1989 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1989 (Internet Archive)
Geography
Agriculture
including forestry, accounts for about 15% of GNP and 19% of employment; highly diversified crop-livestock farming; principal crops — wheat, corn, sunflowers, potatoes, sugar beets; livestock — hogs, cattle, poultry, dairy products; self-sufficient in food output
Aid
donor — $1.8 billion in bilateral aid to non-Communist less developed countries (1962-88)
Budget
revenues $14.0 billion; expenditures $14.2 billion, including capital expenditures of $944 million (1988)
Climate
- temperate; moderated by North Atlantic Current; mild, windy winters; damp, cool summers
- varies from tropical monsoon in south to temperate in north
Coastline
- 4,988 km
- 7,000 km
Comparative area
- slightly smaller than Kentucky
- slightly more than onethird the size of the US
Contiguous zone
24 nm
Continental shelf
- edge of continental margin or 200 nm
- edge of continental margin or 200 nm
Currency
forint (plural — forints); 1 forint (Ft) = 100 filter
Disputes
- Rockall continental shelf dispute involving Denmark, Ireland, and the UK (Ireland and the UK have signed a boundary agreement in the Rockall area)
- boundaries with Bangladesh, China, and Pakistan; water sharing problems with downstream riparians, Bangladesh over the Ganges and Pakistan over the Indus
Electricity
7,250,000 kW capacity; 30,300 million kWh produced, 2,870 kWh per capita (1989)
Environment
- subject to earthquakes and volcanic activity
- droughts, flash floods, severe thunderstorms common; deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing; air and water pollution; desertification
Exchange rates
forints (Ft) per US$1— 62.5 (January 1990), 59.2 (1989), 50.413 (1988), 46.971 (1987), 45.832 (1986), 50.119(1985) Fiscal yean calendar year
Exports
$19.1 billion (f.o.b. 1988); commodities— capital goods 36%, foods 24%, consumer goods 1 8%, fuels and minerals 1 1%, other 1 1%; partners USSR 48%, Eastern Europe 25%, developed countries 16%, less developed countries 8% (1987)
Extended economic zone
- 200 nm
- 200 nm
External debt
$19.6 billion (1989)
GNP
$64.6 billion, per capita $6,108; real growth rate —1.3% (1989 est.)
Imports
$18.3 billion (c.i.f., 1988); commodities— machinery and transport 28%, fuels 20%, chemical products 14%, manufactured consumer goods 16%, agriculture 6%, other 16%; partners— USSR 43%, Eastern Europe 28%, less developed countries 23%, US 3% (1987)
Industrial production
growth rate 0.6% (1988)
Industries
mining, metallurgy, engineering industries, processed foods, textiles, chemicals (especially Pharmaceuticals)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
18% (1989 est.)
Land boundaries
- none
- 14,103 km total; Bangladesh 4,053 km, Bhutan 605 km, Burma 1,463 km, China 3,380, Nepal 1,690 km, Pakistan 2,912 km
Land use
- NEGL% arable land; 0% permanent crops; 23% meadows and pastures; 1% forest and woodland; 76% other
- 55% arable land; 1% permanent crops; 4% meadows and pastures; 23% forest and woodland; 17% other; includes 13% irrigated
Natural resources
- fish, hydroelectric and geothermal power, diatomite
- coal (fourth-largest reserves in the world), iron ore, manganese, mica, bauxite, titanium ore, chromite, natural gas, diamonds, crude oil, limestone
Note
- strategic location between Greenland and Europe; westernmost European country
- dominates South Asian subcontinent; near important Indian Ocean trade routes
Terrain
- mostly plateau interspersed with mountain peaks, icefields; coast deeply indented by bays and fiords
- upland plain (Deccan Plateau) in south, flat to rolling plain along the Ganges, deserts in west, Himalayas in north
Territorial sea
- 1 2 nm
- 12 nm
Total area
- 103,000 km2; land area: 100,250 km2
- 3,287,590 km2; land area: 2,973,190 km2
Unemployment rate
0.4% (1989)
People and Society
