1993 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1993 (Project Gutenberg)
Geography
Area
total area: 103,000 km2 land area: 100,250 km2 comparative area: slightly smaller than Kentucky
Climate
temperate; moderated by North Atlantic Current; mild, windy winters; damp, cool summers
Coastline
4,988 km
Environment
subject to earthquakes and volcanic activity
International disputes
Rockall continental shelf dispute involving Denmark, Ireland, and the UK (Ireland and the UK have signed a boundary agreement in the Rockall area)
Irrigated land
NA km2
Land boundaries
0 km
Land use
arable land: 1% permanent crops: 0% meadows and pastures: 20% forest and woodland: 1% other: 78%
Location
in the North Atlantic Ocean, between Greenland and Norway
Map references
Arctic Region, Europe, North America, Standard Time Zones of the World
Maritime claims
continental shelf: 200 nm or the edge of continental margin exclusive economic zone: 200 nm territorial sea: 12 nm
Natural resources
fish, hydropower, geothermal power, diatomite
Note
strategic location between Greenland and Europe; westernmost European country; more land covered by glaciers than in all of continental Europe
Terrain
mostly plateau interspersed with mountain peaks, icefields; coast deeply indented by bays and fiords
People and Society
Birth rate
16.99 births/1,000 population (1993 est.)
Death rate
6.74 deaths/1,000 population (1993 est.)
Ethnic divisions
homogeneous mixture of descendants of Norwegians and Celts
Infant mortality rate
4 deaths/1,000 live births (1993 est.)
Labor force
127,900 by occupation: commerce, transportation, and services 60.0%, manufacturing 12.5%, fishing and fish processing 11.8%, construction 10.8%, agriculture 4.0% (1990)
Languages
Icelandic
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 78.69 years male: 76.45 years female: 81.04 years (1993 est.)
Literacy
age 15 and over can read and write (1976) total population: 100% male: NA% female: NA%
Nationality
noun: Icelander(s) adjective: Icelandic
Net migration rate
-1.47 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1993 est.)
Population
261,270 (July 1993 est.) note: population data estimates based on average growth rate may differ slightly from official population data because of volatile migration rates
Population growth rate
0.88% (1993 est.)
Religions
Evangelical Lutheran 96%, other Protestant and Roman Catholic 3%, none 1% (1988)
Total fertility rate
2.16 children born/woman (1993 est.)
Government
Administrative divisions
23 counties (syslar, singular - sysla) and 14 independent towns*, (kaupstadhir, singular - kaupstadhur); Akranes*, Akureyri*, Arnessysla,, Austur-Bardhastrandarsysla, Austur-Hunavatnssysla, Austur-Skaftafellssysla, Borgarfjardharsysla, Dalasysla, Eyjafjardharsysla, Gullbringusysla, Hafnarfjordhur*, Husavik*, Isafjordhur*, Keflavik*, Kjosarsysla, Kopavogur*,, Myrasysla, Neskaupstadhur*, Nordhur-Isafjardharsysla, Nordhur-Mulasys-la,, Nordhur-Thingeyjarsysla, Olafsfjordhur*, Rangarvallasysla, Reykjavik*,, Saudharkrokur*, Seydhisfjordhur*, Siglufjordhur*,, Skagafjardharsysla, Snaefellsnes-og Hnappadalssysla, Strandasysla, Sudhur-Mulasysla, Sudhur-Thingeyjarsysla, Vesttmannaeyjar*, Vestur-Bardhastrandarsysla,, Vestur-Hunavatnssysla, Vestur-Isafjardharsysla, Vestur-Skaftafellssysla
Althing
last held on 20 April 1991 (next to be held by April 1995); results - Independence Party 38.6%, Progressive Party 18.9%, Social Democratic Party 15.5%, People's Alliance 14.4%, Womens List 8.3%, Liberals 1.2%, other 3.1%; seats - (63 total) Independence 26, Progressive 13, Social Democratic 10, People's Alliance 9, Womens List 5
Capital
Reykjavik
Chief of State
President Vigdis FINNBOGADOTTIR (since 1 August 1980)
Constitution
16 June 1944, effective 17 June 1944
Digraph
IC
Diplomatic representation in US
chief of mission: (vacant) chancery: 2022 Connecticut Avenue NW, Washington DC 20008 telephone: (202) 265-6653 through 6655
Executive branch
president, prime minister, Cabinet
FAX
- (202) 265-6656 consulate general: New York
- [354] (1) 29139
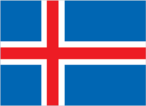
Flag
blue with a red cross outlined in white that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag)
Head of Government
Prime Minister David ODDSSON (since 30 April 1991)
Independence
17 June 1944 (from Denmark)
Judicial branch
Supreme Court (Haestirettur)
Legal system
civil law system based on Danish law; does not accept compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Legislative branch
unicameral Parliament (Althing)
Member of
Australian Group, BIS, CCC, CE, CSCE, EBRD, ECE, EFTA, FAO, GATT, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, IDA, IFC, ILO, IMF, IMO, INMARSAT, INTELSAT, INTERPOL, IOC, ISO (correspondent), ITU, LORCS, MTCR, NACC, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, OECD, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WEU (associate), WHO, WIPO, WMO
Names
conventional long form: Republic of Iceland conventional short form: Iceland local long form: Lyoveldio Island local short form: Island
National holiday
