2011 Edition
CIA World Factbook 2011 Archive (HTML)
Introduction
Background
Since independence from Portugal in 1974, Guinea-Bissau has experienced considerable political and military upheaval. In 1980, a military coup established authoritarian dictator Joao Bernardo 'Nino' VIEIRA as president. Despite setting a path to a market economy and multiparty system, VIEIRA's regime was characterized by the suppression of political opposition and the purging of political rivals. Several coup attempts through the 1980s and early 1990s failed to unseat him. In 1994 VIEIRA was elected president in the country's first free elections. A military mutiny and resulting civil war in 1998 eventually led to VIEIRA's ouster in May 1999. In February 2000, a transitional government turned over power to opposition leader Kumba YALA after he was elected president in transparent polling. In September 2003, after only three years in office, YALA was ousted by the military in a bloodless coup, and businessman Henrique ROSA was sworn in as interim president. In 2005, former President VIEIRA was re-elected president pledging to pursue economic development and national reconciliation; he was assassinated in March 2009. Malam Bacai SANHA was elected in an emergency election held in June 2009.
Geography
Area
- 36,125 sq km 28,120 sq km 8,005 sq km
- total
- 36,125 sq km
- water
- 8,005 sq km
Area - comparative
slightly less than three times the size of Connecticut
Climate
tropical; generally hot and humid; monsoonal-type rainy season (June to November) with southwesterly winds; dry season (December to May) with northeasterly harmattan winds
Coastline
350 km
Elevation extremes
- Atlantic Ocean 0 m unnamed elevation in the eastern part of the country 300 m
- highest point
- unnamed elevation in the eastern part of the country 300 m
- lowest point
- Atlantic Ocean 0 m
Environment - current issues
deforestation; soil erosion; overgrazing; overfishing
Environment - international agreements
- Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands none of the selected agreements
- party to
- Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
- signed, but not ratified
- none of the selected agreements
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural)
- 0.18 cu km/yr (13%/5%/82%) 113 cu m/yr (2000)
- per capita
- 113 cu m/yr (2000)
- total
- 0.18 cu km/yr (13%/5%/82%)
Geographic coordinates
12 00 N, 15 00 W
Geography - note
this small country is swampy along its western coast and low-lying inland
Irrigated land
250 sq km (2008)
Land boundaries
- 724 km Guinea 386 km, Senegal 338 km
- border countries
- Guinea 386 km, Senegal 338 km
- total
- 724 km
Land use
- 8.31% 6.92% 84.77% (2005)
- arable land
- 8.31%
- other
- 84.77% (2005)
- permanent crops
- 6.92%
Location
Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea and Senegal
Map references
Africa
Maritime claims
- 12 nm 200 nm
- exclusive economic zone
- 200 nm
- territorial sea
- 12 nm
Natural hazards
hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze may reduce visibility during dry season; brush fires
Natural resources
fish, timber, phosphates, bauxite, clay, granite, limestone, unexploited deposits of petroleum
Terrain
mostly low coastal plain rising to savanna in east
Total renewable water resources
31 cu km (2003)
People and Society
Age structure
- 40.4% (male 321,889/female 323,202) 56.4% (male 435,986/female 465,117) 3.2% (male 19,975/female 30,508) (2011 est.)
- 0-14 years
- 40.4% (male 321,889/female 323,202)
- 15-64 years
- 56.4% (male 435,986/female 465,117)
- 65 years and over
- 3.2% (male 19,975/female 30,508) (2011 est.)
Birth rate
35.15 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
17.2% (2008)
Death rate
15.27 deaths/1,000 population (July 2011 est.)
Drinking water source
- urban: 83% of population rural: 51% of population total: 61% of population urban: 17% of population rural: 49% of population total: 39% of population (2008)
- rural
- 49% of population
- total
- 39% of population (2008)
- urban
- 17% of population
Education expenditures
NA
Ethnic groups
African 99% (includes Balanta 30%, Fula 20%, Manjaca 14%, Mandinga 13%, Papel 7%), European and mulatto less than 1%
Health expenditures
8.1% of GDP (2009)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
2.5% (2009 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
1,200 (2009 est.)
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
22,000 (2009 est.)