Birth rate
- 18 births/ 1,000 population (1990)
- 30 births/ 1,000 population (1990)
Death rate
- 7 deaths/ 1,000 population (1990)
- 10 deaths/ 1,000 population (1990)
Ethnic divisions
- homogeneous mixture of descendants of Norwegians and Celts
- 72% Indo-Aryan, 25% Dravidian, 3% Mongoloid and other
Infant mortality rate
- 7 deaths/ 1 ,000 live births (1990)
- 89 deaths/ 1 ,000 live births (1990)
Labor force
- 134,429; 55.4% commerce, finance, and services, 14.3% other manufacturing, 5.8% agriculture, 7.9% fish processing, 5.0% fishing (1986)
- 284,400,000; 67% agriculture (FY85)
Language
- Icelandic
- Hindi, English, and 14 other official languages — Bengali, Telgu, Marathi, Tamil, Urdu, Gujarati, Malayalam, Kannada, Oriya, Punjabi, Assamese, Kashmiri, Sindhi, and Sanskrit; 24 languages spoken by a million or more persons eac|); numerous other languages and dialects, for the most part mutually unintelligible; Hindi is the national language and primary tongue of 30% of the people; English enjoys associate status but is the most important language for national, political, and commercial communication; Hindustani, a popular variant of Hindi/ Urdu, is spoken widely throughout northern India
Life expectancy at birth
- 75 years male, 80 years female (1990)
- 57 years male, 59 years female (1990)
Literacy
- 100%
- 36%
Nationality
- noun — Icelanders); adjective— Icelandic
- noun — Indian(s); adjective — Indian
Net migration rate
- 0 migrants/ 1 ,000 population (1990)
- 0 migrants/ 1 ,000 population (1990)
Organized labor
- 60% of labor force
- less than 5% of the labor force
Population
- 257,023 (July 1990), growth rate 1.1% (1990)
- 849,746,001 (July 1990), growth rate 2.0% (1990)
Religion
- 95% Evangelical Lutheran, 3% other Protestant and Roman Catholic, 2% no affiliation
- 82.6% Hindu, 11.4% Muslim, 2.4% Christian, 2.0% Sikh, 0.7% Buddhist, 0.5% Jains, 0.4% other
Total fertility rate
- 2.2 children born/ woman (1990)
- 3.8 children born/ woman (1990)
Government
Administrative divisions
- 23 counties (syslar, singular — sysla) and 1 4 independent towns* (kaupstadar, singular — kaupstadur); Akranes*, Akureyri*, Arnessysla, Austur-Bardhastrandarsysla, Austur-Hunavatnssysla, Austur-Skaftafellssysla, Borgarfjardharsysla, Dalasysla, Eyjafjardharsysla, Gullbringusysla, Hafnarfjordhur*, Husavik*, Isafjordhur*, Keflavik*, Kjdsarsysla, Kdpavogur*, Myrasysla, Neskaupstadhur*, NordhurIsafjardharsysla, Nordhur-Mulasysla, Nordhur-Thingeyjarsysla, Olafsfjordhur*, Rangarvallasysla, Reykjavik*, Saudharkrokur*, SeydhisfjSrdhur*, Siglufjordhur*, Skagafjardharsysla, Snaefellsnes-og Hanppadalssysla, Strandasysla, Sudhur-Mulasysla, Sudhur-Thingeyjarsysla, Vestmannaeyjar*, Vestur-Bardhastrandarsysla, Vestur-Hunavatnssysla, Vestur-Isafjardharsysla, Vestur-Skaftafellssysla
- 24 states and 7 union territories*; Andaman and Nicobar Islands*, Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh*, Dadra and Nagar Haveli*, Delhi*, Goa and Daman and Diu*. Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep*, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Orissa. Pondicherry*, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil N5du, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal; note — Goa may have become a state with Daman and Diu remaining a union territory
Capital
- Reykjavik
- New Delhi
Communists
- less than 100 (est.), some of whom participate in the People's Alliance
- 466,000 members claimed by CPI, 361,000 members claimed by CPI/ M; Communist extremist groups, about 15,000 members
Constitution
- 16 June 1944, effective 17 June 1944
- 26 January 1950
Diplomatic representation
- Ambassador Ingvi S. INGVARSSON; Chancery at 2022 Connecticut Avenue NW, Washington DC 20008; telephone (202) 265-6653 through 6655; there is an Icelandic Consulate General in New York; US — Ambassador Charles E. COBB; Embassy at Laufasvegur 2 1 , Reykjavik (mailing address is FPO New York 09571-0001); telephone [354] (1)29100