Anniversary of the Establishment of the Republic, 17 June (1944)
Political parties and leaders
Independence Party (conservative), David ODDSSON; Progressive Party, Steingrimur HERMANNSSON; Social Democratic Party, Jon Baldvin HANNIBALSSON; People's Alliance (left socialist), Olafur Ragnar GRIMSSON; Women's List
President
last held on 29 June 1988 (next scheduled for June 1996); results - there was no election in 1992 as President Vigdis FINNBOGADOTTIR was unopposed
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Type
republic
US diplomatic representation
chief of mission: (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Jon GUNDERSEN embassy: Laufasvegur 21, Box 40, Reykjavik mailing address: USEMB, PSC 1003, Box 40, FPO AE 09728-0340 telephone: [354] (1) 29100
Economy
Agriculture
accounts for about 25% of GDP; fishing is most important economic activity, contributing nearly 75% to export earnings; principal crops - potatoes, turnips; livestock - cattle, sheep; self-sufficient in crops; fish catch of about 1.4 million metric tons in 1989
Budget
revenues $1.8 billion; expenditures $1.9 billion, including capital expenditures of $191 million (1992)
Currency
1 Icelandic krona (IKr) = 100 aurar
Economic aid
US commitments, including Ex-Im (FY70-81), $19.1 million
Electricity
1,063,000 kW capacity; 5,165 million kWh produced, 19,940 kWh per capita (1992)
Exchange rates
Icelandic kronur (IKr) per US$1 - 63.789 (January 1993), 57.546 (1992), 58.996 (1991), 58.284 (1990), 57.042 (1989), 43.014 (1988)
Exports
$1.5 billion (f.o.b., 1992) commodities: fish and fish products, animal products, aluminum, ferrosilicon, diatomite partners: EC 68% (UK 25%, Germany 12%), US 11%, Japan 8% (1992)
External debt
$3.9 billion (1992 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
Imports
$1.5 billion (c.i.f., 1992) commodities: machinery and transportation equipment, petroleum products, foodstuffs, textiles partners: EC 53% (Germany 14%, Denmark 10%, UK 9%), Norway 14%, US 9% (1992)
Industrial production
growth rate 1.75% (1991 est.)
Industries
fish processing, aluminum smelting, ferro-silicon production, geothermal power
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
3.7% (1992 est.)
National product
GDP - purchasing power equivalent - $4.5 billion (1992)
National product per capita
$17,400 (1992)
National product real growth rate
-3.3% (1992)
Overview
- Iceland's Scandinavian-type economy is basically capitalistic, but with an extensive welfare system, relatively low unemployment, and comparatively even distribution of income. The economy is heavily dependent on the fishing industry, which provides nearly 75% of export earnings and employs 12% of the workforce. In the absence of other natural resources - except energy - Iceland's economy is vulnerable to changing world fish prices. Iceland's economy has been in recession since 1988. The recession deepened in 1992 due to severe cutbacks in fishing quotas and falling world prices for the
- Real GDP declined 3.3% in 1992 and is forecast to contract another 1.5% in 1993. The center-right government's economic goals include reducing the budget and current account deficits, limiting foreign borrowing, containing inflation, revising agricultural and fishing policies, diversifying the economy, and privatizing state-owned industries. The recession has led to a wave of bankruptcies and mergers throughout the economy, as well as the highest unemployment of the post-World War II period. The national unemployment rate reached 5% in early 1993, with some parts of the country experiencing unemployment in the 9-10% range. Inflation, previously a serious problem, declined from double digit rates in the 1980s to only 3.7% in 1992.
- country's main exports
- fish and fish products, aluminum, and ferrosilicon.
Unemployment rate
5% (first quarter 1993)
Communications
Airports
total: 90 usable: 84 with permanent-surface runways: 8 with runways over 3,659 m: with runways 2,440-3,659 m: 1 with runways 1,220-2,439 m: 12
Highways
11,543 km total; 2,690 km hard surfaced, 8,853 km gravel and earth
Merchant marine
10 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 35,832 GRT/53,037 DWT; includes 3 cargo, 3 refrigerated cargo, 2 roll-on/roll-off cargo, 1 oil tanker, 1 chemical tanker
Ports
Reykjavik, Akureyri, Hafnarfjordhur, Keflavik, Seydhisfjordhur, Siglufjordhur, Vestmannaeyjar
Telecommunications
adequate domestic service; coaxial and fiber-optical cables and microwave radio relay for trunk network; 140,000 telephones; broadcast stations - 5 AM, 147 (transmitters and repeaters) FM, 202 (transmitters and repeaters) TV; 2 submarine cables; 1 Atlantic Ocean INTELSAT earth station carries all international traffic; a second INTELSAT earth station is scheduled to be operational in 1993
Military and Security
Branches
Police, Coast Guard note: no armed forces, Iceland's defense is provided by the US-manned Icelandic Defense Force (IDF) headquartered at Keflavik
Defense expenditures
none
Manpower availability
males age 15-49 69,499; fit for military service 61,798 (1993 est.); no conscription or compulsory military service