Hospital bed density
0.96 beds/1,000 population (2009)
Infant mortality rate
- 96.23 deaths/1,000 live births 106.11 deaths/1,000 live births 86.06 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
- female
- 86.06 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
- total
- 96.23 deaths/1,000 live births
Languages
Portuguese (official), Crioulo, African languages
Life expectancy at birth
- 48.7 years 46.8 years 50.67 years (2011 est.)
- female
- 50.67 years (2011 est.)
- total population
- 48.7 years
Literacy
- age 15 and over can read and write 42.4% 58.1% 27.4% (2003 est.)
- definition
- age 15 and over can read and write
- female
- 27.4% (2003 est.)
- male
- 58.1%
- total population
- 42.4%
Major cities - population
BISSAU (capital) 302,000 (2009)
Major infectious diseases
- very high bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever malaria and yellow fever schistosomiasis rabies (2009)
- animal contact disease
- rabies (2009)
- degree of risk
- very high
- food or waterborne diseases
- bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
- vectorborne diseases
- malaria and yellow fever
- water contact disease
- schistosomiasis
Maternal mortality rate
1,000 deaths/100,000 live births (2008)
Median age
- 19.5 years 18.9 years 20 years (2011 est.)
- female
- 20 years (2011 est.)
- male
- 18.9 years
- total
- 19.5 years
Nationality
- Guinean(s) Guinean
- adjective
- Guinean
- noun
- Guinean(s)
Net migration rate
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2011 est.)
Physicians density
0.045 physicians/1,000 population (2008)
Population
1,596,677 (July 2011 est.)
Population growth rate
1.988% (2011 est.)
Religions
Muslim 50%, indigenous beliefs 40%, Christian 10%
Sanitation facility access
- urban: 49% of population rural: 9% of population total: 21% of population urban: 51% of population rural: 91% of population total: 79% of population (2008)
- rural
- 91% of population
- total
- 79% of population (2008)
- urban
- 51% of population
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- 9 years (2006)
- total
- 9 years (2006)
Sex ratio
- 1.03 male(s)/female 1 male(s)/female 0.93 male(s)/female 0.66 male(s)/female 0.95 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
- 15-64 years
- 0.93 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over
- 0.66 male(s)/female
- at birth
- 1.03 male(s)/female
- total population
- 0.95 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
- under 15 years
- 1 male(s)/female
Total fertility rate
4.51 children born/woman (2011 est.)
Urbanization
- 30% of total population (2010) 3% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
- rate of urbanization
- 3% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
- urban population
- 30% of total population (2010)
Government
Administrative divisions
9 regions (regioes, singular - regiao); Bafata, Biombo, Bissau, Bolama, Cacheu, Gabu, Oio, Quinara, Tombali; note - Bolama may have been renamed Bolama/Bijagos
Capital
- Bissau 11 51 N, 15 35 W UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
- geographic coordinates
- 11 51 N, 15 35 W
- name
- Bissau
- time difference
- UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
Constitution
16 May 1984; amended several times
Country name
- Republic of Guinea-Bissau Guinea-Bissau Republica da Guine-Bissau Guine-Bissau Portuguese Guinea
- conventional long form
- Republic of Guinea-Bissau
- conventional short form
- Guinea-Bissau
- former
- Portuguese Guinea
- local long form
- Republica da Guine-Bissau
- local short form
- Guine-Bissau
Diplomatic representation from the US
the US Embassy suspended operations on 14 June 1998 in the midst of violent conflict between forces loyal to then President VIEIRA and military-led junta; the US Ambassador to Senegal is accredited to Guinea-Bissau
Diplomatic representation in the US
- none; note - Guinea-Bissau does not have official representation in Washington, DC
- chief of mission
- none; note - Guinea-Bissau does not have official representation in Washington, DC
Executive branch
- President Malam Bacai SANHA (since 8 September 2009) Prime Minister Carlos GOMES Junior (since 25 December 2008) NA president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (no term limits); election last held on 28 June 2009 with a runoff between the two leading candidates held on 26 July 2009 (next to be held by 2014); prime minister appointed by the president after consultation with party leaders in the legislature Malam Bacai SANHA elected president; percent of vote, second ballot - Malam Bacai SANHA 63.5%, Kumba YALA 36.5%