- Ambassadordesignate Abid HUSSEIN; Chancery at 2107 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington DC 20008; telephone (202) 9397000; there are Indian Consulates General in Chicago, New York, and San Francisco; US— Ambassador William CLARK; Embassy at Shanti Path, Chanakyapuri 110021, New Delhi; telephone [91] (11) 600651; there are US Consulates General in Bombay, Calcutta, and Madras
Elections
- President — last held on 29 June 1980 (next scheduled for June 1992); results— there were no elections in 1984 and 1988 as President Vigdis Finnbogadottir was unopposed; Parliament — last held on 25 April 1987 (next to be held by 25 April 1991); results— Independence 27.2%, Progressive 18.9%, Social Democratic 15.2%, People's Alliance 13.4%, Citizens Party 10.9%, Womens List 10.1%, other 4.3%; seats — (63 total) Independence 18, Progressive 13, Social Democratic 10, People's Alliance 8, Citizens Party 7, Womens List 6, Regional Equality Platform 1
- People 's Assembly — last held 22, 24, 26 November 1989 (next to be held by November 1994, subject to postponement); results — percent of vote by party NA; seats— (544 total), 525 elected — Congress (I) Party 193, Janata Dal Party 141, Bharatiya Janata Party 86, Communist Party of India (Marxist) 32, independents 18, Communist Party of India 12, AIADMK 11, Akali Dal 6, Shiv Sena 4, RSP 4, Forward Bloc 3, BSP 3, Telugu Desam 2, Congress (S) Party 1, others 9
Executive branch
- president, prime minister, Cabinet
- president, vice president, prime minister, Council of Ministers
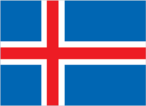
Flag
- blue with a red cross outlined in white that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag)
- three equal horizontal bands of orange (top), white, and green with a blue chakra (24-spoked wheel) centered in the white band; similar to the flag of Niger which has a small orange disk centered in the white band
Independence
- 17 June 1944 (from Denmark)
- 15 August 1947 (from UK)
Judicial branch
- Supreme Court (Haestirettur)
- Supreme Court
Leaders
- Chief of State — President Vigdis FINNBOGADOTTIR (since 1 August 1980); Head of Government — Prime Minister Steingrimur HERMANNSSON (since 28 September 1988) Political parties and leaders: Independence (conservative), Thorsteinn Palsson; Progressive, Steingrimur Hermannsson; Social Democratic, Jon Baldvin Hannibalsson; People's Alliance (left socialist), Olafur Ragnar Grimsson; Citizens Party (conservative nationalist), Julius Solnes; Women's List
- Chief of State — President Ramaswamy Iyer VENKATARAMAN (since 25 July 1987); Vice President Dr. Shankar Dayal SHARMA (since 3 September 1987); Head of Government — Prime Minister Vishwanath Pratap SINGH (since 2 December 1989) Political parties and leaders: Janata Dal Party, Prime Minister V. P. Singh; Congress (I) Party, Rajiv Gandhi; Bharatiya Janata Party, L. K. Advani; Communist Party of India (CPI), C. Rajeswara Rao; Communist Party of India/Marxist (CPI/ M), E. M. S. Namboodiripad; Communist Party of India/Marxist-Leninist (CPI/ ML), Satyanarayan Singh; All-India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazagham (AIADMK), a regional party in Tamil Nadu, Jayalalitha; Dravida Munnetra Kazagham, M. Karunanidhi; Akali Dal factions representing Sikh religious community in the Punjab; Telugu Desam, a regional party in Andhra Pradesh, N. T. Rama Rao; National Conference (NC), a regional party in Jammu and Kashmir, Farooq Abdullah; Asom Gana Parishad, a regional party in Assam, Prafulla Mahanta
Legal system
- civil law system based on Danish law; does not accept compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
- based on English common law; limited judicial review of legislative acts; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations
