1992 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1992 (Project Gutenberg)
Geography
Climate
tropical; generally hot and humid; monsoon-type rainy season (June to November) with southwesterly winds; dry season (December to May) with northeasterly harmattan winds
Coastline
350 km
Comparative area
slightly less than three times the size of Connecticut
Disputes
the International Court of Justice (ICJ) on 12 November 1991 rendered its decision on the Guinea-Bissau/Senegal maritime boundary in favor of Senegal
Environment
hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze may reduce visibility during dry season
Exclusive economic zone
200 nm
Land area
28,000 km2
Land boundaries
724 km; Guinea 386, Senegal 338 km
Land use
arable land 11%; permanent crops 1%; meadows and pastures 43%; forest and woodland 38%; other 7%
Natural resources
unexploited deposits of petroleum, bauxite, phosphates; fish, timber
Terrain
mostly low coastal plain rising to savanna in east
Territorial sea
12 nm
Total area
36,120 km2
People and Society
Birth rate
42 births/1,000 population (1992)
Death rate
18 deaths/1,000 population (1992)
Ethnic divisions
African about 99% (Balanta 30%, Fula 20%, Manjaca 14%, Mandinga 13%, Papel 7%); European and mulatto less than 1%
Infant mortality rate
124 deaths/1,000 live births (1992)
Labor force
403,000 (est.); agriculture 90%, industry, services, and commerce 5%, government 5%; population of working age 53% (1983)
Languages
Portuguese (official); Criolo and numerous African languages
Life expectancy at birth
45 years male, 48 years female (1992)
Literacy
36% (male 50%, female 24%) age 15 and over can read and write (1990 est.)
Nationality
noun - Guinea-Bissauan(s); adjective - Guinea-Bissauan
Net migration rate
0 migrants/1,000 population (1992)
Organized labor
only one trade union - the National Union of Workers of Guinea-Bissau (UNTG)
Population
1,047,137 (July 1992), growth rate 2.4% (1992)
Religions
indigenous beliefs 65%, Muslim 30%, Christian 5%
Total fertility rate
5.7 children born/woman (1992)
Government
Administrative divisions
9 regions (regioes, singular - regiao); Bafata, Biombo, Bissau, Bolama, Cacheu, Gabu, Oio, Quinara, Tombali
Capital
Bissau
Chief of State and Head of Government
President of the Council of State Brig. Gen. Joao Bernardo VIEIRA (assumed power 14 November 1980 and elected President of Council of State on 16 May 1984)
Constitution
16 May 1984
Diplomatic representation
Ambassador Alfredo Lopes CABRAL; Chancery at 918 16th Street NW, Mezzanine Suite, Washington, DC 20006; telephone (202) 872-4222,
Executive branch
president of the Council of State, vice presidents of the Council of State, Council of State, Council of Ministers (cabinet)
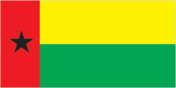
Flag
two equal horizontal bands of yellow (top) and green with a vertical red band on the hoist side; there is a black five-pointed star centered in the red band; uses the popular pan-African colors of Ethiopia; similar to the flag of Cape Verde, which has the black star raised above the center of the red band and is framed by two corn stalks and a yellow clam shell
Independence
10 September 1974 (from Portugal; formerly Portuguese Guinea)
Judicial branch
none; there is a Ministry of Justice in the Council of Ministers
Legal system
NA
Legislative branch
unicameral National People's Assembly (Assembleia Nacional Popular)
Long-form name
Republic of Guinea-Bissau
Member of
ACCT (associate), ACP, AfDB, ECA, ECOWAS, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, ILO, IMF, IMO, IOM (observer), ITU, LORCS, NAM, OAU, OIC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO
National holiday
Independence Day, 10 September (1974)
National People's Assembly
last held 15 June 1989 (next to be held 15 June 1994); results - PAIGC is the only party; seats - (150 total) PAIGC 150, appointed by Regional Councils
Political parties and leaders
