas.
Geography
Area
total: 103,000 sq km land: 100,250 sq km water: 2,750 sq km
Area--comparative
slightly smaller than Kentucky
Climate
temperate; moderated by North Atlantic Current; mild, windy winters; damp, cool summers
Coastline
4,988 km
Elevation extremes
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m highest point: Hvannadalshnukur 2,119 m
Environment--current issues
water pollution from fertilizer runoff; inadequate wastewater treatment
Environment--international agreements
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Environmental Modification, Marine Life Conservation
Geographic coordinates
65 00 N, 18 00 W
Geography--note
strategic location between Greenland and Europe; westernmost European country; more land covered by glaciers than in all of continental Europe
Irrigated land
NA sq km
Land boundaries
0 km
Land use
arable land: 0% permanent crops: 0% permanent pastures: 23% forests and woodland: 1% other: 76% (1993 est.)
Location
Northern Europe, island between the Greenland Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, northwest of the UK
Map references
Arctic Region
Maritime claims
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin exclusive economic zone: 200 nm territorial sea: 12 nm
Natural hazards
earthquakes and volcanic activity
Natural resources
fish, hydropower, geothermal power, diatomite
Terrain
mostly plateau interspersed with mountain peaks, icefields; coast deeply indented by bays and fiords
People and Society
Age structure
0-14 years: 23% (male 32,608; female 31,061) 15-64 years: 65% (male 89,258; female 87,449) 65 years and over: 12% (male 14,510; female 17,626) (1999 est.)
Birth rate
14.87 births/1,000 population (1999 est.)
Death rate
7.01 deaths/1,000 population (1999 est.)
Ethnic groups
homogeneous mixture of descendants of Norwegians and Celts
Infant mortality rate
5.22 deaths/1,000 live births (1999 est.)
Languages
Icelandic
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 78.96 years male: 76.85 years female: 81.19 years (1999 est.)
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write total population: 100% (1976 est.) male: NA% female: NA%
Nationality
noun: Icelander(s) adjective: Icelandic
Net migration rate
-2.17 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1999 est.)
Population
272,512 (July 1999 est.)
Population growth rate
0.57% (1999 est.)
Religions
Evangelical Lutheran 96%, other Protestant and Roman Catholic 3%, none 1% (1988)
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.82 male(s)/female total population: 1 male(s)/female (1999 est.)
Total fertility rate
2.03 children born/woman (1999 est.)
Government
Administrative divisions
23 counties (syslar, singular--sysla) and 14 independent towns* (kaupstadhir, singular--kaupstadhur); Akranes*, Akureyri*, Arnessysla, Austur-Bardhastrandarsysla, Austur-Hunavatnssysla, Austur-Skaftafellssysla, Borgarfjardharsysla, Dalasysla, Eyjafjardharsysla, Gullbringusysla, Hafnarfjordhur*, Husavik*, Isafjordhur*, Keflavik*, Kjosarsysla, Kopavogur*, Myrasysla, Neskaupstadhur*, Nordhur-Isafjardharsysla, Nordhur-Mulasys-la, Nordhur-Thingeyjarsysla, Olafsfjordhur*, Rangarvallasysla, Reykjavik*, Saudharkrokur*, Seydhisfjordhur*, Siglufjordhur*, Skagafjardharsysla, Snaefellsnes-og Hnappadalssysla, Strandasysla, Sudhur-Mulasysla, Sudhur-Thingeyjarsysla, Vesttmannaeyjar*, Vestur-Bardhastrandarsysla, Vestur-Hunavatnssysla, Vestur-Isafjardharsysla, Vestur-Skaftafellssysla
Capital
Reykjavik
Constitution
16 June 1944, effective 17 June 1944
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Iceland conventional short form: Iceland local long form: Lyoveldio Island local short form: Island
Data code
IC
Executive branch
chief of state: President Olafur Ragnar GRIMSSON (since 1 August 1996) head of government: Prime Minister David ODDSSON (since 30 April 1991) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president elections: president elected by popular vote for a four-year term; election last held 29 June 1996 (next to be held NA June 2000); prime minister appointed by the president election results: Olafur Ragnar GRIMSSON elected president; percent of vote--41.4%
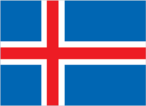
Flag description
blue with a red cross outlined in white that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag)
Government type
constitutional republic
Independence
17 June 1944 (from Denmark)
International organization participation
Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CCC, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECE, EFTA, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Inmarsat, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, ISO, ITU, MTCR, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNMIBH, UNU, UPU, WEU (associate), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTrO Diplomatic representation in the US: chief of mission: Ambassador Jon-Baldvin HANNIBALSSON chancery: Suite 1200, 1156 15th Street NW, Washington, DC 20005 consulate(s) general: New York Diplomatic representation from the US: chief of mission: Ambassador Day Olin MOUNT embassy: Laufasvegur 21, Reykjavik mailing address: US Embassy, PSC 1003, Box 40, FPO AE 09728-0340
Judicial branch
Supreme Court or Haestirettur, justices are appointed for life by the president Political parties and leaders: Independence Party (conservative)
Legal system
civil law system based on Danish law; does not accept compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Legislative branch
unicameral Parliament or Althing (63 seats; members are elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms) elections: last held on 8 April 1995 (next to be held by April 1999) election results: percent of vote by party--Independence Party 37.1%, Progressive Party 23.3%, Social Democratic Party 11.4%, Socialists 14.3%, People's Movement 7.2%, Women's Party 4.9%; seats by party--Independence 25, Progressive 15, Social Democratic 7, Socialists 9, People's Movement 4, Women's Party 3
National holiday
Anniversary of the Establishment of the Republic, 17 June (1944)
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Economy
Agriculture--products
potatoes, turnips; cattle, sheep; fish
Budget
revenues: $1.9 billion expenditures: $2.1 billion, including capital expenditures of $146 million (1996 est.)