Legislative branch
- unicameral Parliament (Althing) with an Upper House (Efri Deild) and a Lower House (Nedri Deild)
- bicameral Parliament (Sansad) consists of an upper house or Government Assembly (Rajya Sabha) and a lower house or People's Assembly (Lok Sabha)
Long-form name
- Republic of Iceland
- Republic of India
Member of
- CCC, Council of Europe, EC (free trade agreement pending resolution of fishing limits issue), EFT A, FAO, GATT, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICES, IDA, IFC, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, INTELSAT, INTERPOL, IPU, ITU, IWC— International Whaling Commission, NATO, Nordic Council, OECD, UN, UNESCO, UPU, WHO, WMO, WSG
- ADB, AIOEC, ANRPC, CCC, Colombo Plan, Commonwealth, ESCAP, FAO, G-77, GATT, IAEA, IBRD, ICAC, ICAO, ICO, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IHO, ILO, ILZSG, IMF, IMO, INTELSAT, INTERPOL, IPU, IRC, ITC, ITU, IWC— International Wheat Council, NAM, SAARC, UN, UNESCO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WSG, WTO
National holiday
- Anniversary of the Establishment of the Republic, 1 7 June (1944)
- Anniversary of the Proclamation of the Republic, 26 January (1950)
Other political or pressure groups
various separatist groups seeking greater communal autonomy; numerous senas or militant/ chauvinistic organizations, including Shiv Sena (in Bombay), Anand Marg, and Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh
Suffrage
- universal at age 20
- universal at age 18
Type
- republic
- federal republic
Economy
Agriculture
- accounts for about 25% of GDP (including fishing); fishing is most important economic activity, contributing nearly 75% to export earnings; principal crops — potatoes and turnips; livestock — cattle, sheep; self-sufficient in crops; fish catch of about 1 .6 million metric tons in
- accounts for about 33% of GNP and employs 67% of labor force; self-sufficient in food grains; principal crops — rice, wheat, oilseeds, cotton, jute, tea, sugarcane, potatoes; livestock — cattle, buffaloes, sheep, goats and poultry; fish catch of about 3 million metric tons ranks India in the world's top 10 fishing nations
Aid
- US commitments, including Ex-Im (FY70-81), $19.1 million
- US commitments, including Ex-Im (FY70-88), $4.2 billion; Western (non-US) countries, ODA and OOF bilateral commitments (1980-87), $18.6 billion; OPEC bilateral aid (1979-89), $315 million; USSR (1970-88), $10.0 billion; Eastern Europe (1970-88), $105 million
Budget
- revenues $1.5 billion; expenditures $1.7 billion, including capital expenditures of $N A million (1988)
- revenues $48 billion; expenditures $53 billion, including capital expenditures of $13.6 billion (1989)
Currency
- krdna (plural — kronur); 1 Icelandic krona (IKr) = 100 aurar
- Indian rupee (plural — rupees); 1 Indian rupee (Re) = 100 paise
Electricity
- 1,063,000 kW capacity; 5,165 million kWh produced, 20,780 kWh per capita (1989)
- 59,000,000 kW capacity; 215,000 million kWh produced, 260 kWh per capita (1989)
Exchange rates
- Icelandic kronur (IKr) per US$1— 60.751 (January 1990), 57.042 (1989), 43.014 (1988), 38.677 (1987), 41.104(1986), 41.508(1985)
- Indian rupees (Rs) per US$1— 16.965 (January 1990), 16.226 (1989), 13.917(1988), 12.962(1987), 12.611 (1986), 12.369(1985)
Exports
- $1.4 billion (f.o.b., 1988); commodities— fish and fish products, animal products, aluminum, diatomite; partners — EC 58.9% (UK 23.3%, FRG 10.3%), US 13.6%, USSR 3.6%
- $17.2 billion (f.o.b., 1989); commodities— tea, coffee, iron ore, fish products, manufactures; partners — EC 25%, USSR and Eastern Europe 17%, US 19%, Japan 10%
External debt
- $1.8 billion (1988)
- $48.7 billion (1989)
Fiscal year
- calendar year
- 1 April31 March
GDP
$4.0 billion, per capita $16,200; real growth rate - 1.8% (1989 est.)
