1989 Edition
CIA World Factbook 1989 (Internet Archive)
Geography
Administrative divisions
9 regions (regioes, singular — regiao); Bafata, Biombo, Bissau, Bolama, Cacheu, Gabu, Oio, Quinara, Tombali
Capital
Bissau
Communists
a few Communists, some sympathizers
Constitution
16 May 1984
Diplomatic representation
Ambassador Alfredo Lopes CABRAL; Chancery (temporary) at the Guinea-Bissauan Permanent Mission to the UN, Suite 604, 21 1 East 43rd Street, New York, NY 10017; telephone (212) 661-3977; US— Ambassador William L. JACOBSEN; Embassy at 17 Avenida Domingos Ramos, Bissau (mailing address is C. P. 297, Bissau); telephone [245] 212816, 21817, 213674
Elections
President of Council of Statelast held 19 June 1989 (next to be held 19 June 1994): results— Brig. Gen. Jo3o Bernardo Vieira was reelected without opposition by the National People's Assembly; National People's Assembly — last held 15 June 1989 (next to be held 15 June 1994); results — PAIGC is the only party; seats — (150 total) PAIGC 150, appointed by Regional Councils; Regional Councils— lust held 1 June 1989 (next to be held 1 June 1994); results— PAIGC is the only party; seats — (473 total) PAIGC 473, by public plebiscite
Executive branch
president of the Council of State, vice presidents of the Council of State, Council of State, Council of Ministers (cabinet)
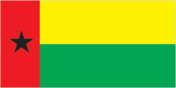
Flag
two equal horizontal bands of yellow (top) and green with a vertical red band on the hoist side; there is a black fivepointed star centered in the red band; uses the popular pan-African colors of Ethiopia; similar to the flag of Cape Verde which has the black star raised above the center of the red band and is framed by two corn stalks and a yellow clam shell
Independence
24 September 1973 (from Portugal; formerly Portuguese Guinea)
Judicial branch
none; there is a Ministry of Justice in the Council of Ministers
Leaders
Chief of State and Head of Government— President of the Council of State Brig. Gen. Joao Bernardo VIEIRA (assumed power 14 November 1980 and elected President of Council of State on 16 May 1984); First Vice President Col. lafai CAMARA (since 7 November 1985); Second Vice President Vasco CABRAL (since 21 June 1989) Political parties and leaders: only party — African Party for the Independence of Guinea-Bissau and Cape Verde (PAIGC), President Joao Bernardo Vieira, leader; Guinea-Bissau (continued) the party decided to retain the binational title despite its formal break with Cape Verde
Legal system
NA
Legislative branch
unicameral National People's Assembly (Assembleia Nacional Popular)
Member of
ACP, AfDB, ECA, ECOWAS, FAO, G-77, GATT (de facto), IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IDB— Islamic Development Bank, IFAD, IFC, ILO, IMF, IMO, IRC, ITU, NAM, OAU, QIC, UN, UNESCO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WMO
National holiday
Independence Day, 24 September (1973)
Suffrage
universal at age 15
Type
republic; highly centralized oneparty regime since September 1974
Economy
Agriculture
accounts for over 50% of GDP, nearly 100% of exports, and 80% of employment; rice is the staple food; other crops include corn, beans, cassava, cashew nuts, peanuts, palm kernels, and cotton; not self-sufficient in food; fishing and forestry potential not fully exploited
Aid
US commitments, including Ex-Im (FY70-88), $46 million; Western (non-US) countries, ODA and OOF bilateral commitments (1970-87), $519 million; OPEC bilateral aid (1979-89), $41 million; Communist countries (1970-88), $68 million
Budget
revenues $20 million; expenditures $25 million, including capital expenditures of$NA(1987)
Currency
Guinea-Bissauan peso (plural — pesos); 1 Guinea-Bissauan peso (PG) = 100 centavos
Electricity
22,000 kW capacity; 28 million kWh produced, 30 kWh per capita (1989)
Exchange rates
Guinea-Bissauan pesos (PG) per US$1 — 650 pesos (December 1989), NA (1988), 851.65 (1987), 238.98 (1986), 173.61 (1985) Fiscal yean calendar year
Exports
$15 million (f.o.b., 1987); commodities— cashews, fish, peanuts, palm kernels; partners — Portugal, Spain, Switzerland, Cape Verde, China
External debt
$465 million (December 1989 est.)
GDP
$152 million, per capita $160 (1988); real growth rate 5.6% (1987)
Imports
$49 million (f.o.b., 1987); commodities— capital equipment, consumer goods, semiprocessed goods, foods, petroleum; partners — Portugal, USSR, EC countries, other Europe, Senegal, US
Industrial production
growth rate — 1 .7% (1986 est.)
Industries
agricultural processing, beer, soft drinks
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
NA%
Overview
Guinea-Bissau ranks among the poorest countries in the world, with a per capita GDP below $200. Agriculture and fishing are the main economic activities, with cashew nuts, peanuts, and palm kernels the primary exports. Exploitation of known mineral deposits is unlikely at present because of a weak infrastructure and the high cost of development. The government's four-year plan (1988-91) has targeted agricultural development as the top priority.
Unemployment rate
NA%
Communications
Airports
37 total, 18 usable; 5 with permanent-surface runways; none with runways over 3,659 m; 1 with runways 2,440-3,659 m; 5 with runways 1, 220-2,439 m
Branches
People's Revolutionary Armed Force (FARP); Army, Navy, and Air Force are separate components Military manpower males 15-49, 215,552; 122,824 fit for military service
Civil air
2 major transport aircraft
Defense expenditures
3.2% of GDP (1987)
Highways
3,218 km; 2,698 km bituminous, remainder earth
Inland waterways
scattered stretches are important to coastal commerce
Ports
Bissau
Telecommunications
poor system of radio relay, open-wire lines, and radiocommunications; 3,000 telephones; stations — 1 AM, 2 FM, 1 TV; 1 Atlantic Ocean INTELSAT earth station Defense Forces