Currency
1 Icelandic krona (IKr) = 100 aurar
Debt--external
$2.2 billion (1996 est.)
Economic aid--recipient
$NA
Economy--overview
Iceland's Scandinavian-type economy is basically capitalistic, yet with an extensive welfare system, low unemployment, and remarkably even distribution of income. The economy depends heavily on the fishing industry, which provides 75% of export earnings and employs 12% of the work force. In the absence of other natural resources--except energy--Iceland's economy is vulnerable to changing world fish prices. The economy remains sensitive to declining fish stocks as well as to drops in world prices for its main exports: fish and fish products, aluminum, and ferrosilicon. The center-right government plans to continue its policies of reducing the budget and current account deficits, limiting foreign borrowing, containing inflation, revising agricultural and fishing policies, diversifying the economy, and privatizing state-owned industries. The government remains opposed to EU membership, primarily because of Icelanders' concern about losing control over their fishing resources. Iceland's economy has been diversifying into manufacturing and service industries in the last decade, and new developments in software production, biotechnology, and financial services are taking place. The tourism sector is also expanding, with the recent trends in ecotourism and whale-watching. Growth is likely to slow in 1999, to a still respectable 4.6%.
Electricity--consumption
5.532 billion kWh (1997)
Electricity--exports
0 kWh (1996)
Electricity--imports
0 kWh (1996)
Electricity--production
5.048 billion kWh (1996)
Electricity--production by source
fossil fuel: 0.06% hydro: 93.43% nuclear: 0% other: 6.51%
Exchange rates
Icelandic kronur (IKr) per US$1--69.250 (January 1999), 70.958 (1998), 70.904 (1997), 66.500 (1996), 64.692 (1995), 69.944 (1994)
Exports
$1.9 billion (f.o.b., 1998)
Exports--commodities
fish and fish products 70%, animal products, aluminum, diatomite and ferrosilicon
Exports--partners
EU 60% (UK 19%, Germany 13%, France 6%, Denmark 6%), US 14% (1997)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP
purchasing power parity--$6.06 billion (1998 est.)
GDP--composition by sector
agriculture: 13% industry: 24% services: 63% (1997 est.)
GDP--per capita
purchasing power parity?$22,400 (1998 est.)
GDP--real growth rate
5.1% (1998 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: NA% highest 10%: NA%
Imports
$2.4 billion (f.o.b., 1998)
Imports--commodities
machinery and equipment, petroleum products, foodstuffs, textiles
Imports--partners
EU 58% (Germany 12%, Norway 12%, UK 10%, Denmark 9%, Sweden 7%), US 9% (1997)
Industrial production growth rate
NA%
Industries
fish processing; aluminum smelting, ferrosilicon production, geothermal power; tourism
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
1.7% (1998)
Labor force
130,000 (1998 est.)
Labor force--by occupation
manufacturing 12.9%, fishing and fish processing 11.8%, construction 10.7%, other services 59.5%, agriculture 5.1% (1996 est.)
Population below poverty line
NA%
Unemployment rate
3% (1998 est.)
Communications
Radio broadcast stations
AM 5, FM 147 (transmitters and repeaters), shortwave 0
Radios
91,500 licensed (1993 est.)
Telephone system
adequate domestic service domestic: the trunk network consists of coaxial and fiber-optic cables and microwave radio relay links international: satellite earth stations--2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean), 1 Inmarsat (Atlantic and Indian Ocean regions); note--Iceland shares the Inmarsat earth station with the other Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Sweden)
Telephones
143,600 (1993 est.)
Television broadcast stations
14 (in addition, there are 156 low-power repeaters) (1997)
Televisions
96,100 (1993 est.)
Transportation
Airports
87 (1998 est.) Airports--with paved runways: total: 10 over 3,047 m: 1 1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 914 to 1,523 m: 5 (1998 est.) Airports--with unpaved runways: total: 77 1,524 to 2,437 m: 3 914 to 1,523 m: 21 under 914 m: 53 (1998 est.)
Highways
total: 12,691 km paved: 3,262 km unpaved: 9,429 km (1997 est.) Ports and harbors: Akureyri, Hornafjordur, Isafjordhur, Keflavik, Raufarhofn, Reykjavik, Seydhisfjordhur, Straumsvik, Vestmannaeyjar
Merchant marine
total: 3 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 13,085 GRT/16,938 DWT ships by type: chemical tanker 1, container 1, oil tanker 1 (1998 est.)
Railways
0 km
Military and Security
Military branches
no regular armed forces; Police, Coast Guard; note--Iceland's defense is provided by the US-manned Icelandic Defense Force (IDF) headquartered at Keflavik
Military expenditures--dollar figure
none
Military manpower--availability
males age 15-49: 70,958 (1999 est.) Military manpower--fit for military service: males age 15-49: 62,570 (1999 est.)
Military--note
Iceland's defense is provided by the US-manned Icelandic Defense Force (IDF) headquartered at Keflavik
Transnational Issues
Disputes--international
Rockall continental shelf dispute involving Denmark, Ireland, and the UK (Ireland and the UK have signed a boundary agreement in the Rockall area)