GNP
$333 billion, per capita $400; real growth rate 5.0% (1989 est.)
Illicit drugs
licit producer of opium poppy for the pharmaceutical trade, but some opium is diverted to international drug markets; major transit country for illicit narcotics produced in neighboring countries
Imports
- $1.6 billion (c.i.f., 1988); commodities— machinery and transportation equipment, petroleum, foodstuffs, textiles; partners—EC 58% (FRG 16%, Denmark 10.4%, UK 9.2%), US 8.5%, USSR 3.9%
- $24.7 billion (c.i.f., 1989); commodities— petroleum, edible oils, textiles, clothing, capital goods; partners — EC 33%, Middle East 19%, Japan 10%, US 9%, USSR and Eastern Europe 8%
Industrial production
- growth rate 4.7% (1987 est.)
- growth rate 8.8% (1989)
Industries
- fish processing, aluminum smelting, ferro-silicon production, hydropower
- textiles, food processing, steel, machinery, transportation equipment, cement, jute manufactures, mining, petroleum, power, chemicals, Pharmaceuticals, electronics
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
- 17.4% (1989 est.)
- 9.5% (1989 est.)
Overview
- Iceland's prosperous Scandinavian-type economy is basically capitalistic, but with extensive welfare measures, low unemployment, and comparatively even distribution of income. The economy is heavily dependent on the fishing industry, which provides nearly 75% of export earnings. In the absence of other natural resources, Iceland's economy is vulnerable to changing world fish prices. National output declined for the second consecutive year in 1989, and two of the largest fish farms filed for bankruptcy. Other economic activities include livestock raising and aluminum smelting. A fall in the fish catch is expected for 1990, resulting in a continuation of the recession.
- India's Malthusian economy is a mixture of traditional village farming and handicrafts, modern agriculture, old and new branches of industry, and a multitude of support services. It presents both the entrepreneurial skills and drives of the capitalist system and widespread government intervention of the socialist mold. Growth of 4% to 5% annually in the 1 980s has softened the impact of population growth on unemployment, social tranquility, and the environment. Agricultural output has continued to expand, reflecting the greater use of modern farming techniques and improved seed that have helped to make India self-sufficient in food grains and a net agricultural exporter. However, tens of millions of villagers, particularly in the south, have not benefited from the green revolution and live in abject poverty. Industry has benefited from a liberalization of controls. The growth rate of the service sector has also been strong.
Unemployment rate
- 1.3% (1989 est.)
- 20% (1989 est.)