- cabinet
- NA
- chief of state
- President Malam Bacai SANHA (since 8 September 2009)
- election results
- Malam Bacai SANHA elected president; percent of vote, second ballot - Malam Bacai SANHA 63.5%, Kumba YALA 36.5%
- elections
- president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (no term limits); election last held on 28 June 2009 with a runoff between the two leading candidates held on 26 July 2009 (next to be held by 2014); prime minister appointed by the president after consultation with party leaders in the legislature
- head of government
- Prime Minister Carlos GOMES Junior (since 25 December 2008)
Flag description
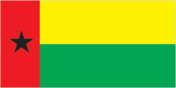
two equal horizontal bands of yellow (top) and green with a vertical red band on the hoist side; there is a black five-pointed star centered in the red band; yellow symbolizes the sun; green denotes hope; red represents blood shed during the struggle for independence; the black star stands for African unity uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia; the flag design was heavily influenced by the Ghanaian flag
Government type
republic
Independence
24 September 1973 (declared); 10 September 1974 (from Portugal)
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; non-party state to the ICCt
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AOSIS, AU, CPLP, ECOWAS, FAO, FZ, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Judicial branch
Supreme Court or Supremo Tribunal da Justica (consists of nine justices appointed by the president and serve at his pleasure; final court of appeals in criminal and civil cases); Regional Courts (one in each of nine regions; first court of appeals for Sectoral Court decisions; hear all felony cases and civil cases valued at more than $1,000); 24 Sectoral Courts (judges are not necessarily trained lawyers; they hear civil cases valued at less than $1,000 and misdemeanor criminal cases)
Legal system
mixed legal system of civil law (influenced by the early French Civil Code) and customary law
Legislative branch
- unicameral National People's Assembly or Assembleia Nacional Popular (100 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms) last held on 16 November 2008 (next to be held in 2012) percent of vote by party - PAIGC 49.8%, PRS 25.3%, PRID 7.5%, PND 2.4%, AD 1.4%, other parties 13.6%; seats by party - PAIGC 67, PRS 28, PRID 3, PND 1, AD 1
- election results
- percent of vote by party - PAIGC 49.8%, PRS 25.3%, PRID 7.5%, PND 2.4%, AD 1.4%, other parties 13.6%; seats by party - PAIGC 67, PRS 28, PRID 3, PND 1, AD 1
- elections
- last held on 16 November 2008 (next to be held in 2012)
National anthem
- "Esta e a Nossa Patria Bem Amada" (This Is Our Beloved Country) Amilcar Lopes CABRAL/XIAO He adopted 1974; a delegation from Portuguese Guinea visited China in 1963 and heard music by XIAO He; Amilcar Lopes CABRA, the leader of Guinea-Bissau's independence movement, asked the composer to create a piece that would inspire his people to struggle for independence
- lyrics/music
- Amilcar Lopes CABRAL/XIAO He
- name
- "Esta e a Nossa Patria Bem Amada" (This Is Our Beloved Country)
National holiday
Independence Day, 24 September (1973)
Political parties and leaders
African Party for the Independence of Guinea-Bissau and Cape Verde or PAIGC [Carlos GOMES Junior]; Democratic Alliance or AD [Victor MANDINGA]; Democratic Social Front or FDS [Rafael BARBOSA]; Electoral Union or UE [Joaquim BALDE]; Guinea-Bissau Civic Forum/Social Democracy or FCGSD [Antonieta Rosa GOMES]; Guinea-Bissau Democratic Party or PDG; Guinea-Bissau Socialist Democratic Party or PDSG [Serifo BALDE]; Labor and Solidarity Party or PST [Lancuba INDJAI]; New Democracy Party or PND; Party for Democratic Convergence or PCD [Victor MANDINGA]; Party for Renewal and Progress or PRP; Party for Social Renewal or PRS [Sory DJALO]; Progress Party or PP; Republican Party for Independence and Development or PRID [Aristides GOMES]; Union of Guinean Patriots or UPG [Francisca VAZ]; Union for Change or UM [Amine SAAD]; United Platform or UP (coalition formed by PCD, FDS, FLING, and RGB-MB); United Popular Alliance or APU; United Social Democratic Party or PUSD [Francisco FADUL]
Political pressure groups and leaders
NA
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Economy
Agriculture - products
rice, corn, beans, cassava (tapioca), cashew nuts, peanuts, palm kernels, cotton; timber; fish
Budget
- $NA $NA
- expenditures
- $NA
- revenues
- $NA
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)
-2.4% of GDP (2010 est.)