3 parties - African Party for the Independence of Guinea-Bissau and Cape Verde (PAIGC), President Joao Bernardo VIEIRA, leader; PAIGC is still the major party and controls all aspects of the Government, but 2 opposition parties registered in late 1991; Democratic Social Front (FDS), Rafael BARBOSA, leader; Bafata Movement, Domingos Fernandes GARNER, leader; Democratic Front, Aristides MENEZES, leader; other parties forming
President of Council of State
last held 19 June 1989 (next to be held NA 1993); results - Brig. Gen. Joao Bernardo VIEIRA was reelected without opposition by the National People's Assembly
Suffrage
universal at age 15
Type
republic; highly centralized multiparty since mid-1991; the African Party for the Independence of Guinea-Bissau and Cape Verde (PAIGC) held an extraordinary party congress in December 1990 and established a two-year transition program during which the constitution will be revised, allowing for multiple political parties and a presidential election in 1993
Economy
Agriculture
accounts for over 50% of GDP, nearly 100% of exports, and 90% of employment; rice is the staple food; other crops include corn, beans, cassava, cashew nuts, peanuts, palm kernels, and cotton; not self-sufficient in food; fishing and forestry potential not fully exploited
Budget
revenues $22.7 million; expenditures $30.8 million, including capital expenditures of $18.0 million (1989 est.)
Currency
Guinea-Bissauan peso (plural - pesos); 1 Guinea-Bissauan peso (PG) = 100 centavos
Economic aid
US commitments, including Ex-Im (FY70-89), $49 million; Western (non-US) countries, ODA and OOF bilateral commitments (1970-89), $615 million; OPEC bilateral aid (1979-89), $41 million; Communist countries (1970-89), $68 million
Electricity
22,000 kW capacity; 30 million kWh produced, 30 kWh per capita (1991)
Exchange rates
Guinea-Bissauan pesos (PG) per US$1 - 1987.2 (1989), 1363.6 (1988), 851.65 (1987), 238.98 (1986)
Exports
$14.2 million (f.o.b., 1989 est.) commodities: cashews, fish, peanuts, palm kernels partners: Portugal, Senegal, France, The Gambia, Netherlands, Spain
External debt
$462 million (December 1990 est.)
Fiscal year
calendar year
GDP
exchange rate conversion - $162 million, per capita $160; real growth rate 5.0% (1989)
Imports
$68.9 million (f.o.b., 1989 est.) commodities: capital equipment, consumer goods, semiprocessed goods, foods, petroleum partners: Portugal, Netherlands, Senegal, USSR, Germany
Industrial production
growth rate - 1.0% (1989 est.); accounts for 10% of GDP (1989 est.)
Industries
agricultural processing, beer, soft drinks
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
25% (1990 est.)
Overview
Guinea-Bissau ranks among the poorest countries in the world, with a per capita GDP below $200. Agriculture and fishing are the main economic activities. Cashew nuts, peanuts, and palm kernels are the primary exports. Exploitation of known mineral deposits is unlikely at present because of a weak infrastructure and the high cost of development. The government's four-year plan (1988-91) has targeted agricultural development as the top priority.
Unemployment rate
NA%
Communications
Airports
34 total, 15 usable; 4 with permanent-surface runways; none with runways over 3,659 m; 1 with runways 2,440-3,659 m; 5 with runways 1,220-2,439 m
Civil air
2 major transport aircraft
Highways
3,218 km; 2,698 km bituminous, remainder earth
Inland waterways
scattered stretches are important to coastal commerce
Ports
Bissau
Telecommunications
poor system of radio relay, open-wire lines, and radiocommunications; 3,000 telephones; broadcast stations - 2 AM, 3 FM, 1 TV
Military and Security
Branches
People's Revolutionary Armed Force (FARP; including Army, Navy, Air Force), paramilitary force
Defense expenditures
exchange rate conversion - $9.3 million, 5-6% of GDP (1987)
Manpower availability
males 15-49, 228,856; 130,580 fit for military service