Communications
Airports
- 90 total, 90 usable; 20 with permanent-surface runways; 2 with runways over 3,659 m; 10 with runways 2,440-3,659 m; 15 with runways 1,2202,439 m
- 99 total, 92 usable; 4 with permanent-surface runways; none with runways over 3,659 m; 1 with runways 2,440-3,659 m; 14 with runways 1,2202,439 m
- 345 total, 292 usable; 202 with permanent-surface runways; 2 with runways over 3,659 m; 57 with runways 2,440-3,659 m; 91 with runways 1,2202,439 m
Branches
- Hungarian People's Army, Frontier Guard, Air and Air Defense Command Military manpower males 15-49, 2,645,016; 2,112,651 fit for military service; 86,481 reach military age (18) annually
- Police, Coast Guard Military manpower males 1 5-49, 68,688; 61,553 fit for military service; no conscription or compulsory military service
Civil air
20 major transport aircraft
Defense expenditures
- 43.7 billion forints, NA% of total budget (1989); note— conversion of the military budget into US dollars using the official administratively set exchange rate would produce misleading results 125 km Greenland Sea .l.ltjordhur Hafnarfjttrdhur North Atlantic Ocean
- none Laccadive Sea SrrrrKionil map \ 111 Nicobar .; Islands \
Highways
- 130,000 km total; 29,701 km national highway system — 26,727 km asphalt and bitumen, 146 km concrete, 55 km stone and road brick, 2,345 km macadam, 428 km unpaved; 58,495 km country roads (66% unpaved), and 41,804 km (est.) other roads (70% unpaved) (1987)
- 12,343 km total; 166 km bitumen and concrete; 1 ,284 km bituminous treated and gravel; 10,893 km earth
- 1,633,300 km total (1986); 515,300 km secondary and 1,118,000 km gravel, crushed stone, or earth
Inland waterways
- 1,622 km (1986)
- 16,180 km; 3,631 km navigable by large vessels
Merchant marine
- 16 cargo ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 77,141 GRT/ 103,189 DWT Civil ain 22 major transport aircraft
- 18 ships (1,000 CRT or over) totaling 62,867 GRT/87,610 DWT; includes 9 cargo, 2 refrigerated cargo, 1 container, 2 roll-on/roll-off cargo, 1 petroleum, oils, and lubricants (POL) tanker, 1 chemical tanker, 2 bulk
- 296 ships (1,000 CRT or over) totaling 5,855,842 GRT/ 9,790,260 DWT; includes 1 short-sea passenger, 8 passenger-cargo, 95 cargo, 1 roll-on/ roll-off cargo, 8 container, 53 petroleum, oils, and lubricants (POL) tanker, 10 chemical tanker, 9 combination ore/ oil, 109 bulk, 2 combination bulk Civil air 93 major transport aircraft
Pipelines
- crude oil, 1,204 km; refined products, 600 km; natural gas, 3,800 km (1986)
- crude oil, 3,497 km; refined products, 1 ,703 km; natural gas, 902 km (1989) India (continued) Indian Ocean
Ports
- Budapest and Dunaujvaros are river ports on the Danube; maritime outlets are Rostock (GDR), Gdansk (Poland), Gdynia (Poland), Szczecin (Poland), Galati (Romania), and Braila (Romania)
- Reykjavik, Akureyri, Hafnarfjordhur, Keflavik, Seydhisfjordhur, Siglufjordur, Vestmannaeyjar; numerous minor ports Iceland (continued) India
- Bombay, Calcutta, Cochin, Kandla, Madras, New Mangalore, Port Blair (Andaman Islands)
Railroads
- 7,770 km total; 7,513 km 1.435-meter standard gauge, 222 km narrow gauge (mostly 0.760-meter), 35 km 1.524-meter broad gauge; 1,138 km double track, 2,088 km electrified; all government owned (1987)
- 61,850 km total (1986); 33,553 km 1.676-meter broad gauge, 24,051 km 1 .000-meter gauge, 4,246 km narrow gauge (0.762 meter and 0.610 meter); 12,617 km is double track; 6,500 km is electrified
Telecommunications
- stations — 13 AM, 11 FM, 21 TV; 8 Soviet TV relays; 3,500,000 TV sets; 5,500,000 receiver sets; at least 1 satellite earth station Defense Forces
- adequate domestic service, wire and radio communication system; 135,000 telephones; stations — 10 AM, 17 (43 relays) FM, 14 (132 relays) TV; 2 submarine cables; 1 Atlantic Ocean INTELSAT earth station Defense Forces
- poor domestic telephone service, international radio communications adequate; 3,200,000 telephones; stations— 170 AM, no FM, 14 TV (government controlled); domestic satellite system for communications and TV; 3 Indian Ocean INTELSAT earth stations; submarine cables to Sri Lanka, Malaysia, and