Central bank discount rate
4.25% (31 December 2009) 4.75% (31 December 2008)
Commercial bank prime lending rate
15% (31 December 2010 est.) 15% (31 December 2009 est.)
Current account balance
-$82.6 million (2010 est.) -$120.1 million (2009 est.)
Debt - external
$941.5 million (2000 est.)
Economy - overview
One of the poorest countries in the world, Guinea-Bissau's legal economy depends mainly on farming and fishing, but trafficking narcotics is probably the most lucrative trade. Cashew crops have increased remarkably in recent years. Guinea-Bissau exports fish and seafood along with small amounts of peanuts, palm kernels, and timber. Rice is the major crop and staple food. However, intermittent fighting between Senegalese-backed government troops and a military junta destroyed much of the country's infrastructure and caused widespread damage to the economy in 1998; the civil war led to a 28% drop in GDP that year, with partial recovery in 1999-2002. In December 2003, the World Bank, IMF, and UNDP were forced to step in to provide emergency budgetary support in the amount of $107 million for 2004, representing over 80% of the total national budget. The combination of limited economic prospects, a weak and faction-ridden government, and favorable geography have made this West African country a way station for drugs bound for Europe.
Electricity - consumption
65.1 million kWh (2008 est.)
Electricity - exports
0 kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - imports
0 kWh (2009 est.)
Electricity - production
70 million kWh (2008 est.)
Exchange rates
Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar - 495.28 (2010) 472.19 (2009) 493.51 (2007) 522.59 (2006)
Exports
$126 million (2010 est.) $117.5 million (2009 est.)
Exports - commodities
fish, shrimp; cashew nuts, peanuts, palm kernels, sawn lumber
Exports - partners
India 76.9%, Nigeria 16.6% (2010)
GDP - composition by sector
- 55.2% 12.8% 32% (2010 est.)
- agriculture
- 55.2%
- industry
- 12.8%
- services
- 32% (2010 est.)
GDP - per capita (PPP)
$1,100 (2010 est.) $1,100 (2009 est.) $1,100 (2008 est.) data are in 2010 US dollars
GDP - real growth rate
3.5% (2010 est.) 3% (2009 est.) 3.2% (2008 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$837 million (2010 est.)
GDP (purchasing power parity)
$1.784 billion (2010 est.) $1.724 billion (2009 est.) $1.674 billion (2008 est.) data are in 2010 US dollars
Household income or consumption by percentage share
- 2.9% 28% (2002)
- highest 10%
- 28% (2002)
- lowest 10%
- 2.9%
Imports
$206.1 million (2010 est.) $202.3 million (2009 est.)
Imports - commodities
foodstuffs, machinery and transport equipment, petroleum products
Imports - partners
Senegal 21.8%, Portugal 20.5%, Brazil 5.6%, Cuba 4.1% (2010)
Industrial production growth rate
4.7% (2003 est.)
Industries
agricultural products processing, beer, soft drinks
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.5% (2010 est.) -1.7% (2009 est.)
Investment (gross fixed)
12.7% of GDP (2010 est.)
Labor force
632,700 (2007)
Labor force - by occupation
- 82% 18% (2000 est.)
- agriculture
- 82%
- industry and services
- 18% (2000 est.)
Market value of publicly traded shares
$NA
Natural gas - consumption
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - exports
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - imports
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - production
0 cu m (2009 est.)
Natural gas - proved reserves
0 cu m (1 January 2011 est.)
Oil - consumption
3,000 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - exports
0 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - imports
2,565 bbl/day (2009 est.)
Oil - production
0 bbl/day (2010 est.)
Oil - proved reserves
0 bbl (1 January 2011 est.)
Population below poverty line
NA%
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$NA (31 December 2010 est.) $168.6 million (31 December 2009 est.)
Stock of broad money
$258.1 million (31 December 2010 est.) $209.3 million (31 December 2009 est.)
Stock of domestic credit
$95.33 million (31 December 2010 est.) $42.56 million (31 December 2009 est.)
Stock of narrow money
$238.5 million (31 December 2010 est.) $192.1 million (31 December 2009 est.)
Taxes and other revenues
19.2% of GDP (2010 est.)
Unemployment rate
NA%
Communications
Broadcast media
1 state-owned TV station and a second station, RTP Africa, is operated by Portuguese public broadcaster Radio e Televisao de Portugal (RTP); 1 state-owned radio station, several private radio stations, and some community radio stations; multiple international broadcasters are available (2007)
Internet country code
.gw
Internet hosts
82 (2010)
Internet users
37,100 (2009)
Telephone system
- small system including a combination of microwave radio relay, open-wire lines, radiotelephone, and mobile-cellular communications fixed-line teledensity less than 1 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular teledensity reached 35 per 100 in 2009 country code - 245 (2008)
- domestic
- fixed-line teledensity less than 1 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular teledensity reached 35 per 100 in 2009
- general assessment
- small system including a combination of microwave radio relay, open-wire lines, radiotelephone, and mobile-cellular communications
- international
- country code - 245 (2008)
Telephones - main lines in use
5,000 (2010)
Telephones - mobile cellular
594,100 (2010)
Transportation
Airports
9 (2010)
Airports - with paved runways
- 1 (2010)
- 1,524 to 2,437 m
- 1 (2010)
- over 3,047 m
- 1
- total
- 2
Airports - with unpaved runways
- 3 (2010)
- 1,524 to 2,437 m
- 1
- 914 to 1,523 m
- 3
- total
- 7
- under 914 m
- 3 (2010)
Ports and terminals
Bissau, Buba, Cacheu, Farim
Roadways
- 3,455 km 965 km 2,490 km (2002)
- total
- 3,455 km
- unpaved
- 2,490 km (2002)
Waterways
(rivers are navigable for some distance; many inlets and creeks give shallow-water access to much of interior) (2009)
Military and Security
Manpower available for military service
- 370,790 372,171 (2010 est.)
- females age 16-49
- 372,171 (2010 est.)
- males age 16-49
- 370,790
Manpower fit for military service
- 205,460 212,277 (2010 est.)
- females age 16-49
- 212,277 (2010 est.)
- males age 16-49
- 205,460
Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually
- 17,639 17,865 (2010 est.)
- female
- 17,865 (2010 est.)
- male
- 17,639
Military branches
- People's Revolutionary Armed Force (FARP): Army, Navy, National Air Force (Forca Aerea Nacional); Presidential Guard (2011)
- People's Revolutionary Armed Force (FARP)
- Army, Navy, National Air Force (Forca Aerea Nacional); Presidential Guard (2011)
Military expenditures
3.1% of GDP (2005 est.)
Military service age and obligation
18-25 years of age for selective compulsory military service (Air Force service is voluntary); 16 years of age or younger with parental consent, for voluntary service (2010)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international
in 2006, political instability within Senegal's Casamance region resulted in thousands of Senegalese refugees, cross-border raids, and arms smuggling into Guinea-Bissau
Illicit drugs
increasingly important transit country for South American cocaine enroute to Europe; enabling environment for trafficker operations thanks to pervasive corruption; archipelago-like geography around the capital facilitates drug smuggling
Refugees and internally displaced persons
- 7,454 (Senegal) (2007)
- refugees (country of origin)
- 7,454 (Senegal) (2007)
Trafficking in persons
- Guinea-Bissau is a country of origin for children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; the scope of the problem of trafficking women or men for forced labor or forced prostitution is unknown; boys reportedly were transported to southern Senegal for forced manual and agricultural labor; girls may be subjected to forced domestic service and child prostitution in Senegal Tier 3 - Guinea-Bissau is not making significant efforts to comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; the government acknowledged that human trafficking is a problem in the country and took steps to enact legislation outlawing all forms of trafficking; Guinea-Bissau did not increase efforts to prosecute and punish trafficking offenders; the government did not take steps to proactively identify victims and lacked resources to provide victim services directly, but provided some resources to NGOs that care for victims (2011)
- current situation
- Guinea-Bissau is a country of origin for children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; the scope of the problem of trafficking women or men for forced labor or forced prostitution is unknown; boys reportedly were transported to southern Senegal for forced manual and agricultural labor; girls may be subjected to forced domestic service and child prostitution in Senegal
- tier rating
- Tier 3 - Guinea-Bissau is not making significant efforts to comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; the government acknowledged that human trafficking is a problem in the country and took steps to enact legislation outlawing all forms of trafficking; Guinea-Bissau did not increase efforts to prosecute and punish trafficking offenders; the government did not take steps to proactively identify victims and lacked resources to provide victim services directly, but provided some resources to NGOs that care for victims (2011)